首先我们要把spingboot 打包成jar 包
编写shell启动 命令,下载 是编写的一个通用的启动命令
jar_file=loveMM.jar springboot的jar
pid_file=loveMM.pid
log_file=loveMM.log 日志文件
pid_dir=/var/run/
pid_path="${pid_dir}$pid_file"
cd $(dirname "$0")
# wait_for_start(pid_file, timeout)
function wait_for_start(){
pid_file=$1
t=10
if test $# -ge 2 && test $2 -gt 0
then
t=$2
fi
while test $t -ge 0
do
if test -s $pid_file
then
pid=`cat "$pid_file"`
if kill -0 $pid 2>/dev/null
then
# success
return 0
fi
fi
(( t-- ))
sleep 1
done
# fail
return 1
}
function wait_for_stop(){
pid=$1
t=10
if test $# -ge 2 && test $2 -gt 0
then
t=$2
fi
while test $t -ge 0
do
if kill -0 $pid 2>/dev/null
then
(( t-- ))
sleep 1
else
# success
return 0
fi
done
# fail
return 1
}
function start_jar(){
java_path=`command -v java`
if ! test -x "$java_path"; then
echo "java not installed"
elif ! command -v daemonize > /dev/null; then
echo "daemonize not installed"
elif test -s "$jar_file"; then
echo "Starting $jar_file"
daemonize -a -c "$(pwd)" -e "$log_file" -o "$log_file" -p "$pid_path" -l "$pid_path" "$java_path" -jar "$jar_file"
if ! test $? -eq 0 ;then
return 1
fi
wait_for_start "$pid_path" 10
if test $? -eq 0 ;then
echo "start $jar_file success"
return 0
fi
fi
echo "start $jar_file fail"
}
function stop_jar(){
if test -s "$pid_path"
then
real_pid=`cat "$pid_path"`
if (kill -0 $real_pid 2>/dev/null)
then
echo "Shutting down $jar_file"
kill -s 15 $real_pid
wait_for_stop $real_pid 10
if test $? -ne 0; then
echo "wait for $real_pid timeout, force kill"
kill -9 $real_pid
else
echo "$jar_file is shutdown"
fi
else
echo "$jar_file $real_pid is not runing"
rm -f "$pid_path"
fi
else
echo "$jar_file is not runing"
fi
ps -ef | grep $jar_file | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9 2>/dev/null
}
function status_jar(){
if test -s "$pid_path"
then
real_pid=`cat "$pid_path"`
if (kill -0 $real_pid 2>/dev/null)
then
echo "$jar_file is runing"
else
echo "$jar_file $real_pid is not runing"
fi
else
echo "$jar_file is not runing"
fi
}
case $1 in
start)
start_jar
;;
stop)
stop_jar
;;
status)
status_jar
;;
restart)
stop_jar
start_jar
;;
*)
echo "unknow arg $1"
esac
如果 遇到 "daemonize not installed" ,在linux 调用
yum -y install daemonize 安装
cd 到 jar 的根目录 ,执行启动命令
sh service.sh start 启动 ,stop 停止,
启动后开始配置nginx,我的jar 启动的是8081 端口,
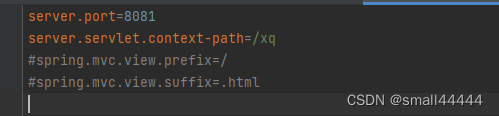
那么在nginx 里添加 路径
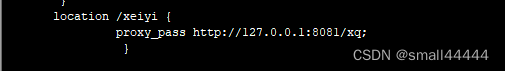
通过代理,我们在浏览器就可以方法啦
http://ip/xeiyi 这样就可以了,记录一下




 本文介绍了如何将SpringBoot应用打包成jar,并在Linux环境中使用shell脚本进行启动、停止和状态检查。同时,文章还讲解了在Linux上安装daemonize的必要性,以及如何通过Nginx配置反向代理,将应用服务暴露在8081端口对外提供访问。
本文介绍了如何将SpringBoot应用打包成jar,并在Linux环境中使用shell脚本进行启动、停止和状态检查。同时,文章还讲解了在Linux上安装daemonize的必要性,以及如何通过Nginx配置反向代理,将应用服务暴露在8081端口对外提供访问。
















 603
603

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








