一、合并两个有序链表
1、题目描述
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists
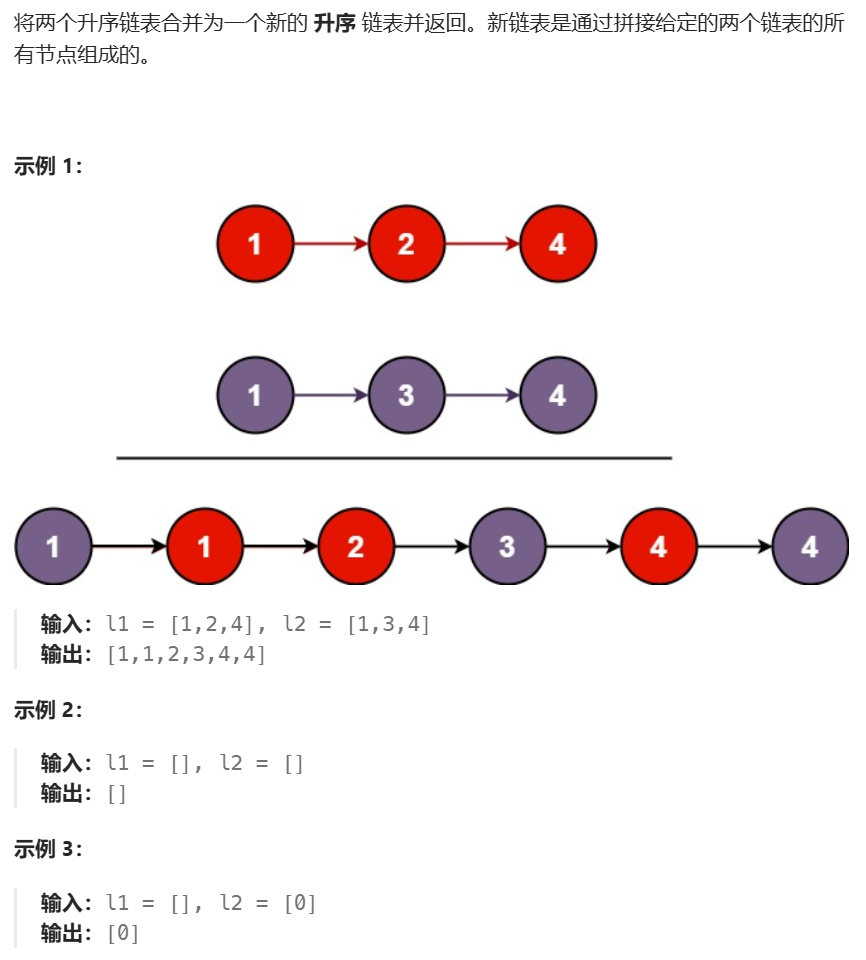
2、算法分析
这道题和之前的合并两个有序数组的思路很像,创建空链表即可,可以很轻松地写出如下代码。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if(list1 == NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2 == NULL)
{
return list1;
}
//创建空链表
ListNode* newHead = NULL;
ListNode* newTail = NULL;
ListNode* l1 = list1;
ListNode* l2 = list2;
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val >= l2->val)
{
//l2尾插到新链表中
if(newHead == NULL)
{
newHead = newTail = l2;
}
else
{
//链表非空
newTail->next = l2;
newTail = newTail->next;
}
l2 = l2->next;
}
else
{
//l1尾插到新链表中
if(newHead == NULL)
{
newHead = newTail = l1;
}
else
{
newTail->next = l1;
newTail = newTail->next;
}
l1 = l1->next;
}
}
//要么l1为空,要么l2为空
if(l1)
newTail->next = l1;
if(l2)
newTail->next = l2;
return newHead;
}虽然这个代码可以运行通过,但有个很严重的问题——太过冗余!虽然我们可以将尾插的代码封装成函数来解决,但是这里我提供一个更好的方法。导致代码冗余的根本原因就在于我们创建的是一个空的新链表,因此要进行if…else…语句判断,那我直接一开始向系统申请一块空间,创建新的非空的链表不就可以了。至于新的非空链表的val值是什么,我们不用在乎,因为这个非空链表起的是一个占位置的作用(在后续的链表学习中,这种起到占位置作用的节点,我们称之为“哨兵位”)。所有节点按题目要求尾插完成后,新链表就是如下图所示的样子:
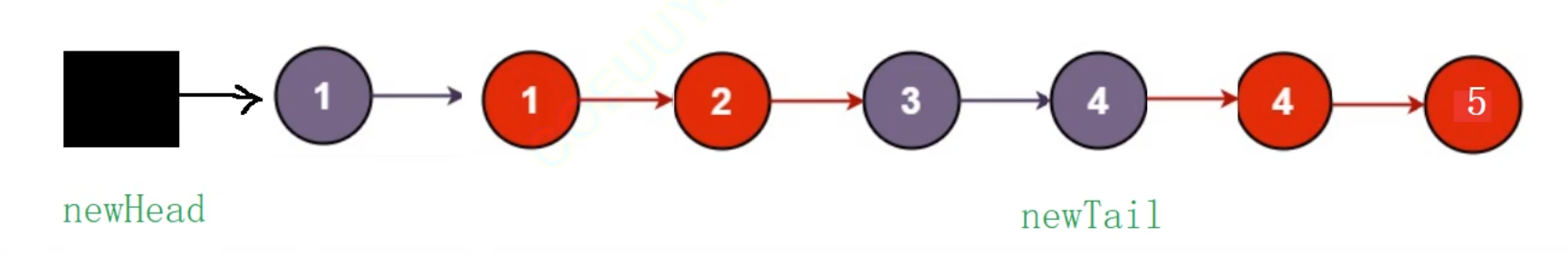
这里要注意,我们此时不能返回newHead,而是应该返回newHead的下一个节点才对。并且我们向系统申请的空间在结束后也要释放(虽然在OJ平台上是否释放不会影响整体程序,但还是要养成好习惯~)
3、参考代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if(list1 == NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2 == NULL)
{
return list1;
}
//创建非空链表
ListNode* newHead, *newTail;
newHead = newTail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
ListNode* l1 = list1;
ListNode* l2 = list2;
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val >= l2->val)
{
//l2尾插到新链表中
newTail->next = l2;
newTail = newTail->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
else
{
//l1尾插到新链表中
newTail->next = l1;
newTail = newTail->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
}
//要么l1为空,要么l2为空
if(l1)
{
newTail->next = l1;
}
if(l2)
{
newTail->next = l2;
}
ListNode* retHead = newHead->next;
free(newHead);
newHead = NULL;
return retHead;
}二、链表的回文结构
1、题目描述
https://www.nowcoder.com/share/jump/1753713495724

2、算法分析
提到回文结构,我们会很自然地想到去定义两个指针,一个指向头,一个指向尾,比较两个值是否相等,再让头指针往后走,尾指针往前走。但这道题是一个单向链表,尾指针没有办法往前走。所以这个方法不太行。那我们又想到,找到中间位置,从中间位置向两边走,但是同理还是不行。既然在链表中我们无法判断是否回文,那我们创建一个新数组,把链表的值遍历到新数组中,在数组中判断回文结构不就可以了吗?这里注意,题目中明确指出空间复杂度为O(1),因此这里我们创建一个定长数组arr[900]即可。(题目说了保证链表长度小于等于900)
根据上述思路,给出参考代码如下:
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList
{
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A)
{
//创建数组
int arr[900] = {0};
//遍历链表,将链表中的值保存在数组中
ListNode* pcur = A;
int i = 0;
while(pcur)
{
arr[i] = pcur->val;
i++;
pcur = pcur->next;
}
//判断数组是否为回文结构
int left = 0;
int right = i - 1;
while(left < right)
{
if(arr[left] != arr[right])
{
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
};但是这个方法毕竟是应试,有点“投机取巧”,所以这里给出更严谨、更合理的方法。
思路2:找链表的中间结点,将中间节点作为新的链表的头结点进行反转链表。

3、参考代码
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
//找中间节点
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* slow, *fast;
slow = fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
//反转链表
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
if(head == nullptr)
{
return head;
}
ListNode* n1, *n2, *n3;
n1 = nullptr;
n2 = head;
n3 = n2->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A)
{
//找中间节点
ListNode* mid = middleNode(A);
//反转中间节点之后的链表
ListNode* right = reverseList(mid);
//遍历原链表和反转之后的链表
ListNode* left = A;
while(right)
{
if(left->val != right->val)
{
return false;
}
left = left->next;
right = right->next;
}
return true;
}
};三、相交链表
1、题目描述
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists
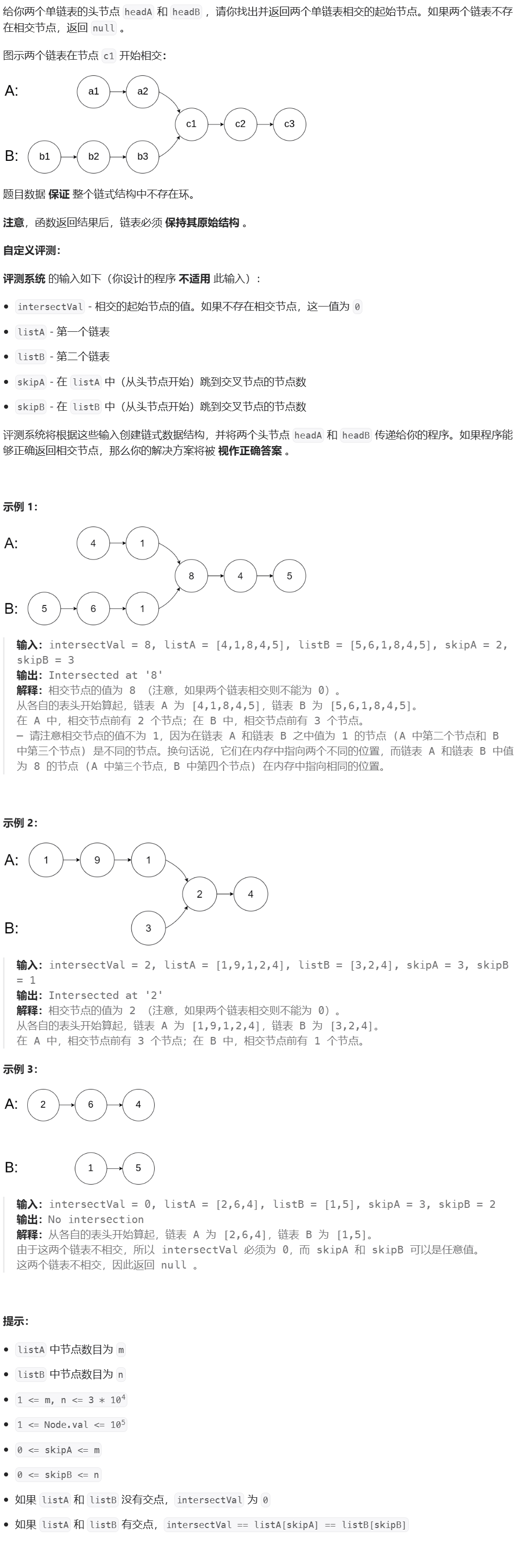
2、算法分析
思路:求两个链表的长度并计算长度差,长链表先走长度差步,然后两个链表同时往后遍历。
3、参考代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
//求两个链表的长度
ListNode* pa = headA;
ListNode* pb = headB;
int sizeA = 0, sizeB = 0;
while(pa)
{
sizeA++;
pa = pa->next;
}
while(pb)
{
sizeB++;
pb = pb->next;
}
//计算长度差
int gap = abs(sizeA - sizeB);//abs函数:用于求绝对值
//让长链表先走gap步
ListNode* shortList = headA;
ListNode* longList = headB;
if(sizeA > sizeB)
{
longList = headA;
shortList = headB;
}
while(gap--)
{
longList = longList->next;
}
//longList和shortList在同一起跑线
while(shortList)
{
if(longList == shortList)
{
return longList;
}
shortList = shortList->next;
longList = longList->next;
}
return NULL;
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








