作为一个6年安卓老开发,我从来没有使用过MVP,看到一堆的接口,火气不打一处来。因为面试的需要,勉强研究了下MVP是什么,优缺点。
数据、View、Presenter,View 将操作给 Presenter,Presenter 去获取数据,数
据获取好了返回给 Presenter,Presenter 去刷新 View。PV,PM 双向依赖
1.接口爆炸
2.Presenter 很重
3.解耦
看的再多不亲自体验,翠花来上代码:
先看下业务,一个输入框,当字符长度小于5时候提示,
“内容太短了,还不到5个字符”,字符长度大于10,提示“内容太长了,超过10个字符了”。

1.Model 代码:
1.1 model
model 负责创建模型所需要的数据
public class Model {
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
String content;
}
1.2 ModelInterface
ModelInterface负责定义 页面数据变动时,业务功能。接口只负责定义动作,具体实现有显现类完成。
public interface ModelInterface {
void handleContent(Model model, OnBusinessHandleLisenner listner);
}
1.4 ModelIml
实现类负责具体业务检验,以及业务校验下的接口回调。
public class ModelIml implements ModelInterface {
@Override
public void handleContent(Model model, OnBusinessHandleLisenner listner) {
if (model.content.length() > 10) {
listner.contentTooLong();
} else if (model.content.length() < 5) {
listner.contentTooShort();
}
}
}
2.View 代码:
2.1 activity
ublic class MVPActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements ViewInterFace{
private TextView tv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.e("MainActivity","onCreate");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_mvp);
final EditText et = findViewById(R.id.et);
tv = findViewById(R.id.tv);
final Presenter presenter = new Presenter(MVPActivity.this);
//焦点监听
et.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence charSequence, int i, int i1, int i2) {
}
//选择内容正在变动
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence charSequence, int i, int i1, int i2) {
//事件的发起
Model model = new Model();
model.setContent(charSequence.toString());
presenter.contentChange(model);
}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable editable) {
}
});
}
@Override
public void onSetContentLong() {
tv.setText("内容太长了,超过10个字符了");
}
@Override
public void onSetContentShort() {
tv.setText("内容太短了,还不到5个字符");
}
}
xml代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".activity.MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et"
android:hint="请输入内容"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp">
</EditText>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="内容太短了,还不到5个字符"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="@color/colorPrimary">
</TextView>
</LinearLayout>
2.2 ViewInterFace
public interface ViewInterFace {
void onSetContentLong();
void onSetContentShort();
}
3 Presenter
3.1 OnBusinessHandleLisenner
public interface OnBusinessHandleLisenner {
void contentTooLong();
void contentTooShort();
}
3.2 PresenterInterface
public interface PresenterInterface {
void contentChange(Model model);
}
3.3 Presenter
public class Presenter implements PresenterInterface, OnBusinessHandleLisenner {
ViewInterFace viewInterFace;
private final ModelIml modelIml;
public Presenter(ViewInterFace viewInterFace) {
//1.构造方法设置 viewInterFace
this.viewInterFace = viewInterFace;
//2.创建ModelIml 实例
modelIml = new ModelIml();
}
@Override
public void contentChange(Model model) {
//3.响应事件
modelIml.handleContent(model, Presenter.this);
}
@Override
public void contentTooLong() {
//4.回调处理视图
if (viewInterFace != null) {
viewInterFace.onSetContentLong();
}
}
@Override
public void contentTooShort() {
if (viewInterFace != null) {
viewInterFace.onSetContentShort();
}
}
}
一个简单业务下来,需要四个接口,8个对象。接口把人整到懵逼,所以数接口重一点也不夸张。
整个presenter,承担了 维护,业务数据承接,业务数据传递,业务接口回调,界面更新 等功能。
为了整明白整个架构,画了一张图:
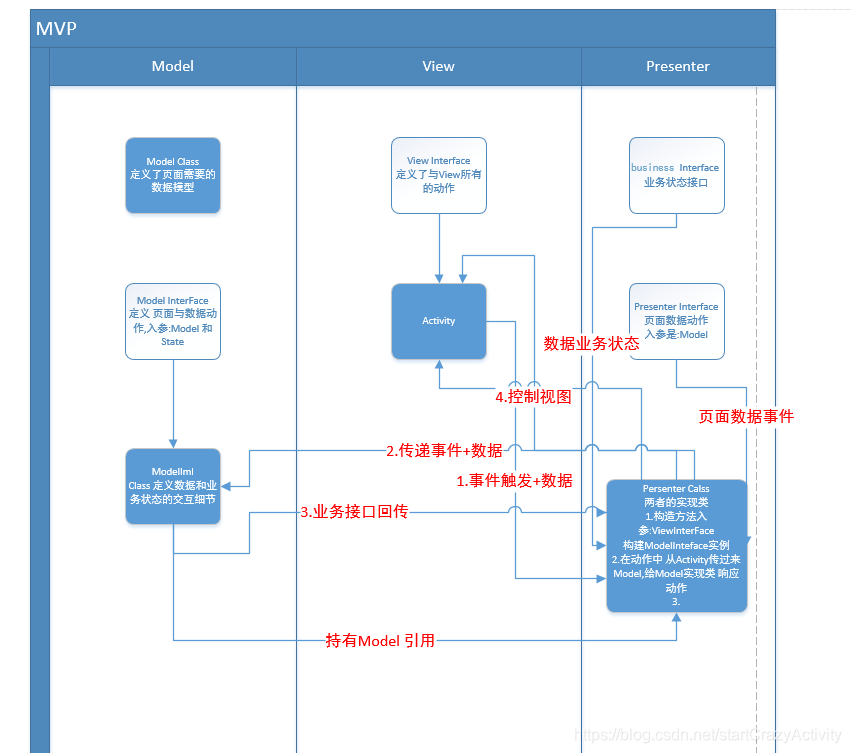
Presenter 做的事情有:
1.实现Persenter Interface 和 Business Interface。
2.构造方法入参是,ViewInterFace 。
3.构造方法中创建,ModelIml 实例。
4.在activity 中定义 响应 交互的方法调用。
5.传递响应给ModelIml。
6.回调 Business Interface。
7.Business Interface回调中调用 ViewInterFace(即actiivty)更新视图。







 本文通过一个简单的Android应用示例,探讨了MVP(Model-View-Presenter)架构模式。作者作为六年经验的安卓开发者,指出MVP模式在实际应用中的问题,如接口爆炸、Presenter权重过高以及解耦效果。在示例中,展示了如何在输入框验证字符长度的场景下运用MVP,涉及四个接口和八个对象,对此表示困惑。作者认为这种复杂性使得MVP在小规模项目中显得过于繁琐。
本文通过一个简单的Android应用示例,探讨了MVP(Model-View-Presenter)架构模式。作者作为六年经验的安卓开发者,指出MVP模式在实际应用中的问题,如接口爆炸、Presenter权重过高以及解耦效果。在示例中,展示了如何在输入框验证字符长度的场景下运用MVP,涉及四个接口和八个对象,对此表示困惑。作者认为这种复杂性使得MVP在小规模项目中显得过于繁琐。
















 1474
1474

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








