文章目录
1. 自动类型转换
1. 定义:
java程序在进行赋值或者运算时,精度小的类型自动转换为精度大的数据类型,这就是自动类型转换。
2. 复习一下所有的基本数据类型【背】:
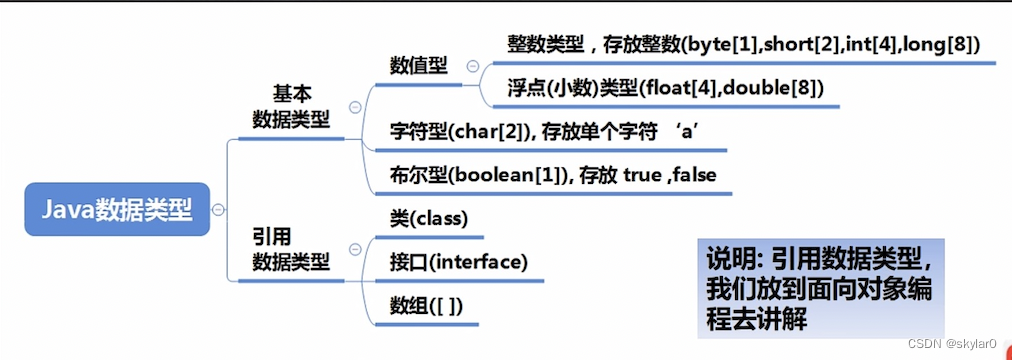
3. 数据类型排序(容量)【背】:
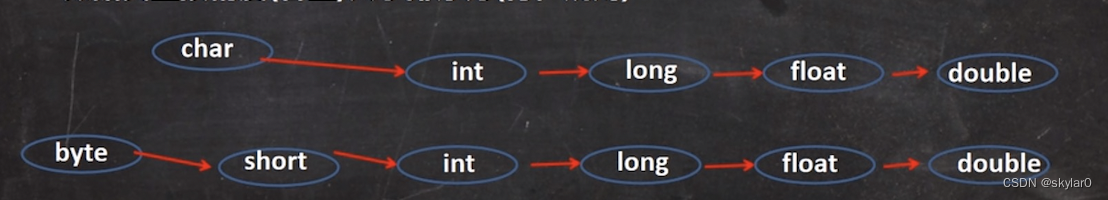
4. 举例:
(1)int a = 'c'; --------对的,char < int 可以自动转换。
(2)double d = 80; ---------对的, int < double 可以自动转换。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示自动转换
int num = 'a'; //可以
double d1 = 80; //可以
System.out.println(num); //输出:97
System.out.println(d1); //输出:80.0
}
}
2. 自动类型转换细节(6点)
- 多种类型数据的混合运算,系统会先把所有数据自动转换成容量最大的那种数据类型,然后再计算。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//细节一:
int n1 = 10; //可以
float d1 = n1 + 1.1;//❌1.1是double(float后带一个F)double > float。
double d1 = n1 + 1.1; //对的。
float d1 = n1 + 1.1F; //对的。 规定1.1为float类型。
}
}
- 当把容量大的数据类型赋值给容量小的数据类型会报错。大->小,会报错。反之则自动转换。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
int n2 = 1.1; //错,会报错。double(8) > int(4)
}
}
- (byte, short)和 char 之间不能互相自动转换。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//当把数字赋值给byte时,先判断是否数字在[-128,127],在区间内就可以。
byte b1 = 10; //可以
char c1 = b1; //错误。byte不能自动转换为char。
}
}
- byte,short,char三者可以计算,在计算时先转换为int类型。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
byte b1 = 1;
byte b2 = 2;
short s1 = 1;
short s2 = b2 + s1; //错误。 byte和short运算后的结果为int类型。int>short。
int s2 = b2 + s1; //对的。
byte b3 = b1 + b2; //错误。byte之间计算的结果也是int类型。
}
}
- boolean不参与类型转换。
- 自动提升原则:表达式结果的类型自动提升为操作数中最大的类型。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
byte b4 = 1;
short s3 = 100;
int num200 = 1;
double num300 = 1.1;
double d1 = b4 + s3 + num200 + num300; //double为最大的类型,结果必须为double。
}
}
3. 强制类型转换(4点)
3.1 定义:
自动类型转换的逆过程,将容量大的数据类型转换为容量小的数据类型【大 - > 小】。使用时要加上强制转换符(), 但可能造成精度降低 / 溢出,要格外注意。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//演示强制类型转换
int n1 = (int)1.9;
System.out.println("n1=" + n1); //输出n1=1。精度损失
int n2 = 2000;
byte b1 = (byte)n2;
System.out.println("b1=" + b1); //输出b1=-48。数据溢出
}
}
3.2 细节
- 当数据从大到小,就需要使用强制转换。
- 强转符号只针对于最近的数有效,往往需要小括号()来提升优先级。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//强转符号就近原则。
int x = (int)10*3.5+6*1.5; //输出44.0。double
int x = (int)(10*3.5+6*1.5); //输出44。int
}
}
- char类型可以保存int的常数值,但不能保存int的变量值,需要强转。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//强转符号就近原则。
char c1 = 100; //可以。
int m = 100;
char c2 = m; //不可以
char c3 = (char)m; //可以
System.out.println(c3); //输出100对应的字符。输出d
}
}
- byte、short和char类型在运算时,当作int类型。
4.练习
- 判断是否能够通过编译:
- short s = 12; //可以
s = s-9; //错误。short运算会先转成int,int不能赋给short s。 - byte b = 10; //可以
b = b + 11; //不可以。byte运算会先转换成int,int不能赋给byte。
b = (byte)(b + 11); // 可以。将int强制转换成byte,再赋给byte。 - char c = ‘a’; //可以
int I = 16; //可以
float d = .314F; //可以
double result = c + I + d; // int和float运算会先转成float,float赋值给double,可以。 - byte b = 16; //可以
short s = 14; // 可以
short t = s + b; //int不能赋给short。
- short s = 12; //可以
4. string和基础数据类型的转换
4.1 定义:
在程序开发中,经常需要将基础数据类型 + string互相转换。
4.2 基础类型–>string
语法:基础类型的值 + “”
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//基础数据类型-->string
int n1 = 100;
float f1 = 1.1F;
double d1 = 4.5;
boolean b1 = true;
String s1 = n1 + "";
String s2 = f1 + "";
String s3 = d1 + "";
String s4 = b1 + "";
System.out.println(s1 + " " + s2 + " " + s3 + " " + s4);
//输出 100 1.1 4.5 true
}
}
4.3 string -> 基础类型【体验】
- 语法:通过基本类型的包装类调用parseXX方法即可。
- 怎么把字符串转换成字符char: 是指取string的第一个字符。
public class var01 {
//编写一个main方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//string --> 基础数据类型
String s5 = "123";
//会在OOP将对象和方法的时候详细说。
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(s5);
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(s5);
float num3 = Float.parseFloat(s5);
Long num4 = Long.parseLong(s5);
Byte num5 = Byte.parseByte(s5);
short num6 = Short.parseShort(s5);
Boolean b = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
System.out.println(num1); //123
System.out.println(num2); //123.0
System.out.println(num3); //123.0
System.out.println(num4); //123
System.out.println(num5); //123
System.out.println(num6); //123
System.out.println(b); //true
//怎么把字符串转换成字符char: 是指取string的第一个字符。
//解读:s5.charAt(0)得到s5的第一个字符 ‘1’
System.out.println(s5.charAt(0))
}
}
4.4注意事项:
- 在string --> 基础数据类型时,要确保string能够转成有效的数据。
比如:可以实现“123” --> 整数123。但是“hello”不能转成整数。 - 如果格式不对,会抛出异常,程序会终止。这个问题在异常处理章节会处理。




 本文详细介绍了Java中的自动类型转换规则,包括基本数据类型之间的转换、混合运算的处理,以及强制类型转换的使用,同时涵盖string与其他基础类型之间的转换过程和注意事项。
本文详细介绍了Java中的自动类型转换规则,包括基本数据类型之间的转换、混合运算的处理,以及强制类型转换的使用,同时涵盖string与其他基础类型之间的转换过程和注意事项。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








