类与对象
类与对象的定义与使用
类的定义
class 类名{
静态的属性
动态的方法
}
public class Student {
/**
*静态的属性
*/
public String name;
private double height;
private String classId;
public Student(String name, double height, String classId) {
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
this.classId = classId;
}
/**
* 动态的方法
*/
public void introduceMyself()
{
System.out.println("姓名"+name+"身高"
+height+"班级"+classId);
}
}
对象定义
类名 对象名
Student student;
对象使用
对象名.方法名/属性
Student student=new Student("zs",2.2,"152");
student.introduceMyself();
String str=student.name;
引用
Java中对象的赋值都是引用(地址),java 8大基本类型是 值 赋值
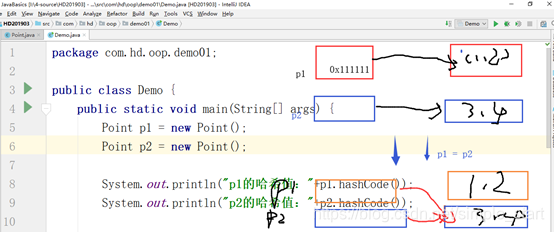
构造函数 和垃圾回收
构造器,创建对象的时候,会调用该方法。
public class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
一个类的构造器可以有多个,每个构造器中参数个数,或类型不一样
如果一个类的构造器是私有的,不能new对象。
垃圾回收
当对象即将被回收的时候,调用的方法
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
super.finalize();
}
垃圾回收,由系统定时触发,一般有一个单独的线程回收
访问权限控制和封装
封装需要考虑一个对象有哪些属性和方法
public:公有
prorected 保护
private 私有
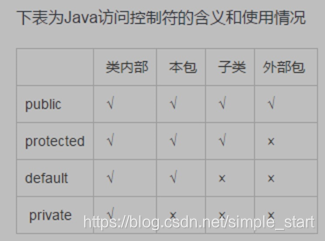
属性用 private 并为属性生产公有 get/set 方法
方法用public
静态
需求:有一个班级,有很多个学生,Student类,在创建对象的时候,学生的ID,实现自增长,
New Student() id =1;
New Student() id =2;
public class Student {
/**
*静态的属性
*/
public String name;
private int id;
private static int num=0;
public Student(String name) {
this.id=++num;
this.name = name;
}
}
静态static 能够用来修饰变量、方法、类、代码块
静态成员变量
该成员属于类,不属于谋和具体的对象
访问类名.变量名
如果一个值,很多对象都使用,并且值不变,“男1”“女0”
public class Student {
/**
*静态的属性
*/
public String name;
private int id;
private byte sex;
private static int num=1;
private static byte man=1;
private static byte woman=0;
public Student(String name,byte sex) {
this.id=++num;
this.sex=sex;
this.name = name;
}
public void introduceMyself()
{
System.out.println("姓名 "+name+" id"
+id+" sex"+sex);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student=new Student(" zs",Student.man);//sex 的值为1;
Student student1=new Student(" ls",Student.woman);//sex 的值为0;
student.introduceMyself();
student1.introduceMyself();
}
}
结果
姓名 zs id2 sex1
姓名 ls id3 sex0
静态常量(常用)
public final static byte MALE =0;
public final static byte FEMALE = 1;
性别:男、女
订单状态:未支付、已支付、待收货、已收货、已评论、退款申请
静态方法
该方法属于类
类名.方法名
静态方法里面不能使用this
静态方法里面只能访问静态成员
静态代码块
static{
//…代码只会被执行一次,类加载的时候被执行
}
继承与多态
继承
继承就是允许后辈使用前辈的功能
继承作用
使用了代码重用,解决了代码冗余和不好维护
重写
子类重写了父类的方法,子类的方法名称和参数和父类一样;
权限关系
如果父类属性希望可被子类访问,可以将属性定义成protected
多态
运行时的多态, 也即是这个对象到底是什么类型,需要运行的时候知道
抽象类与接口
抽象方法
一个方法只有声明,没有实现,需要使用abstract 修饰
抽象类
一个类中包含一个抽象方法,该类被称为抽象类
抽象类不能直接new对象
抽象类的作用
为后代进行规划,凡是他的后代,必须实现它未完成的方法
接口
一个类中所有的方法都是抽象的,正是因为都是抽象的,所以抽象修饰符abstract写不写都没有所谓
接口使用一个关键词interface修饰
接口中只有方法,没有属性
不能直接new对象,但是存在以下情况
new一个接口,并且告知里头方法的实现
new形状类型,计算面积和周长
public interface Shape {
public double area();
public double pee() ;
}
class Circle implements Shape{
@Override
public double area() {
return 10;
}
@Override
public double pee() {
return 20;
}
}
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle circle = new Circle();
System.out.println(circle.area());
System.out.println(circle.pee());
Shape shape =new Shape() {
@Override
public double area() {
return 10*10;
}
@Override
public double pee() {
return 10*4;
}
};
}
}
子类实现接口
匿名内部类
这个类没有名字,如果一个类,你只是使用一次的话,可以使用匿名类
泛型
泛型是一种 类型 参数化的机制,参数的类型可以不固定,真正实现了代码重用,达到一劳永逸的目标。
class Fruit {
public String toString() {
return "Fruit"; }
}
class Apple extends Fruit {
public String toString(){ return "Apple"; }
}
class Person {
public String toString(){ return "Person"; }
}
class ClassName<T> {//主类,把你文件名改成ClassName.java
void show_1(T t){
System.out.println("show_1 "+ t.toString());
}
<E> void show_2(E e){
System.out.println("show_2 "+e.toString());
}
<T> void show_3(T t){
System.out.println("show_3 "+t.toString());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassName<Fruit> o = new ClassName<Fruit>();
Fruit f = new Fruit();
Apple a = new Apple();
Person p = new Person();
System.out.println("show_1 演示________________________");
o.show_1( f );
o.show_1( a );
// o.show_1( p ); // 楼主把这行代码去掉注释看一下,是不能编译通过的。因为在
// ClassName<Fruit>中已经限定了全局的T为Fruit,所以不能再加入Person;
System.out.println("show_2 演示________________________");
o.show_2( f );
o.show_2( a );
o.show_2( p );
System.out.println("show_3 演示________________________");
o.show_3( f );
o.show_3( a );
o.show_3( p );
}
}
/*
<span style="color: #800080;">程序输出:
show_1 演示________________________
show_1 Fruit
show_1 Apple
show_2 演示________________________
show_2 Fruit
show_2 Apple
show_2 Person
show_3 演示________________________
show_3 Fruit
show_3 Apple
show_3 Person</span>
https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/390171178
*/





















 22万+
22万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








