一,JDBC简述
JDBA(Java DataBase Connectivity) java数据库连接
是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API ,可以为多种关系型数据库提供统一访问,它由一组使用Java语言编写的类和接口组成,提供了诸如:查询,新增,修改,删除更新数据库中数据的方法。
有了JDBC规范(接口),不同的数据库开发商根据规范中的方法进行实现,开发人员面对的是统一的接口。
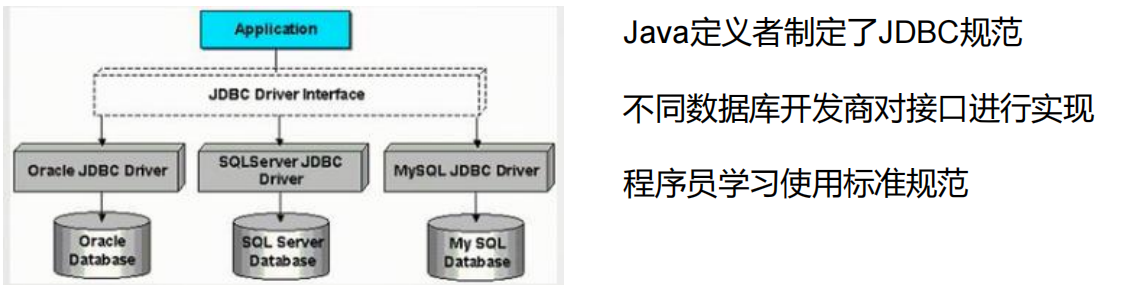
JDBC API:
供程序员调用的接口与类,集成在java.sql包中
DriverManager类作用:管理各种不同的JDBC驱动
Connection 接口:与特定的数据库的连接
Statement 接口:执行sql
PreparedStatement 接口:执行sql
ResultSet 接口:接收查询结果
二,JDBA搭建
1.建立与数据库的连接:
这需要使用DriverManager.getConnection()方法来创建一个Connection对象,它代表一个物理连接的数据库。
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,pass);
url:jdbc:masql://ip:端口(3306)/数据库名?severTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
user:用户名(root)
pass:密码
如下处代码,使用JDBC连接了数据库中的nba库
package demo;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JdbcUtill {
static String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/nba?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";//数据库地址
static String user = "root";//数据库用户名
static String dbpwd = "root";//数据库密码
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,dbpwd);
return connection;
}
}
2.获得Satement执行sql语句
Statement st = connection.createStatement();
Satement中的方法:
Int executeUpdate(String sql)用于执行ddl语句和dml(增,删,改)语句,返回操作的行数
用于执行ddl语句返回0
用于执行dml语句返回操作的行数
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "C++";
int h = 198;
int w = 200;
/*
1.建立与数据库的链接
*/
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/nba?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";//数据库地址
String user = "root";//数据库用户名
String dbpwd = "root";//数据库密码
try {
/*
建立与数据库的链接通道,返回一个连接对象 Connection对象表示一个与数据库的通道
*/
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,dbpwd);
// System.out.println(connection);
//2.发送sql
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// System.out.println(statement);//com.mysql.cj.jdbc.StatementImpl@71248c21
// int row = statement.executeUpdate("insert into player(name,height,weight)value('"+name+"','"+198+"','"+w+"')");
statement.executeUpdate("delete from player where name = 'c++'");
// System.out.println(row);//返回插入行数
// statement.executeQuery();
//3.关闭与数据库的各种链接
statement.close();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("数据库链接失败");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/*
增加
*/
public static void add(int height,String name) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();//获得数据库链接对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();//发送sql
statement.executeUpdate("insert into player(name,height,birthday)values('"+name+"','"+height+"',now())");
//双引双加,字符串类型加单引,数值类型不用加
connection.close();//断开发送sql语句
statement.close();//断开数据库链接
}
/*
修改
*/
public static void update(int id,int height,String name) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.executeUpdate("update player set name = '"+name+"',height = "+height+" where id = "+id);
}
/*
删除
*/
public static void delete(String name) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.executeUpdate("delete from player where name = "+"name");
connection.close();
statement.close();
}
Result executeQuery(String sql);用于执行查询语句,返回一个ResultSet集合
3.获得PrepareStatement执行sql语句
在sql语句中参数位置使用占位符,使用setXX方法向sql中设置参数
PrepareStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
PrepareStatement中的常用方法:
Int executeUpdate()用于执行ddl语句和dml(增,删,改)语句,返回操作的行数
用于执行ddl语句返回0
用于执行dml语句返回操作的行数
Result executeQuery(String sql);用于执行查询语句,返回一个ResultSet集合
public static void add(int height,String name) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();//获得数据库链接对象
//?是占位符,表示此处要接受一个值
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement("insert into player(height,name)value(?,?)");//预编译处理sql
ps.setObject(1,height);//存在几个占位符,就要使用几个setObject语句
ps.setObject(2,name);
ps.executeUpdate();//执行sql
ps.close();
connection.close();
}
public static void update(int id,int height,String name) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement("update player set height=?,name=?where id=?");
ps.setObject(1,height);
ps.setObject(2,name);
ps.setObject(3,id);
ps.executeUpdate();
ps.close();
connection.close();
}
/*
删除
*/
public static void delete(int id) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement("delete from player where id=?");
ps.setObject(1,id);
ps.executeUpdate();
ps.close();
connection.close();
}
注:每次运行结束时需关闭数据库的链接通道
每次操作完成后关闭所有与数据库交互的通道
三,PreparedStatement和Statement
PreparedStatement和Statement都是执行sql语句各有不同的使用场景
二者之间存在差异
基于以下原因
1.代码的可读性和可维护性。
虽然用PreparedStatement来带替Statement对时代码多处几行,但这样的代码无论从可读性还是可维护性上来说。都比直接用Statement的代码高很多档次:
stmt.executeUpdate("insert into tb_name (col1,col2,col2,col4) values
('"+var1+"','"+var2+"',"+var3+",'"+var4+"')");
perstmt = con.prepareStatement("insert into tb_name (col1,col2,col2,col4) values
(?,?,?,?)");
perstmt.setString(1,var1);
perstmt.setString(2,var2);
perstmt.setString(3,var3);
perstmt.setString(4,var4);
perstmt.executeUpdate(); //prestmt是 PreparedStatement 对象实例
2.最重要的一点是极大的提高了安全性.
防止sql注入
String sql = "delete from user where id =" +num:
如果我们将[or 1 = 1]作为id传入进来?
delete from tb_name where id = 1 or 1 = 1;
因为1 = 1肯定成立
而如果使用预编译语句.你传入的任何内容就不会和原来的语句发生任何匹配的关系. 预编译模式中每个占位符处,只能插入一个值,而会过滤其他语句
有下处代码可知,preparedStatement会自动检测是否被攻击
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Demo4.delete("1 or 1=1");
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void delete(String id) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.executeUpdate("delete from player where id = "+id+"");
statement.close();
connection.close();
// Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();
// PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement("delete from player where id = ?");//检测是否被攻击,相较于Statement更安全
// ps.setObject(1,id);
// ps.executeUpdate();
// ps.close();
// connection.close();
//
}
}
四,结果集处理
1,PreparedStatement和Statement中的executeQuery()方法中会返回一个ResuleSet对象,查询结果就封装在此对象中
2,使用ResultSet中的next()方法获得下一行数据
3,使用getXXX(String name)方法获得值
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//通过id,查询信息,并返回对应的对象f
Player player = Demo5.findPlayerById(20);
System.out.println(player);
}
public static Player findPlayerById(int id) throws SQLException {
//获得链接对象
Connection connection = JdbcUtill.getConnection();
//封装sql
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement("select id,name from player where id = ?");
ps.setObject(1,id);
ResultSet resultSet = ps.executeQuery();//executeQuery()执行后,将数据封装到一个ResultSet对象中
//将ResultSet对象中的数据取出,放到一个Player对象中,以便后续使用
Player player = new Player();
while (resultSet.next()){//next()指向结果中数据
player.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
player.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
}
return player;
}




















 3987
3987

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








