第六章:文件操作
1、文件操作
所有的变量、数据和计算过程放在内存里面完成的。
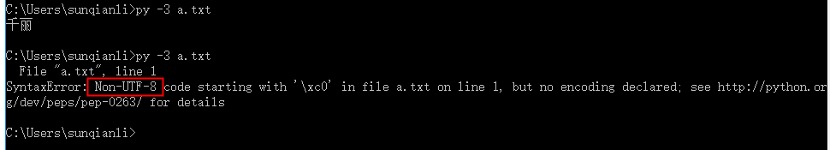
文件以a.txt形式存在,一定要将文件的编码修改为“utf-8”才能执行出此文件的运行结果。
步骤:在e盘的根目录创建一个a.txt文件,保存文件的时候将编码修改为“utf-8”,在c盘的用户下创建a.py。



2、执行只读文件


fp=open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
print(fp.read())
fp.close()

3、读完文件将文件关闭
fp=open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
datal = fp.readline()
data = fp.readlines()
print(fp.read())
fp.close()

4、找出文件中所有包含某个单词的行数。
fp=open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
data = fp.readlines()
fp.close()
num=0
for line in data:
if "test" in line:
num+=1
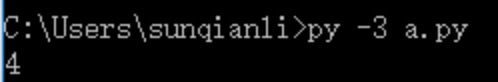
print(num)
找出文件中包含某个单词并且打印出来
fp=open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
data = fp.readlines()
fp.close()
num=0
for line in data:
if "test" in line:
print(line,end="")
num+=1
print(num)

5、只读文件strip()的使用
文件读取的时候,行的末尾包含回车符号的。
fp=open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
data = fp.readlines()
fp.close()
num=0
for line in data:
if "test" in line:
print(line.strip())
num+=1
print(num)

⚠️Lstrip从左边去掉空白字符,rstrip从右边去掉空白字符,strip两边的空白字符都去掉。
6、read、readlines的区别
Read()是将所有的内容读到一个字符串里面
Readlines()是将所有的行都读到一个列表里,列表中的每一个内容是一行。
Readline()
如果文件很大,你用read(),用readline()来读超大的文件。
原则:
内存在电脑中是个稀缺的资源,如果你大量的占用,程序肯定不是最优的。
小文件,直接用read读速度会稍为快一些。
7、常用的文件读写添加
r:read只允许读
w:write只允许写
r+:read and write
w+:write and read
a+:append and read
a:append只允许加
rb:read binary
wb:write binary
ab:append binary
w:清空写
w+:先清空所有文件的内容,然后写入,然后你才可以读取你写入的内容。
r+:不清空内容,可以同时读和写入内容
a+:追加写,所有写的内容都在文件的最后。
8、写文件
fp=open("e:\\a.txt","w",encoding="utf-8")

p=open("e:\\a.txt","w",encoding="utf-8")
fp.write("test12")
fp.write("test34")
fp.close()
fp = open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8"
print(fp.readlines())
fp.close()
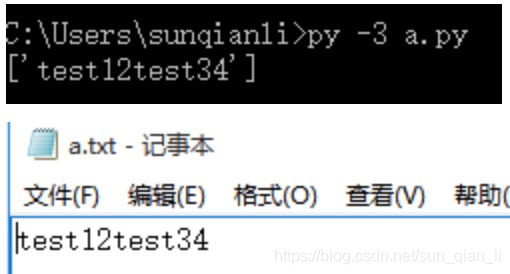
fp=open("e:\\a.txt","w",encoding="utf-8")
fp.write("test12\n")
fp.write("test34\n")
fp.close()
fp = open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
print(fp.readlines())
fp.close()

如果文件不存在,会新建一个文件
文件不关闭时,写入的内容,如果太少,实际写的内容,并不会立刻写到磁盘上。
如果你没写close,直接python进程关闭了,
操作系统也会自动把内容写入。
服务器框有一个进程会将所有的资源都耗尽,所以文件打开之后一定要关闭。
自动关闭打开的文件With open()
9、With会自动的关闭文件
with open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
print(fp.read())
With == open+close()
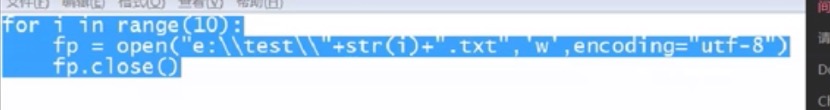
练习题:写一个文件,里面写入从gloryroad1—gloryroad100
写入之后再读出来

with open("e:\\a.txt","w",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
for i in range(0,101):
fp.write("gloryroad"+str(i)+"\n")

常见的错误:

⚠️文件名称敲错了,或者是文件不存在
10、追加文件内容a
with open("e:\\a.txt","a",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write("nihao\n")

11、r+新添加内容写第一行
with open("e:\\a.txt","r+",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write("good day\n")

总结:
a模式写是在文件的最后面写
r+的写是在文件的最开始,而且会将原来的覆盖了。
⚠️r+覆盖内容是由写入长度的多少来决定的。
12、文件游标的位置
012345678910
111213、、、
(1)文件打开的时候,r或者w都是默认文件0的这个位置。
Realine()
with open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
while(fp.readline()):
fp.readline()
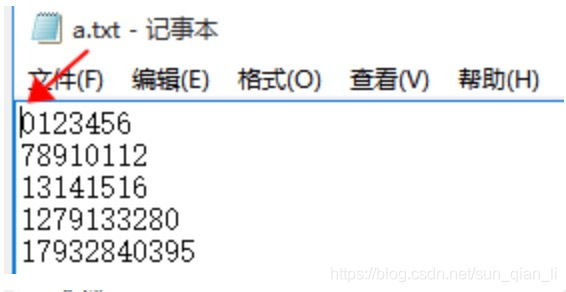
(2)跳行执行:
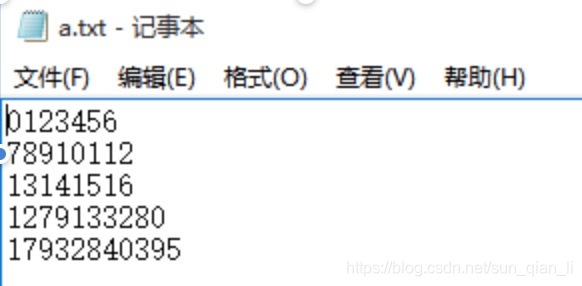
with open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
while(fp.readline()):
print(fp.readline())
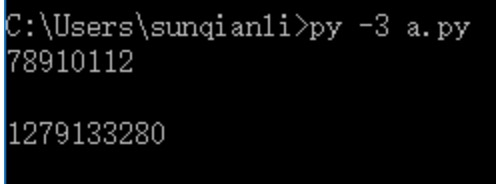
13、查看文件的游标在那个位置
with open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
print(fp.tell())
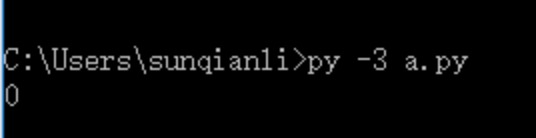
查看游标执行到什么位置了:
with open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
print(fp.tell())
print(fp.readline())
print(fp.tell())

with open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.read()
print(fp.redline())
14、参数
Seek(offset,whence)
Offset:坐标,整数表示从前向后,复数表示从后向前,0表示从文件最开始的游标。
Whence:0,1,2,0表示从文件最开始位置,0,0
“1”表示从当前位置开始,基于当前的相对位置,来重置坐标
10.Seek(5,1)10-5,现在的坐标位置是15
2:表示从文件的末尾开始,做相对位置,来重置坐标
Seek(-5,2)-末尾向前数5个字符
注意:1和2使用基于rb模式
with open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
while(fp.readline()):
print(fp.readline())
seek(0,0)
with open("e:\\a.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.readline()
fp.seek(3,0)
print(fp.tell())





















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








