配置SELinux
我们已经在Selinux的由来和安全上下文中了解到SELinux的基本概念。
我们知道SELinux会对进程和文件进行权限控制,而让阻止某些进程访问不该访问的文件。
实际上,在真实场景中,虽然SELinux为默认的内核模块,然而实际上,我们还是可以控制其开启和执行。
首先,让我们查看默认的当前的SELinux配置:
$ cat /etc/sysconfig/selinux
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=enforcing
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
则我们可看到默认的政策是targeted,工作模式默认为enforcing,而在该文件中,我们看到工作模式有三种选择:
- enforcing: 强制模式。违反SELinux规则的行为将被阻止并记录到日志中。
- permissive: 宽容模式。违反SELinux规则的行为将会被记录在日志中,但并不会被阻止。
- disabled: 关闭模式。关闭SELinux。不用MAC控制,使用DAC控制。
除了查看配置文件这种永久生效的,我们还可以进行实时查看和更新配置,如:
# 查看当前工作模式
$ getenforce
Enforcing
# 查看setenforce命令
$ setenforce --help
usage: setenforce [ Enforcing | Permissive | 1 | 0 ]
# 更改SELinux工作模式为Permissive
$ sudo setenforce 0
$ getenforce
Permissive
# 查看整个SELinux服务状态
$ sestatus
SELinux status: enabled
SELinuxfs mount: /sys/fs/selinux
SELinux root directory: /etc/selinux
Loaded policy name: targeted
Current mode: permissive
Mode from config file: enforcing
Policy MLS status: enabled
Policy deny_unknown status: allowed
Max kernel policy version: 28
# 查看配置文件
$ cat /etc/sysconfig/selinux
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=enforcing
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
实时更新的这种方式,只能临时生效,如果需要真正更改SELinux的方式,则我们需要更改配置文件, 然后重新启动机器,才能让新的工作模式生效。
则我们可以总结整个SELINUX的工作流程如下: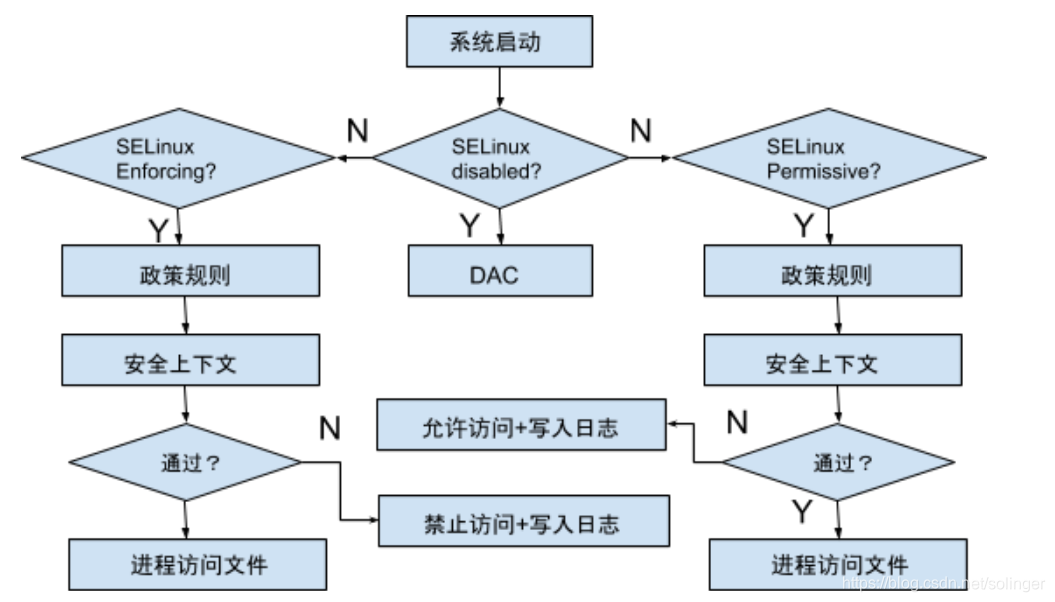
配置文件安全上下文
我们已经在Selinux的由来和安全上下文了解到如何查文件和进程的安全上下文,我们也已知在政策和上下文校验上如果失败的话,进程则无法访问文件,出现这种问题,我们可以通过手动配置安全上下文来满足条件。反之亦然。下面我们通过配置安全上下文来模拟我们提高的工作流程:
-
Permissive出现warning但可访问
[wlin@localhost ~]$ getenforce Permissive [wlin@localhost ~]$ ps auxZ | grep httpd unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 wlin 9032 0.0 0.0 112652 964 pts/0 S+ 19:35 0:00 grep --color=auto httpd system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 root 28651 0.0 0.0 221920 5004 ? Ss 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28655 0.0 0.0 224140 3904 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28656 0.0 0.0 224140 3908 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28657 0.0 0.0 224140 3884 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28658 0.0 0.0 224140 3884 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28659 0.0 0.0 224140 3904 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 30077 0.0 0.0 224140 3844 ? S 14:23 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND [wlin@localhost ~]$ ls -alZ /var/www/html/index.html -rw-r--r--. root root system_u:object_r:unlabeled_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html [wlin@localhost ~]$ curl http://localhost:80 helloselinux则我们可看到可正常访问,则获得警告如下:
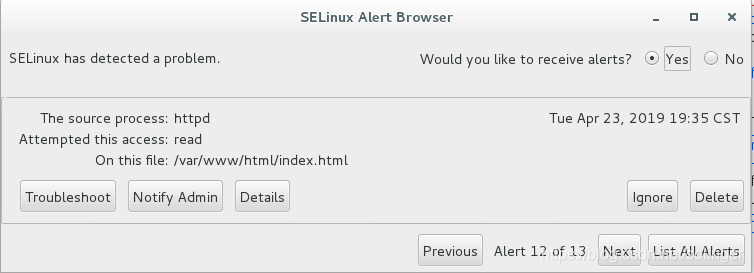
-
enforcing不允许访问
[wlin@localhost ~]$ sudo setenforce 1 [wlin@localhost ~]$ getenforce Enforcing [wlin@localhost ~]$ curl http://localhost:80 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd"><html><head> <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Apache HTTP Server Test Page powered by CentOS</title> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <!-- Bootstrap --> <link href="/noindex/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="noindex/css/open-sans.css" type="text/css" /> -
配置正确的安全上下文,可访问:
$ ps auxZ | grep httpd unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 wlin 9287 0.0 0.0 112652 968 pts/0 S+ 19:38 0:00 grep --color=auto httpd system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 root 28651 0.0 0.0 221920 5004 ? Ss 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28655 0.0 0.0 224140 3904 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28656 0.0 0.0 224140 3908 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28657 0.0 0.0 224140 3884 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28658 0.0 0.0 224140 3884 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 28659 0.0 0.0 224140 3904 ? S 13:55 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 30077 0.0 0.0 224140 3888 ? S 14:23 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND $ ls -alZ /var/www/html/index.html -rw-r--r--. root root system_u:object_r:unlabeled_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html $ sudo chcon -t httpd_sys_content_t /var/www/html/index.html $ getenforce Enforcing $ !curl curl http://localhost:80 helloselinux
除了使用chcon -t 来配置文件上下文,我们可以通过命令restorecon来还原文件上下文,如下:
$ ls -alZ /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html
$ sudo chcon -t unlabeled_t /var/www/html/index.html
$ ls -alZ /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root system_u:object_r:unlabeled_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html
$ sudo restorecon /var/www/html/index.html
$ ls -alZ /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html
另外,这两个命令还可以都通过-a参数来实现对目录的安全上下文。
自然,我们还有其他指令来实现对文件安全上下文的查看和修改。例如semanage等。
内容太多不好吸收我们这里不再继续讲解。





 本文介绍了SELinux的基本概念,强调了它在进程和文件权限控制中的作用。文章详细阐述了如何查看和更改SELinux的配置,包括工作模式的选择(强制、宽容、关闭)以及如何临时和永久改变工作模式。此外,还讨论了如何通过配置文件安全上下文解决进程无法访问文件的问题,提到了chcon和restorecon命令的应用,以及semanage等其他用于管理文件安全上下文的工具。
本文介绍了SELinux的基本概念,强调了它在进程和文件权限控制中的作用。文章详细阐述了如何查看和更改SELinux的配置,包括工作模式的选择(强制、宽容、关闭)以及如何临时和永久改变工作模式。此外,还讨论了如何通过配置文件安全上下文解决进程无法访问文件的问题,提到了chcon和restorecon命令的应用,以及semanage等其他用于管理文件安全上下文的工具。
















 2581
2581

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








