JDK动态代理是代理模式的一种实现方式,其只能代理接口。
使用步骤:
- 新建一个接口
- 为接口创建一个实现类
- 创建代理类实现java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler接口
- 调用Proxy.newProxyInstance方法创建代理对象实例
废话不多说直接上码:
- 先设计一个接口Test
public interface Test {
public void hello();
}
- 实现这个接口
public class TestImpl implements Test{
@Override
public void hello() {
System.out.println("Hello!");
}
}
- 然后创建一个代理类(实现java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler接口)
public class GeneralProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler{//这个泛型可有可无
private T target;
public GeneralProxy(T target) {
this.target = target;
}
/**
* @param proxy 真实代理对象com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
* @param method 我们所要调用某个对象真实的方法的Method对象
* @param args 代理对象方法传递的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result=method.invoke(this.target, args);
return result;
}
}
- 最后使用Proxy.newProxyInstance方法产生一个代理对象实例,强转后即可调用被代理接口中的方法。
因为在参数中传入了一组接口信息,因此代理对象只要实现了这些接口,那么在调用时就可以将其强转为该接口类型,这也是为什么JDK代理只能代理接口的原因
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test target = new TestImpl();
Test test = (Test)Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new GeneralProxy(target));
/*
这个test对象其实是$Proxy0代理对象,而非Test对象,
只因这个[代理对象]实现了[被代理对象]的所有接口,
因此才能被强转为[被代理对象]的某一接口类型,
在调用hello方法时实际上是进入了GeneralProxy中的invoke方法里
*/
test.hello();
}
(转)解释一下Proxy.newProxyInstance这个方法中的各个参数:
ClassLoader loader:一个ClassLoader对象,定义了由哪个ClassLoader对象来对生成的代理对象进行加载
Class<?>[] interfaces:一个Interface对象的数组,表示的是我将要给我需要代理的对象提供一组什么接口,如果我提供了一组接口给它,那么这个代理对象就宣称实现了该接口(多态),这样我就能调用这组接口中的方法了
InvocationHandler h:一个InvocationHandler对象,表示的是当我这个动态代理对象在调用方法的时候,会关联到哪一个InvocationHandler对象上
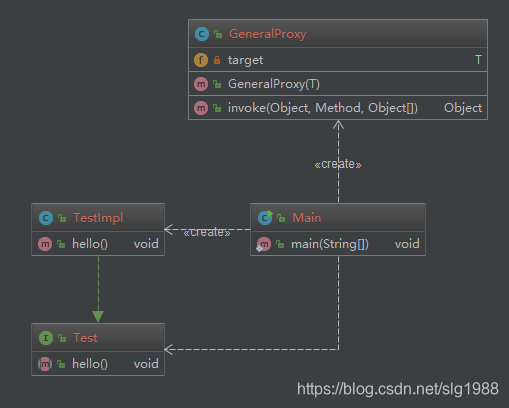
- 生成的UML类图是这样子的:
最后附上JDK中Proxy类中的newProxyInstance方法源码和分析:
(转)这里查看JDK1.8.0_65的源码,通过debug学习JDK动态代理的实现原理
大概流程:
1、为接口创建代理类的字节码文件
2、使用ClassLoader将字节码文件加载到JVM
3、创建代理类实例对象,执行对象的目标方法
/**
* Returns an instance of a proxy class for the specified interfaces
* that dispatches method invocations to the specified invocation
* handler.
*
* <p>{@code Proxy.newProxyInstance} throws
* {@code IllegalArgumentException} for the same reasons that
* {@code Proxy.getProxyClass} does.
*
* @param loader the class loader to define the proxy class
* @param interfaces the list of interfaces for the proxy class
* to implement
* @param h the invocation handler to dispatch method invocations to
* @return a proxy instance with the specified invocation handler of a
* proxy class that is defined by the specified class loader
* and that implements the specified interfaces
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if any of the restrictions on the
* parameters that may be passed to {@code getProxyClass}
* are violated
* @throws SecurityException if a security manager, <em>s</em>, is present
* and any of the following conditions is met:
* <ul>
* <li> the given {@code loader} is {@code null} and
* the caller's class loader is not {@code null} and the
* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission
* s.checkPermission} with
* {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} permission
* denies access;</li>
* <li> for each proxy interface, {@code intf},
* the caller's class loader is not the same as or an
* ancestor of the class loader for {@code intf} and
* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess
* s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to {@code intf};</li>
* <li> any of the given proxy interfaces is non-public and the
* caller class is not in the same {@linkplain Package runtime package}
* as the non-public interface and the invocation of
* {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission s.checkPermission} with
* {@code ReflectPermission("newProxyInPackage.{package name}")}
* permission denies access.</li>
* </ul>
* @throws NullPointerException if the {@code interfaces} array
* argument or any of its elements are {@code null}, or
* if the invocation handler, {@code h}, is
* {@code null}
*/
@CallerSensitive
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
// 判断InvocationHandler是否为空,若为空,抛出空指针异常
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
* 生成接口的代理类的字节码文件
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
* 使用自定义的InvocationHandler作为参数,调用构造函数获取代理类对象实例
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}







 本文详细介绍了JDK动态代理的实现原理,包括如何为接口创建代理类,使用Proxy.newProxyInstance方法生成代理对象实例,以及动态代理的工作流程。通过代码示例展示了动态代理的具体操作。
本文详细介绍了JDK动态代理的实现原理,包括如何为接口创建代理类,使用Proxy.newProxyInstance方法生成代理对象实例,以及动态代理的工作流程。通过代码示例展示了动态代理的具体操作。
















 1525
1525

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








