Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
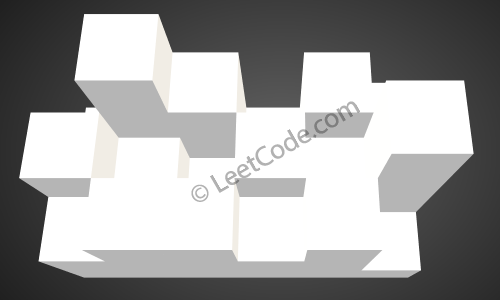 The above image represents the elevation map
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
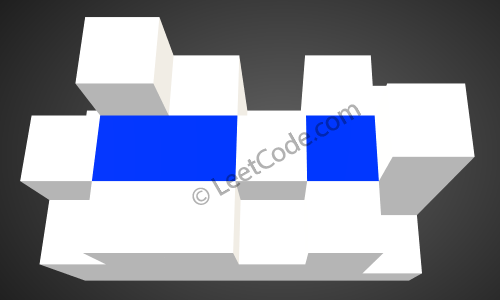
After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
使用min—heap的方式进行处理,可以非常好的解决这个问题。
java
class Cell {
int x;
int y;
int z;
public Cell(int x, int y, int z) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
}
public class Solution {
public int trapRainWater(int[][] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 || arr[0] == null || arr[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
Comparator<Cell> cmp = new Comparator<Cell>() {
public int compare(Cell c1, Cell c2) {
return c1.z - c2.z;
}
};
PriorityQueue<Cell> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(1, cmp);
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[arr.length][arr[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
heap.offer(new Cell(i, 0, arr[i][0]));
heap.offer(new Cell(i, arr[0].length - 1, arr[i][arr[0].length - 1]));
visit[i][0] = true;
visit[i][arr[0].length - 1] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr[0].length; i++) {
heap.offer(new Cell(0, i, arr[0][i]));
heap.offer(new Cell(arr.length - 1, i, arr[arr.length - 1][i]));
visit[0][i] = true;
visit[arr.length - 1][i] = true;
}
int res = 0;
int[] dir_x = new int[] {0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dir_y = new int[] {1, -1, 0, 0};
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
Cell cell = heap.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int n_x = cell.x + dir_x[i];
int n_y = cell.y + dir_y[i];
if (n_x >= 0 && n_x < arr.length && n_y >= 0 && n_y < arr[0].length && !visit[n_x][n_y]) {
heap.offer(new Cell(n_x, n_y, Math.max(cell.z, arr[n_x][n_y])));
visit[n_x][n_y] = true;
res += Math.max(0, cell.z - arr[n_x][n_y]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}




 本文介绍了一种利用最小堆解决二维地图中雨水收集问题的方法。通过遍历边界并将内部单元格与周围较高单元格比较,逐步填充内部区域,计算总的积水体积。
本文介绍了一种利用最小堆解决二维地图中雨水收集问题的方法。通过遍历边界并将内部单元格与周围较高单元格比较,逐步填充内部区域,计算总的积水体积。

















 207
207

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










