目录
一、删除链表中等于给定值 key 的所有节点。
删除链表中等于给定值 key 的所有节点.
解题思路 & 内存图:

代码示例:
//删除所有值为 key 的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (this.head == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
ListNode prev = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if (this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
}
二、反转一个单链表
反转一个单链表.
解题思路 & 内存图:
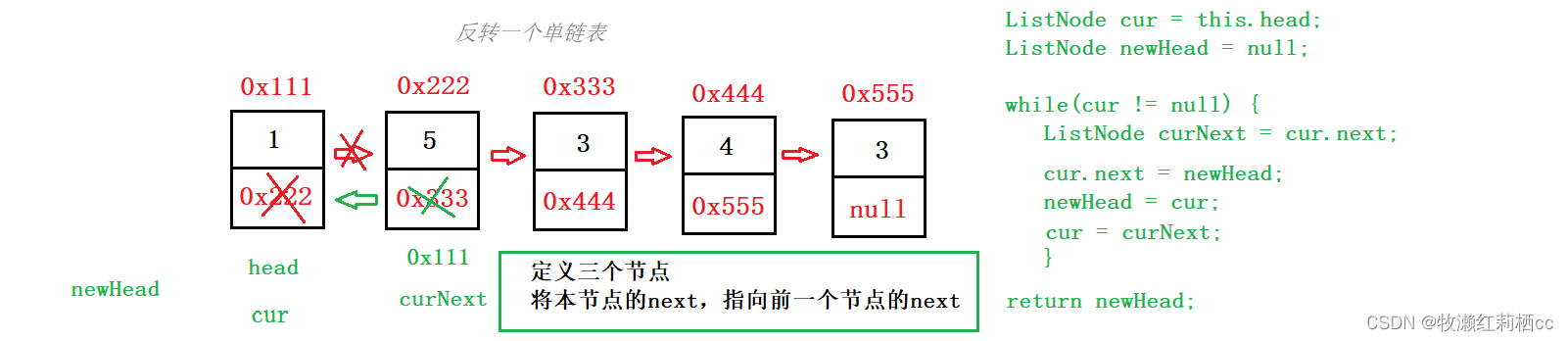
代码示例:
//反转一个单链表
public ListNode reverseList() {
if (this.head == null || this.head.next == null) {
return this.head;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
ListNode newHead = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
this.head = newHead;
return this.head;
}
三、找链表中间结点
给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
解题思路 & 内存图:

代码示例:
//找到链表中的中间结点
public ListNode findMiddleNode(){
if (this.head == null || this.head.next == null) {
return this.head;
}
ListNode fast = this.head;
ListNode slow = this.head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
四、找到倒数第 k 个结点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
解题思路 & 内存图:

代码示例:
//输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
public ListNode findLastKey(int k) {
if (k <= 0 || k > size()) {
System.out.println("k有问题");
return null;
}
if (this.head == null) {
System.out.println("空表");
return null;
}
ListNode fast = this.head;
ListNode slow = this.head;
while (k > 0) {
k--;
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
五、链表合并
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。
新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
解题思路 & 内存图:

代码示例: 代码返回的是整个新链表,而不是内存图的新结点。
//将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。
//新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
public MyLinkedList mergeTwoLists(MyLinkedList List1) {
if (List1.head == null && this.head == null) return null;
if (List1.head == null) return this;
if (this.head == null) return List1;
ListNode headA = List1.head;
ListNode headB = this.head;
ListNode newHead = null;
boolean isFlag = true;
if (headA.val < headB.val) {
newHead = headA;
headA = headA.next;
isFlag = true;
}else {
newHead = headB;
headB = headB.next;
isFlag = false;
}
ListNode cur = newHead;
while (headA != null && headB != null) {
if (headA.val < headB.val) {
cur.next = headA;
headA = headA.next;
}else {
cur.next = headB;
headB = headB.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (headA == null) cur.next = headB;
if (headB == null) cur.next = headA;
if (isFlag == true) {
return List1;
}else {
return this;
}
}
六、根据给定值分割链表
编写代码,以给定值 x 为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于 x 的结点排在大于或等于 x 的结点之前。
解题思路 & 内存图:

代码示例:
//编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,
// 所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前.
public ListNode partition(int x) {
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
ListNode as = null;
ListNode ae = null;
ListNode bs = null;
ListNode be = null;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x) {
//第一次赋值
if (as == null) {
as = cur;
ae = cur;
}else {
//不是第一次赋值
ae.next = cur;
ae = cur; //
}
}else {
//第一次赋值
if (bs == null) {
bs = cur;
be = cur;
}else {
//不是第一次赋值
be.next = cur;
be = cur;
// be = be.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
//前段as为空
if (as == null) {
return bs;
}
//后段bs为空
if (bs == null) {
ae.next = null;
return as;
}
//都有数据,两段连起来
ae.next = bs;
//结尾不要忘记置为空
be.next = null;
return as;
}
七、删除重复结点
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。
解题思路 & 内存图:
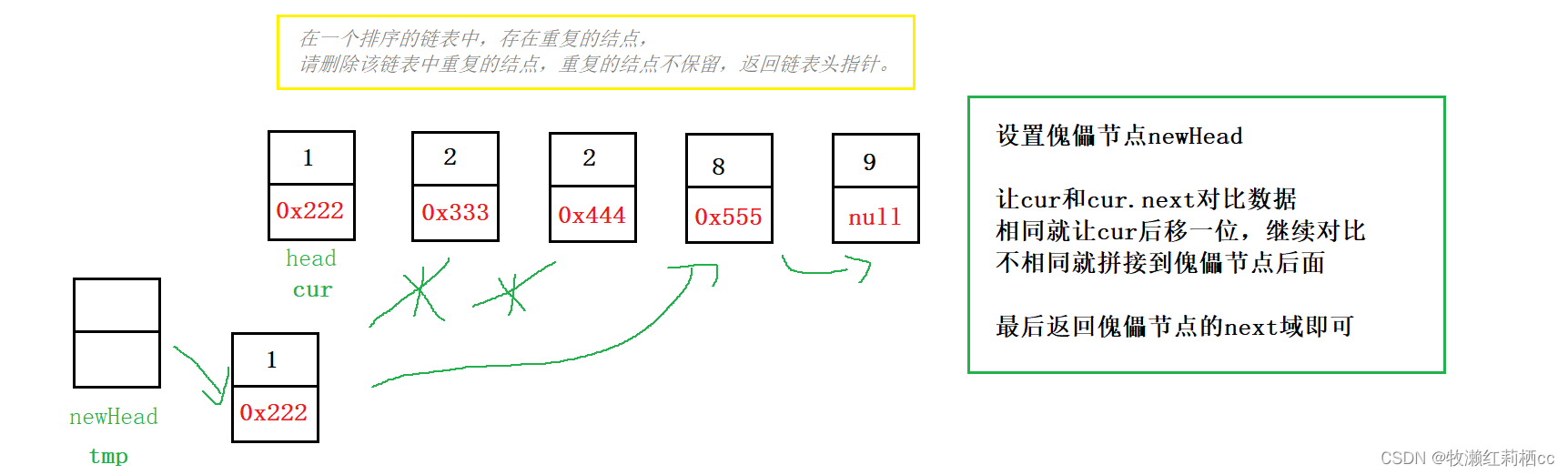
代码示例:
//在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,
// 请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。
public ListNode deleteDuplication(){
if (this.head == null) return null;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = this.head;
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.next != null && cur.val == cur.next.val) {
while (cur.next != null && cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = cur.next; //多走一步,渡过最后一个重复节点
}else {
tmp.next = cur;
cur = cur.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
tmp.next = null;
return newHead.next;
}
八、链表的回文结构
链表的回文结构
解题思路 & 内存图:

代码示例:
//回文链表
public boolean chkPalindrome() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
if (this.head.next == null) {
return true;
}
//1.找中间节点
ListNode slow = this.head;
ListNode fast = this.head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//2.进行反转
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
//3.前后对比
while (this.head != slow) {
if (this.head.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
//偶数情况
if (this.head.next == slow) {
return true;
}
this.head = this.head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
九、找两个链表的第一个公共结点
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点

解题思路 & 内存图:
因为相交之后的链表长度是一样的,
所以相交之前的链表有差值。
计算出两条链表的差值 len,让长的链表先走 len 步
再让两条链表一起走,直到相遇就是链表相交的点。
代码示例:
//找链表相交的节点
public static ListNode getIntersectionNode1(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null) return null;
if (headB == null) return null;
//判断链表哪条长度长
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
ListNode p1 = headA;
ListNode p2 = headB;
//各自计算链表长度
while (p1 != null) {
lenA++;
p1 = p1.next;
}
while (p2 != null) {
lenB++;
p2 = p2.next;
}
p1 = headA;
p2 = headB;
//保证链表长的是p1
int len = lenA - lenB;
if (len < 0) {
p1 = headB;
p2 = headA;
len = lenB - lenA;
}
//让长链表先走
while (len != 0) {
p1 = p1.next;
len--;
}
//两条链表一起走,相等就是相遇点
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
//判断是不是走完链表都没有相遇
if (p1 == null && p2 == null) {
return null;
}
return p1;
}
//创建两条链表相交
public static void createCute(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
headB.next.next = headA.next.next;
}
十、判断链表是否有环
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环
解题思路 & 内存图:
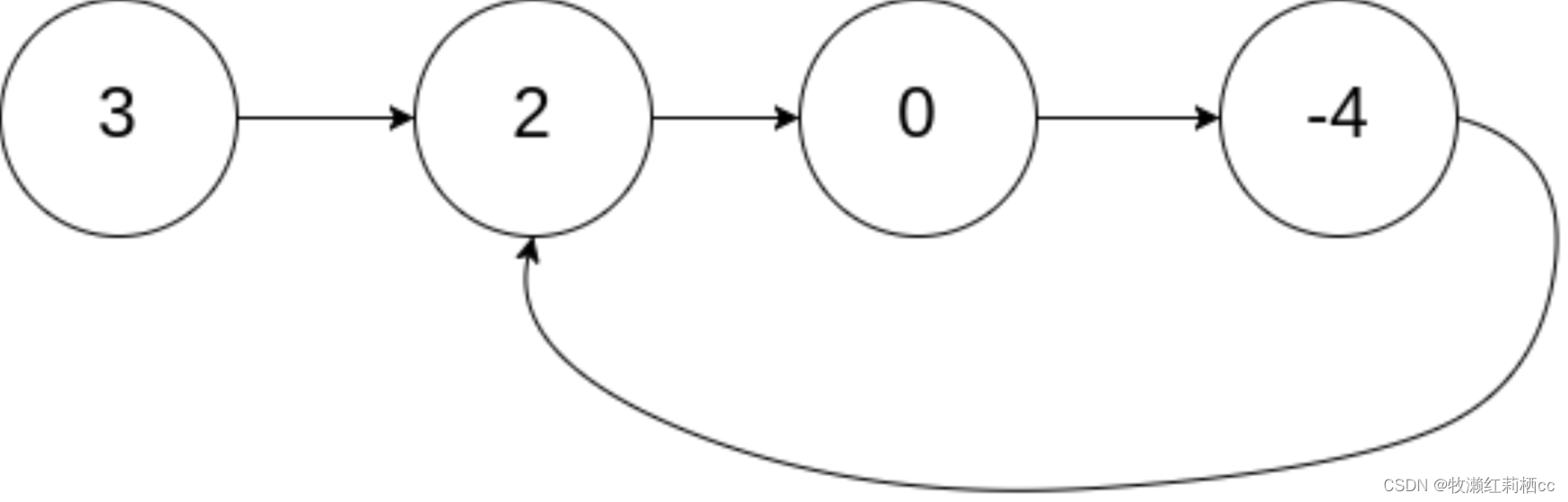
1. 直接设置快慢节点 fast 和 slow
2. 把快慢节点放在 循环中让它们跑
3. 等它们再次相遇,就表示该链表是有环链表
代码示例:
//创建有环链表
public void createCycle(){
ListNode cur = this.head;
//需要用到cur.next
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
//判断到最后,直接给它连接上前面的节点
cur.next = this.head.next;
}
//判断链表是否有环
public boolean hasCycle() {
ListNode fast = this.head;
ListNode slow = this.head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
十一、判断链表入环的第一个节点
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。
如果链表无环,则返回 null。
解题思路 & 内存图:

这就涉及到了数学...
可以推导公式,最后得出:
1. 快慢节点按照 2:1 的速度比例移动,记录下第一个相遇点。
2. 让 slow 慢节点回归头节点,fast 快节点不动。
3. 二者按照 1:1 的速度比例再次移动。
4. 再次相遇,这时的位置节点就是环形链表的入口点。
代码示例:
//判断环形链表的入环节点
public ListNode detectCycle(){
//1.让快慢节点按2:1的速度比例移动,直到相遇。
ListNode fast = this.head;
ListNode slow = this.head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
//防止不是环形链表
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null;
}
//2.相遇后,让slow节点回到this.head。
slow = this.head;
//3.再次一起移动,按照1:1速度移动,再次相遇就是入环节点。
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
十二、其它
链接: 牛客 OJ链接
链接: Leetcode OJ链接










 本文详细介绍了链表的基本操作,包括删除指定元素、反转链表、查找中间节点等常见问题的解决方法,并提供了清晰的代码实现。
本文详细介绍了链表的基本操作,包括删除指定元素、反转链表、查找中间节点等常见问题的解决方法,并提供了清晰的代码实现。
















 7880
7880

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








