JAVA学习(小白向)—循环队列—2021-06-06
循环队列原理
head表示队列队首
tail表示队列队尾
当head=tail时表示队列为空
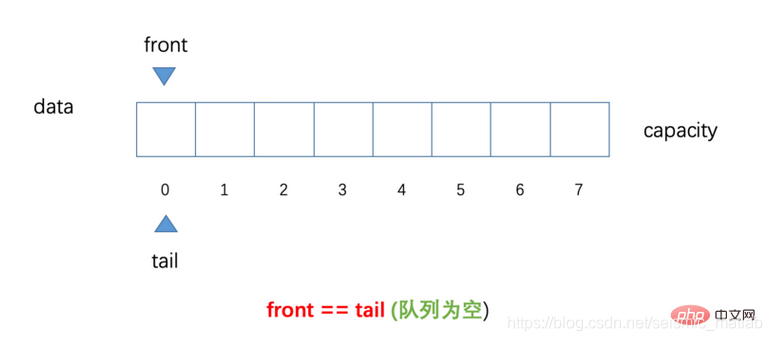
上图中front相当于代码里的head,此时队列为空。
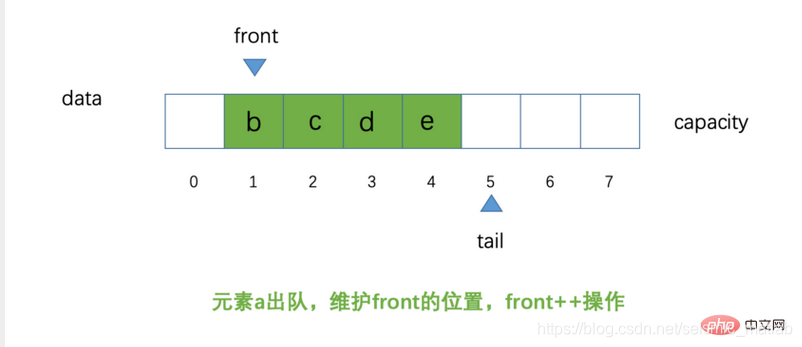
当添加元素后,指针往后移动,执行tail++

当移除元素时,同理head指针往前移动,执行head++
代码
package a16;
/**
* *******************************
* Circle int queue.
* @author hengyuzuo
* *******************************
*/
public class CircleIntQueue {
/**
* The total space. One space can never be used.
*/
public static final int TOTAL_SPACE = 10;
/**
* The data.
*/
int[] data;
/**
* The index of the head.
*/
int head;
/**
* The index of the tail.
*/
int tail;
/**
*******************
* The constructor
*******************
*/
public CircleIntQueue() {
data = new int[TOTAL_SPACE];
head = 0;
tail = 0;
}// Of the first constructor
/**
*********************
* Enqueue.
*
* @param paraValue
* The value of the new node.
*********************
*/
public void enqueue(int paraValue) {
if ((tail + 1) % TOTAL_SPACE == head) {
System.out.println("Queue full.");
return;
} // Of if
data[tail % TOTAL_SPACE] = paraValue;
tail++;
}// Of enqueue
/**
*********************
* Dequeue.
*
* @return The value at the head.
*********************
*/
public int dequeue() {
if (head == tail) {
System.out.println("No element in the queue");
return -1;
} // Of if
int resultValue = data[head];
head++;
return resultValue;
}// Of dequeue
/**
*********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "";
if (head == tail) {
return "empty";
} // Of if
for (int i = head; i < tail; i++) {
resultString += data[i % TOTAL_SPACE] + ", ";
} // Of for i
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args
* Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
CircleIntQueue tempQueue = new CircleIntQueue();
System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + tempQueue.toString());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i + 1);
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
int tempValue = tempQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("Dequeue " + tempValue + ", the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i + 10);
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
tempValue = tempQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("Dequeue " + tempValue + ", the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i + 100);
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
} // Of for i
}// Of main
}// Of CircleIntQueue
其中
循环队列的体现就在于,当10号位满了执行tail++时
for (int i = head; i < tail; i++) {
resultString += data[i % TOTAL_SPACE] + ", ";
能够通过求余总空间来将指针指向开头,当再继续添加元素求余时,head=tail,此时就满足满队列
if ((tail + 1) % TOTAL_SPACE == head) {
System.out.println("Queue full.");
return;
运行结果
Initialized, the list is: empty
Enqueue, the queue is: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
Dequeue 1, the queue is: 2, 3, 4, 5,
Enqueue, the queue is: 2, 3, 4, 5, 10,
Enqueue, the queue is: 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11,
Enqueue, the queue is: 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 12,
Enqueue, the queue is: 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 12, 13,
Enqueue, the queue is: 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
Queue full.
Enqueue, the queue is: 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
Dequeue 2, the queue is: 3, 4, 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
Dequeue 3, the queue is: 4, 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
Dequeue 4, the queue is: 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
Enqueue, the queue is: 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 100,
Enqueue, the queue is: 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 100, 101,
Enqueue, the queue is: 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 100, 101, 102,
Queue full.
Enqueue, the queue is: 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 100, 101, 102,
Queue full.
Enqueue, the queue is: 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 100, 101, 102,
Queue full.
Enqueue, the queue is: 5, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 100, 101, 102,




 本文详细介绍了循环队列的原理,包括head和tail指针的作用,队列空的判断,以及如何在满队列和移除元素时进行操作。通过实例代码演示了队列的 enqueue 和 dequeue 方法,适合初学者理解 Java 循环队列的使用。
本文详细介绍了循环队列的原理,包括head和tail指针的作用,队列空的判断,以及如何在满队列和移除元素时进行操作。通过实例代码演示了队列的 enqueue 和 dequeue 方法,适合初学者理解 Java 循环队列的使用。
















 487
487

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








