文章目录
一、TSP 问题
1. TSP概述
旅行商问题(TSP),它被称为NP完全问题,它是:
给出了N个点(“城市”),以及每对城市之间的交通成本。假设一名商品推销员从一个给定的城市出发,必须访问每个城市一次,因此需要往返一次。目的是找到一个最佳的旅游路线,其中往返的总成本最小。
更正式地说,TSP可以被表述为图论的问题:给定一个由N个顶点组成的图G,G(即一个循环)中的边的闭合序列恰好通过G的每个顶点一次,称为哈密顿循环。给定一组N个顶点(城市)上的完全加权图G,则TSP是通过G找到最短哈密顿圈的问题。从计算的角度来看,这意味着确定非重复序列1, 2, ...., N,其中城市从1到N连续编号,排列表示权重和最小的访问顺序。

二、GA 算法
1. GA概述
遗传算法基于自然选择和遗传学的思想。这些是对随机搜索的智能利用,提供了历史数据,以将搜索引导到解决方案空间中性能更好的区域。它们通常用于生成优化问题和搜索问题的高质量解决方案。
遗传算法模拟了自然选择的过程,这意味着那些能够适应环境变化的物种能够生存和繁殖到下一代。简单地说,他们在连续一代的个体中模拟“适者生存”来解决问题。每一代都由一群个体组成,每个个体代表搜索空间中的一个点和可能的解决方案。每个个体都表示为字符串/整数/浮点/位。这个字符串类似于染色体(Chromosome)。
2. 搜索空间

3. 算法思路
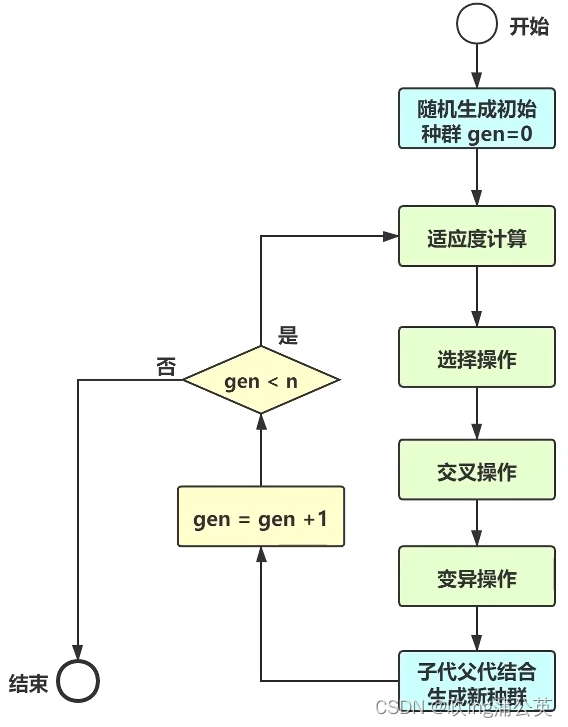
伪代码:
- 随机初始化种群p
- 确定种群的适应度
- 直到收敛重复:
a) 从种群中选择父母
b) 交叉并产生新的种群
c) 对新种群执行变异
d) 计算新种群的适应度
三、算法实现
1. 传统方法
在传统的方法中,染色体被设计成代表N(城市计数)基因的代用品。每个基因都有一个数字,这是一个标记的透明度。因此,n基因具有被访问城市的标签。换句话说,这个染色体是1到N序列排列的直接编码。
这种方法的问题很明显的。从一个验证染色体的群体开始,普通的交叉和变异的计算会引起问题。这正是由普通计算产生的后代极有很大的可能出现没有剩余的有效染色体的现象。解决办法可分为以下三类:
- 取消资格:这个想法是允许那些无效染色体的产生,但是分配如此低的fit值,使他们在即将到来的选择过程中被淘汰。这种简单计算的缺点是花费的时间长。基因引擎将大部分时间用于生成无效染色体,然后消除它们。
- 修复:在这种方法中,会生成无效的染色体,然后将其输入一个中间过程,其中它们被转化为有效的过程。这里的关键思想是做最少的修改,以便保留交叉的优点。
- 发明专用运算符:而不是创建无效的染色体,遗传算法对运算符进行修改,只生成有效的染色体。
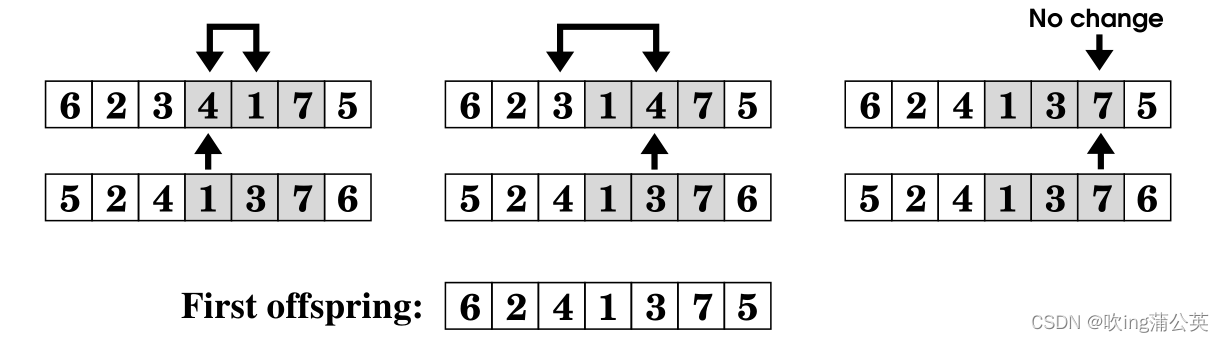
这种方法有以下缺点:
- 染色体的变异并不限于交换的部分。
- 变异不是在单个点进行的。
- 简单的位串交叉和变异实现将不起作用,因此效率不高。
2. 改进方法
输入:perm = 置换的数组
输出:inv = 存放逆序的数组

输入:inv
输出:perm

改进思路是,调用逆序的格式设定置换的值。让基因的每一个元素保持置换值的N数量并且按自然数的格式。而基因最大的长度在每一次循环减1。
在传统的遗传算法,基因是使用二进制格式来表示,这样的方式的缺点很容易解决,我们可以调用限制它的长度的方法来解决。这样的话所有的交叉和变异会生成有效的染色体。
3. 实现代码
import random
import math
import itertools
import copy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def length(p1,p2):
return math.sqrt((p1[0]-p2[0])**2 + (p1[1]-p2[1])**2)
def solve_tsp_dynamic(points):
#calc all lengths
all_distances = [[length(x,y) for y in points] for x in points]
#initial value - just distance from 0 to every other point + keep the track of edges
A = {(frozenset([0, idx+1]), idx+1): (dist, [0,idx+1]) for idx,dist in enumerate(all_distances[0][1:])}
cnt = len(points)
for m in range(2, cnt):
B = {}
for S in [frozenset(C) | {0} for C in itertools.combinations(range(1, cnt), m)]:
for j in S - {0}:
B[(S, j)] = min( [(A[(S-{j},k)][0] + all_distances[k][j], A[(S-{j},k)][1] + [j]) for k in S if k != 0 and k!=j]) #this will use 0th index of tuple for ordering, the same as if key=itemgetter(0) used
A = B
res = min([(A[d][0] + all_distances[0][d[1]], A[d][1]) for d in iter(A)])
return res[1]
num_points = 10 # do not put large values - too much memory
max_point = 20
points = [[random.randint(1,max_point),random.randint(1,max_point)] for i in range(num_points)]
#print points
sol = solve_tsp_dynamic(points)
#print sol
#point_list = points
point_list = [
[60,200],
[180,200],
[80,180],
[140,180],
[20,160],
[100,160],
[200,160],
[140,140],
[40,120],
[100,120],
[180,100],
[60,80],
[120,80],
[180,60],
[20,40],
[100,40],
[200,40],
[20,20],
[60,20],
[160,20]
]
class chromozome:
global point_list #list of [x,y] points
def __init__(self,travel_order = [],random = True):
self.list_len = len(point_list)
#self.crossover = str_len/2 #default crossover is at mid of the string
self.random = random
self.travel_order = travel_order
if self.random:
#print "str set as random"
self.travel_order = self.randomize()
def randomize(self):
#randomly generate a path using the given point_list
#lis = range(0,self.list_len) #generes an array of 1..n #does not give optimal for 0 to nth path(read below)
lis = list(range(1,self.list_len-1))
#print lis
random.shuffle(lis)
return lis
def get_len(self):
return len(self.travel_order)
def get_list(self):
return self.travel_order
def mate(self,parent2):
#print "parent1:",self.travel_order
#print "parent2:",parent2
child1 = [-1]*len(self.travel_order)
child2 = [-1]*len(self.travel_order)
random_break_point1,random_break_point2 = 0,0
while random_break_point2==random_break_point1:
random_break_point1 = random.randint(1,len(self.travel_order)-2)
#print random_break_point1
random_break_point2 = random.randint(len(self.travel_order)-random_break_point1-1,len(self.travel_order)-2)
#print random_break_point2
start = min(random_break_point1,random_break_point2)
end = max(random_break_point1,random_break_point2)
#print "after filling only mid:"
child1[start:end+1] = self.travel_order[start:end+1]
#print child1
child2[start:end+1] = parent2[start:end+1]
#print child2
#completing child1:
filled = abs(start-end)+1
not_filled = len(self.travel_order)-filled
temp_start_child = end+1
temp_start_parent = end+1
#print "to be filled:",not_filled
while not_filled > 0:
temp_start_child = temp_start_child % len(self.travel_order)
temp_start_parent = temp_start_parent % len(self.travel_order)
if parent2[temp_start_parent] not in child1:
child1[temp_start_child] = parent2[temp_start_parent]
temp_start_child+=1
not_filled-=1
temp_start_parent+=1
#print "after filling all:"
#print child1
not_filled = len(self.travel_order)-filled
temp_start_child = end+1
temp_start_parent = end+1
#print "to be filled:",not_filled
while not_filled > 0:
temp_start_child = temp_start_child % len(self.travel_order)
temp_start_parent = temp_start_parent % len(self.travel_order)
if self.travel_order[temp_start_parent] not in child2:
child2[temp_start_child] = self.travel_order[temp_start_parent]
temp_start_child+=1
not_filled-=1
temp_start_parent+=1
#print "after filling all:"
#print child2
#print len(child1),len(child2)
return [chromozome(child1,False),chromozome(child2,False)]
def mutate(self,chance):
if random.random() < chance:
randinex1 = random.randint(0,len(self.travel_order)-1)
randinex2 = random.randint(0,len(self.travel_order)-1)
self.travel_order[randinex2],self.travel_order[randinex1] = self.travel_order[randinex1],self.travel_order[randinex2]
class evolve:
def __init__(self,point_list,max_generation):
self.final = []
self.start = chromozome()
self.population = []
self.max_generation = max_generation
self.point_list = point_list
self.populate()
def length(self,p1,p2):
return math.sqrt((p1[0]-p2[0])**2 + (p1[1]-p2[1])**2)
def calculate_fitness(self,gene):
#calculate the total of travelling in the given order
gene_copy = copy.deepcopy(gene)
gene_copy.append(max(gene)+1)
gene_copy = [0]+gene_copy
cost = 0
for i in range(len(gene_copy)-1):
cost += self.length(self.point_list[gene_copy[i]],self.point_list[gene_copy[i+1]])
return cost
def populate(self,n=30):
#fill the population randomly
while n > 1:
self.population.append(chromozome())
n-=1
def sort_by_cost(self):
self.population = sorted(self.population,key = lambda x:self.calculate_fitness(x.get_list()))
def print_str(self,population,print_len,print_all=False):
print ("-"*50)
if print_all:
print_len = len(population)-1
for x in population[0:print_len]:
print(x.get_str(),"len: ",x.get_len()," Cost:",self.cost(x))
print ("-"*50)
def start_evolving(self):
#each generation, sort the population by cost and mate the top 2 members and put the children in back in the list by removing the bottom 2 members(highest cost)
while self.max_generation > 0:
self.sort_by_cost()
childrenAB = self.population[0].mate(self.population[1].get_list())
#childrenAB is a list of [childA,childB]
self.population[len(self.population)-2:] = childrenAB
for index in range(len(self.population)):
#mutate it and check the cost
self.population[index].mutate(0.15) #mutate with a % chance
self.max_generation -= 1
print ("lowest cost path after n generations:",[0]+self.population[0].get_list()+[19])
print ("lowest cost is:",self.calculate_fitness(self.population[0].get_list()))
return self.population[0].get_list()
e = evolve(point_list,1000)
sol = e.start_evolving()
actual_path = [point_list[x] for x in sol]
#optimal_sol = solve_tsp_dynamic(point_list) #842.833082597 is the optimal solution
#print optimal_sol #[0, 4, 8, 11, 14, 17, 18, 15, 12, 19, 16, 13, 10, 6, 1, 3, 7, 9, 5, 2]
print ("near-optimal solution:",sol,)
print ("cost:",e.calculate_fitness(sol))
#Plotting the solution on a 2d graph
actual_path_x = [pair[0] for pair in actual_path]
actual_path_y = [pair[1] for pair in actual_path]
plt.plot(actual_path_x, actual_path_y, marker="o", markerfacecolor="r")
plt.show()4. 运行结果


案例是参考了下面的论文。

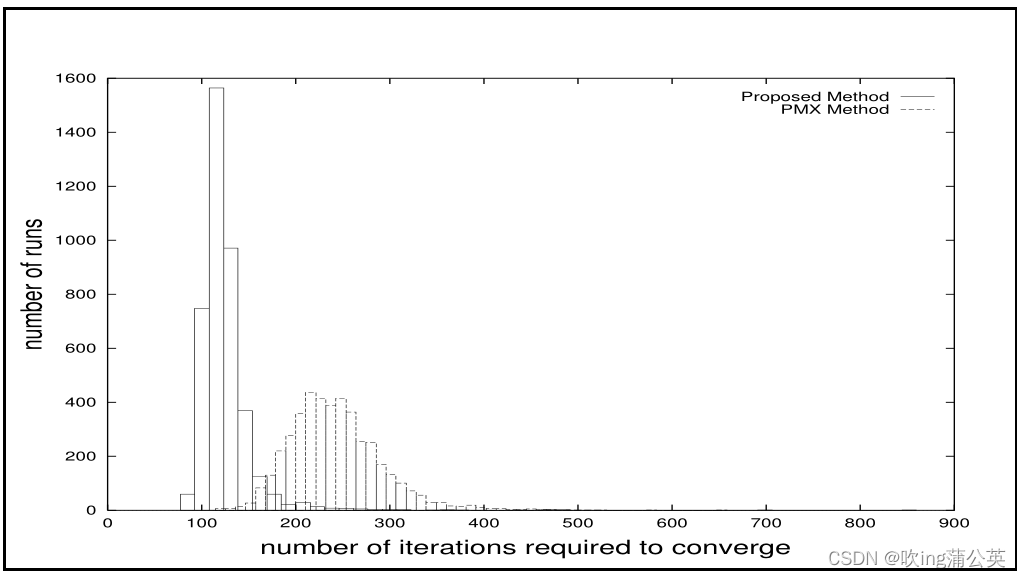
在论文里,提出的案例是调用德国,Bavaria省的29个城市的路线为例。调用传统方法和本论文提出的改进方法两个方法设置了同样的参数进行对比。以下是代码的运行结果。
从此结果可以得知,改进方法比传统方法生成了更多比较好的解,但是数量比传统方法少了1%。通过4000此的训练,改进方法生成了平均2259的解,而传统的方法生成了平均2242的解。

对于所提出的方法,直到达到收敛的迭代次数平均为110.5。PMX平均需要248次迭代才能收敛。收敛的稳定性度量也有利于新提出的方法:对于所提出的方法,迭代次数的标准偏差为30.9,而对于PMX,标准偏差为48.9。
四、结论
本文章介绍了新的置换表示GA基因的方法。与传统的遗传算法相比,本文章提出的新方法主要是不限制GA基因的交叉和变异。从实验结果得知,提出的新方法具有比传统方法更好的效果,它收敛率比传统方法高2.2%。
五、参考文献
Göktürk Üçoluk (2002) Genetic Algorithm Solution of the TSP Avoiding Special Crossover and Mutation, Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing, 8:3, 265-272, DOI: 10.1080/10798587.2000.10642829























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








