constraints 和 trigger 是为 relational database提供服务,是SQL的标准,系统变化可以很多。
(Integrity)Constraints
用来限制正当的数据库状态,例子如下
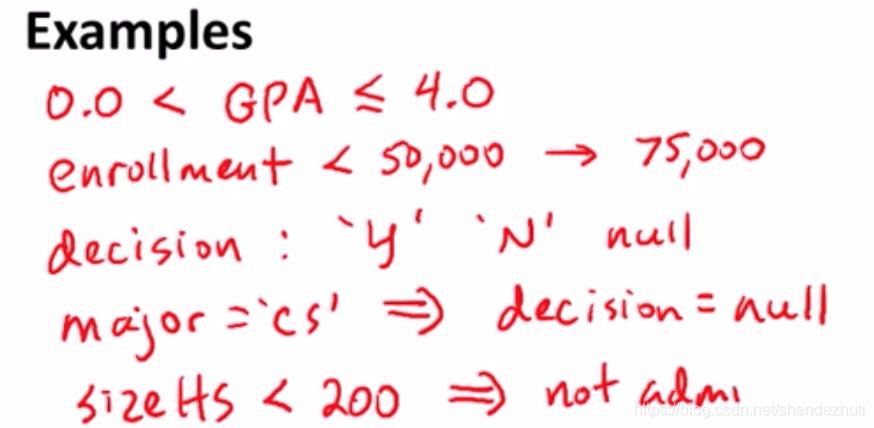
为什么要用constraint
- 检查Data-entry errors (insert时)
- correctness criteria (update时)
- enforce consistency
声明和执行 constraint
声明Declaration
- 初始声明时检查
- 或者之后
执行Enforcement
- 每一次改变后检查
- 每一次transaction后检查
Constraints类型
- Non-null constraints
插入数据不为空
- Key constraints
被声明为key的attribute值必须是unique的
- Attribute-based and tuple-based constraints
某个atribute的值必须满足定义的要求 或者一整个tuple都要满足要求
- General assertions
比较一般性的声明
- Referential Integrity (foreign key) constraints
=Integrity of reference=No dangling pointer 注意pointer其实是有方向的,要根据我们数据库数据的意义来看。
指每个表R列A中的值必须出现在表S列B中
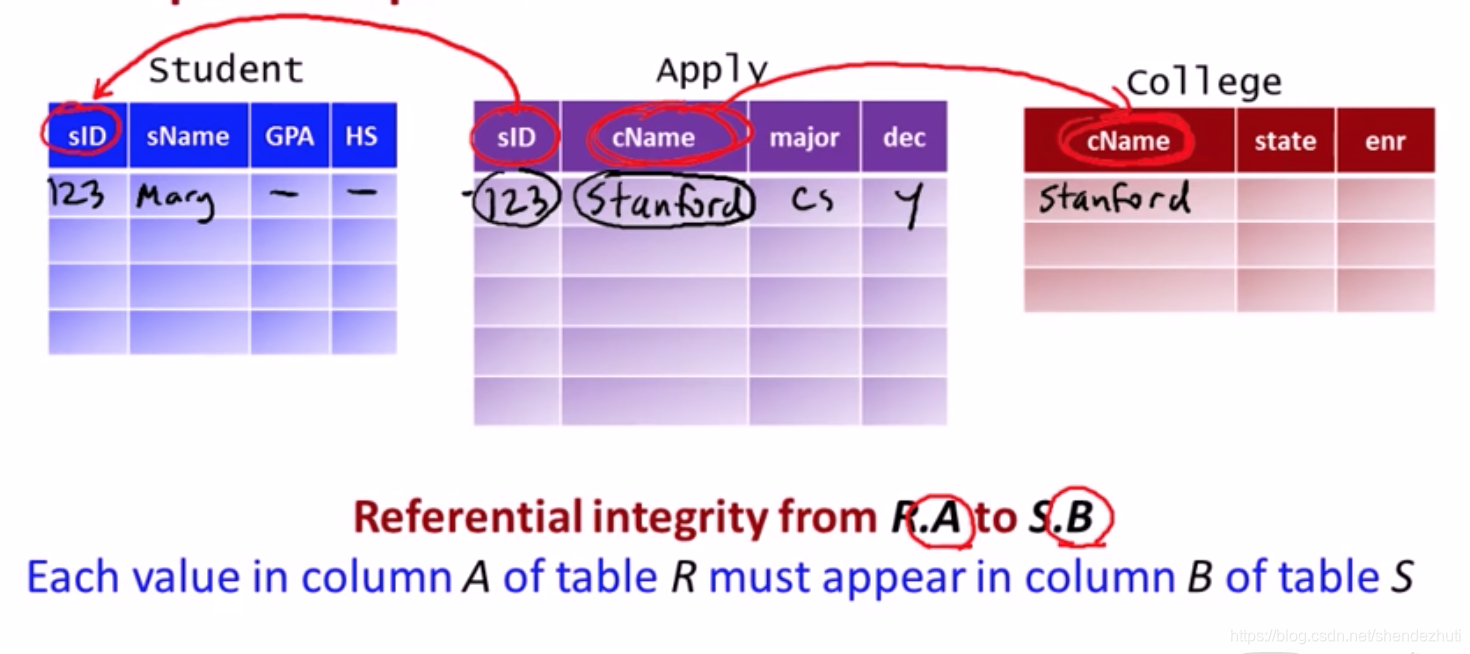
- A is called the “foreign key”
- B is usually required to be the primary key for table S or at least unique
- Multi-attribute foreign keys are allowed
可能违反reference integrity的一些操作
- 插入数据入R
- 删除数据从S
- 更新R.A
- 更新S.B
特殊操作

利用cascade可以实现自动删除,即删除S中某个tuple后,自动删除对应R中的tuple
Trigger
检查数据库的改变,检查状态并且初始化,当某个条件发生时,执行某个动作。
比如 enrollment>=35000, reject all application
为什么使用Trigger
将逻辑操作从application转移到数据库系统
Trigger创建模式
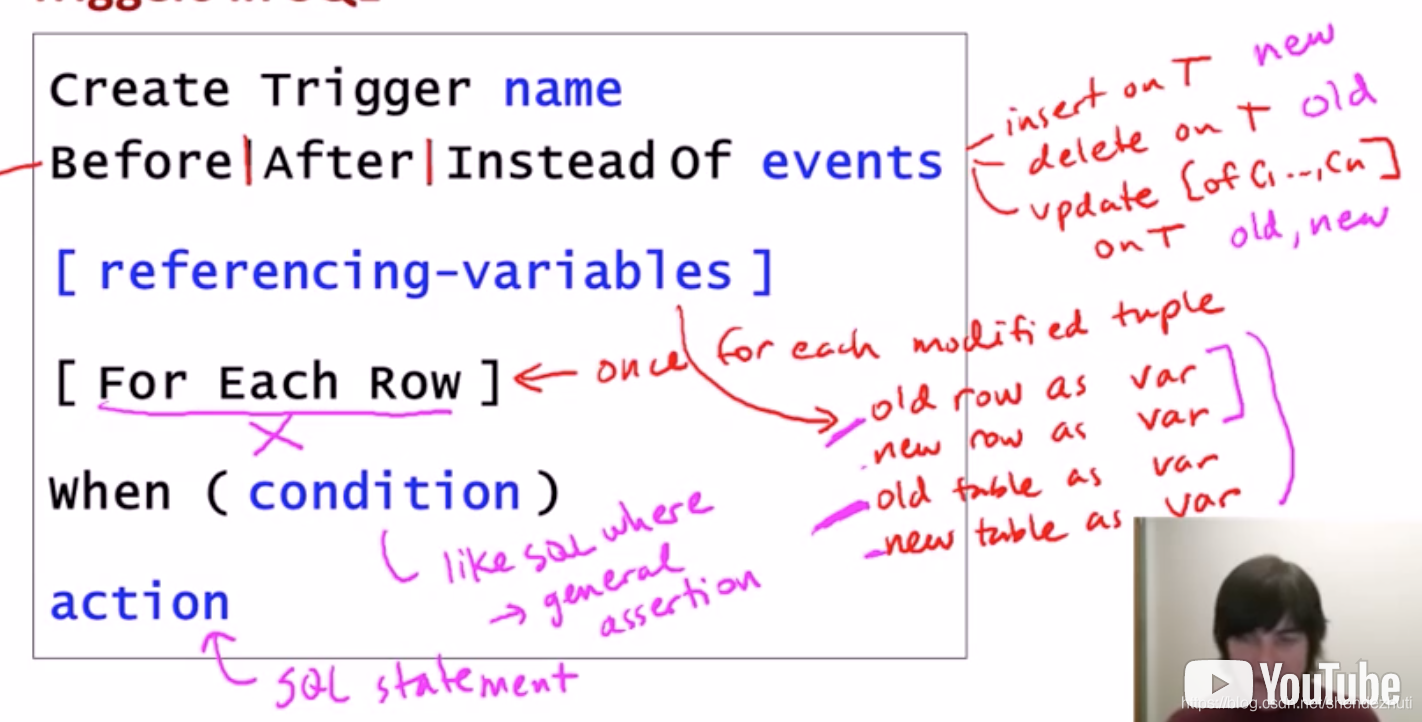
events:一般是对数据库的修改操作
condition: sql语言
1) Move monitoring logic from apps into DBMS
2) Enforce constraints
- Beyond what constraint system supports
- Automatic constraint “repair
比较棘手的地方
§ Row-level vs. Statement-level
– New/Old Row and New/Old Table
– Before, Instead Of
§ 许多的trigger同时产生
§ 一个trigger引发其他的trigger (chaining)
– Also self-triggering, cycles, nested invocations
§ Conditions in When vs. as part of action
不同的trigger实现差别可能非常的大
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








