lambda表达式的核心在于函数式接口;函数式接口的核心(只有一个方法)
函数式接口针对函数式编程,java.util.funciton将函数式编程分为如下4个部分:
1)功能型函数接口
public interface Function<T,R> R apply(T t);
特点:有一个形参,返回一个结果。
2)供给型函数接口
public interface Supplier T get()
特点:无参,但有返回值类型,并返回一个结果。
3)消费型接口
public interface Consumer void accept(T t);
特点:有参数类型,但是没有返回值。
4)断言型接口
public interface Predicate boolean test(T t);
特点:有参数,返回值类型为boolean类型。
1.功能型函数接口
package com.xunpu.function;
import java.util.function.Function;
/**
* 功能型函数接口
* public Function<T,R> R apply(T t);
* 步骤:
* 1.定义函数接口 Function<T,R> function=lambda表达式
* 2.R res=function.apply(T类型的数据)
*/
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<Object,String> function=(value)->{
return value.toString();
};
System.out.println(function.apply(new Person("张三",20)));
System.out.println(function.apply("hello"));
function=String::valueOf;
System.out.println(function.apply(12345).length());//5
}
}

2.供给型函数
package com.xunpu.function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* 供给型函数
* public interface Supplier T get();
* 特点:无参,但是有返回值。
* 步骤:
* 1.定义函数接口 Supplier<R> supplier=lambda表达式
* 2.调用 R res=supplier.get();
*/
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//返回一个Person对象
Supplier<Person> supplier=()->{
return new Person("Alice",20);
};
Person p=supplier.get();
System.out.println(p);
//引用对象方法
Supplier<String> supplier1="hello"::toUpperCase;
System.out.println(supplier1.get());
}
}
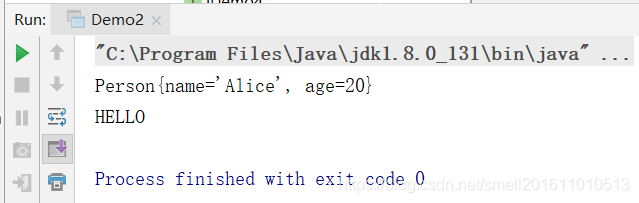
package com.xunpu.function;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* 功能型与供给型结合使用
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//相当于 y=f(x)-->String类型 x=g()-->Supplier类型(应用中是Person类型)
Function<Supplier<Person>,String> function=(s)->{
return s.get().toString();
};
Supplier<Person> s=()->{
return new Person("Mike",18);
};
String str=function.apply(s);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(function.apply(s));
}
}
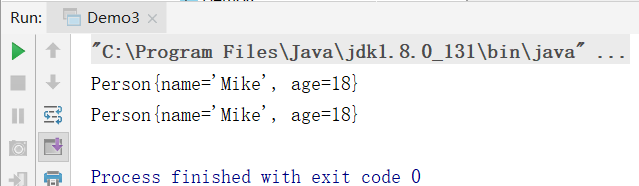
3.消费型函数接口
public interface Consumer void accept(T t);
特点:有参数,无返回值。
package com.xunpu.function;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
/**
* 3.消费型函数接口
* public interface Consumer void accept(T t)
* 特点:有参数,无返回值。
* 步骤:
* 1.定义函数接口 Consumer<T> consumer=lambda表达式
* 2.执行函数 consumer.accept();
*/
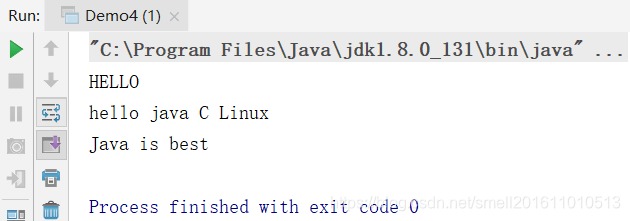
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//T=String 将str变为大写
Consumer<String> consumer=(str)->{
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
};
consumer.accept("hello");
//T=String[]
Consumer<String[]> consumer1=(strs)->{
for(String item:strs){
System.out.print(item+" ");
}
};
consumer1.accept(new String[]{"hello","java","C","Linux"});
System.out.println();
Consumer<String> consumer2=System.out::println;//out是对象,对象方法引用。
consumer2.accept("Java is best");
}
}
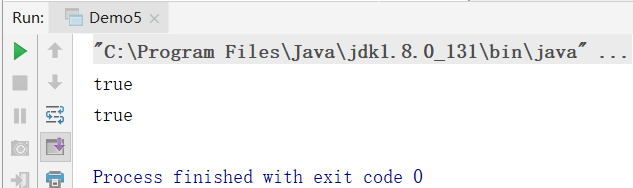
4.断言型函数接口
public interface Predicate boolean test(T t);
特点:有参数,返回值类型为boolean类型。
package com.xunpu.function;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
* 4.断言型函数接口
* public interface Predicate boolean test(T t);
* 特点:有参数,返回值类型为boolean型
* 步骤:
* 1.定义函数式接口 Predicate predicate=lambda表达式
* 2.执行 predicate.test(t);
*/
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Predicate<String> predicate=String::startsWith;因为startsWith()是成员方法,并非静态方法。故应引用对象方法,而不是静态方法。
//判断字符串是否以给定的字符开始
Predicate<String> predicate="hello"::startsWith;
System.out.println(predicate.test("h"));
//判断给定的对象是否由Person对象实例化而来
Predicate<Object> predicate1=(obj)->{
return obj instanceof Person;
};
Person p=new Person("张三",20);
System.out.println(predicate1.test(p));
}
}








 本文深入探讨Java函数式编程的四大核心接口:功能型、供给型、消费型与断言型,通过具体示例讲解如何运用lambda表达式实现简洁高效的代码设计。
本文深入探讨Java函数式编程的四大核心接口:功能型、供给型、消费型与断言型,通过具体示例讲解如何运用lambda表达式实现简洁高效的代码设计。
















 3365
3365

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








