pyecharts
在过去,在python进行数据可视化通常使用matplotlib,虽然matplotlib简洁明了,但是图表样式较为单调,难以满足美观和交互需要。
因此,通常在html的页面上展示的时候,往往使用echarts进行绘图。但是,echarts虽然很好,却需要编写javascript代码,如果对js不够了解,使用会有一定的难度。
好消息是,现在通过pyecharts,无需编写js代码,仅使用python编程,一样也可以进行echarts绘图了!
这全都要得益于pyecharts库,pyecharts的官方网站
快速使用
安装
通过pip进行安装:pip install pyecharts
查看是否安装成功
import pyecharts
print(pyecharts.__version__)绘图
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "毛衣", "领带", "裤子", "风衣", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家A", [114, 55, 27, 101, 125, 27, 105])
.add_yaxis("商家B", [57, 134, 137, 129, 145, 60, 49])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="商场销售情况"))
)
bar.render("bar_chart.html")结果
运行代码以后,可以得到一个生成的html文件,如下所示:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Awesome-pyecharts</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://assets.pyecharts.org/assets/v5/echarts.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body >
<div id="506c18ae21364e4aa31896cee8918ebb" class="chart-container" style="width:900px; height:500px; "></div>
<script>
var chart_506c18ae21364e4aa31896cee8918ebb = echarts.init(
document.getElementById('506c18ae21364e4aa31896cee8918ebb'), 'white', {renderer: 'canvas'});
var option_506c18ae21364e4aa31896cee8918ebb = {
"animation": true,
"animationThreshold": 2000,
"animationDuration": 1000,
"animationEasing": "cubicOut",
"animationDelay": 0,
"animationDurationUpdate": 300,
"animationEasingUpdate": "cubicOut",
"animationDelayUpdate": 0,
"aria": {
"enabled": false
},
"color": [
"#5470c6",
"#91cc75",
"#fac858",
"#ee6666",
"#73c0de",
"#3ba272",
"#fc8452",
"#9a60b4",
"#ea7ccc"
],
"series": [
{
"type": "bar",
"name": "\u5546\u5bb6A",
"legendHoverLink": true,
"data": [
114,
55,
27,
101,
125,
27,
105
],
"realtimeSort": false,
"showBackground": false,
"stackStrategy": "samesign",
"cursor": "pointer",
"barMinHeight": 0,
"barCategoryGap": "20%",
"barGap": "30%",
"large": false,
"largeThreshold": 400,
"seriesLayoutBy": "column",
"datasetIndex": 0,
"clip": true,
"zlevel": 0,
"z": 2,
"label": {
"show": true,
"margin": 8,
"valueAnimation": false
}
},
{
"type": "bar",
"name": "\u5546\u5bb6B",
"legendHoverLink": true,
"data": [
57,
134,
137,
129,
145,
60,
49
],
"realtimeSort": false,
"showBackground": false,
"stackStrategy": "samesign",
"cursor": "pointer",
"barMinHeight": 0,
"barCategoryGap": "20%",
"barGap": "30%",
"large": false,
"largeThreshold": 400,
"seriesLayoutBy": "column",
"datasetIndex": 0,
"clip": true,
"zlevel": 0,
"z": 2,
"label": {
"show": true,
"margin": 8,
"valueAnimation": false
}
}
],
"legend": [
{
"data": [
"\u5546\u5bb6A",
"\u5546\u5bb6B"
],
"selected": {},
"show": true,
"padding": 5,
"itemGap": 10,
"itemWidth": 25,
"itemHeight": 14,
"backgroundColor": "transparent",
"borderColor": "#ccc",
"borderRadius": 0,
"pageButtonItemGap": 5,
"pageButtonPosition": "end",
"pageFormatter": "{current}/{total}",
"pageIconColor": "#2f4554",
"pageIconInactiveColor": "#aaa",
"pageIconSize": 15,
"animationDurationUpdate": 800,
"selector": false,
"selectorPosition": "auto",
"selectorItemGap": 7,
"selectorButtonGap": 10
}
],
"tooltip": {
"show": true,
"trigger": "item",
"triggerOn": "mousemove|click",
"axisPointer": {
"type": "line"
},
"showContent": true,
"alwaysShowContent": false,
"showDelay": 0,
"hideDelay": 100,
"enterable": false,
"confine": false,
"appendToBody": false,
"transitionDuration": 0.4,
"textStyle": {
"fontSize": 14
},
"borderWidth": 0,
"padding": 5,
"order": "seriesAsc"
},
"xAxis": [
{
"show": true,
"scale": false,
"nameLocation": "end",
"nameGap": 15,
"gridIndex": 0,
"inverse": false,
"offset": 0,
"splitNumber": 5,
"minInterval": 0,
"splitLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"show": true,
"width": 1,
"opacity": 1,
"curveness": 0,
"type": "solid"
}
},
"animation": true,
"animationThreshold": 2000,
"animationDuration": 1000,
"animationEasing": "cubicOut",
"animationDelay": 0,
"animationDurationUpdate": 300,
"animationEasingUpdate": "cubicOut",
"animationDelayUpdate": 0,
"data": [
"\u886c\u886b",
"\u6bdb\u8863",
"\u9886\u5e26",
"\u88e4\u5b50",
"\u98ce\u8863",
"\u9ad8\u8ddf\u978b",
"\u889c\u5b50"
]
}
],
"yAxis": [
{
"show": true,
"scale": false,
"nameLocation": "end",
"nameGap": 15,
"gridIndex": 0,
"inverse": false,
"offset": 0,
"splitNumber": 5,
"minInterval": 0,
"splitLine": {
"show": true,
"lineStyle": {
"show": true,
"width": 1,
"opacity": 1,
"curveness": 0,
"type": "solid"
}
},
"animation": true,
"animationThreshold": 2000,
"animationDuration": 1000,
"animationEasing": "cubicOut",
"animationDelay": 0,
"animationDurationUpdate": 300,
"animationEasingUpdate": "cubicOut",
"animationDelayUpdate": 0
}
],
"title": [
{
"show": true,
"text": "\u5546\u573a\u9500\u552e\u60c5\u51b5",
"target": "blank",
"subtarget": "blank",
"padding": 5,
"itemGap": 10,
"textAlign": "auto",
"textVerticalAlign": "auto",
"triggerEvent": false
}
]
};
chart_506c18ae21364e4aa31896cee8918ebb.setOption(option_506c18ae21364e4aa31896cee8918ebb);
</script>
</body>
</html>效果
打开生成的页面以后,可以看到这样的页面
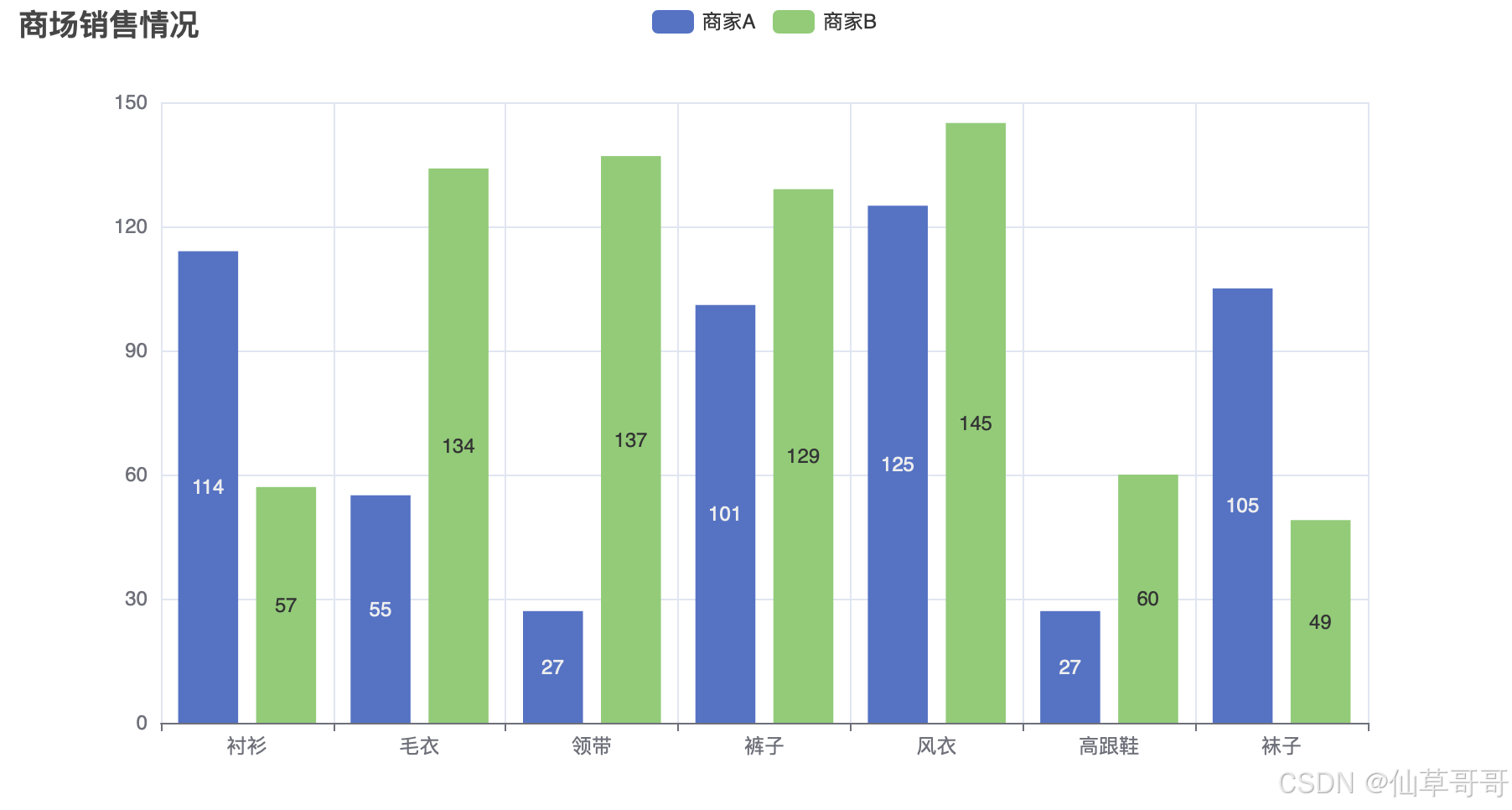
如何使用生成结果
方法一:直接通过html打开
那么,生成的页面,该怎么样使用呢?
刚刚通过render()方法,成功生成了一个html文件,这个文件可以直接打开。因此,可以直接通过打开这个页面,进行使用。
方法二:嵌入其他页面
当然,虽然生成的页面很好,但是毕竟只有单独的一个页面,这样一个页面可能不能满足我们的需要。因此,另一种使用方法是,通过iframe将其嵌入其他页面。
<iframe src="在此处填写要嵌入的页面地址" width="600" height="400"></iframe>此时,你可以正常的创建你自己的页面,然后将图表引入需要的位置。
方法三:生成html字符串
通过render_embed()的方法,可以生成html的字符串,然后通过将该字符串动态引入,实现页面的显示。
常用于flask/django的动态内容生成之中
from flask import Flask, render_template_string
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
app = Flask(__name__)
def create_chart():
bar = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(["衬衫", "毛衣", "领带", "裤子", "风衣", "高跟鞋", "袜子"])
.add_yaxis("商家A", [114, 55, 27, 101, 125, 27, 105])
.add_yaxis("商家B", [57, 134, 137, 129, 145, 60, 49])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="某商场销售情况"))
)
return bar.render_embed()
@app.route("/")
def index():
chart_html = create_chart()
return render_template_string(
"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>pyecharts 示例</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>我的图表</h1>
<div id="chart">
{{ chart_html | safe }}
</div>
</body>
</html>
""",
chart_html=chart_html
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run()常见图表绘制
条形图
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
x_data = ["苹果", "香蕉", "橘子", "葡萄", "桃子"]
y_data = [12, 34, 45, 20, 15]
bar = Bar()
bar.add_xaxis(x_data)
bar.add_yaxis("销量", y_data)
bar.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="水果销量", subtitle="2024年11月"),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(axislabel_opts=opts.LabelOpts(rotate=45))
)
bar.render("bar_chart.html")
饼图
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from pyecharts import options as opts
data = [("苹果", 40), ("香蕉", 25), ("橙子", 20), ("葡萄", 15)]
pie = (
Pie()
.add(
"",
data,
radius=["40%", "75%"],
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True, formatter="{b}: {c} ({d}%)"),
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="水果分布", subtitle="2024年11月"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(orient="vertical", pos_top="15%", pos_left="2%"),
)
)
pie.render("pie_chart.html")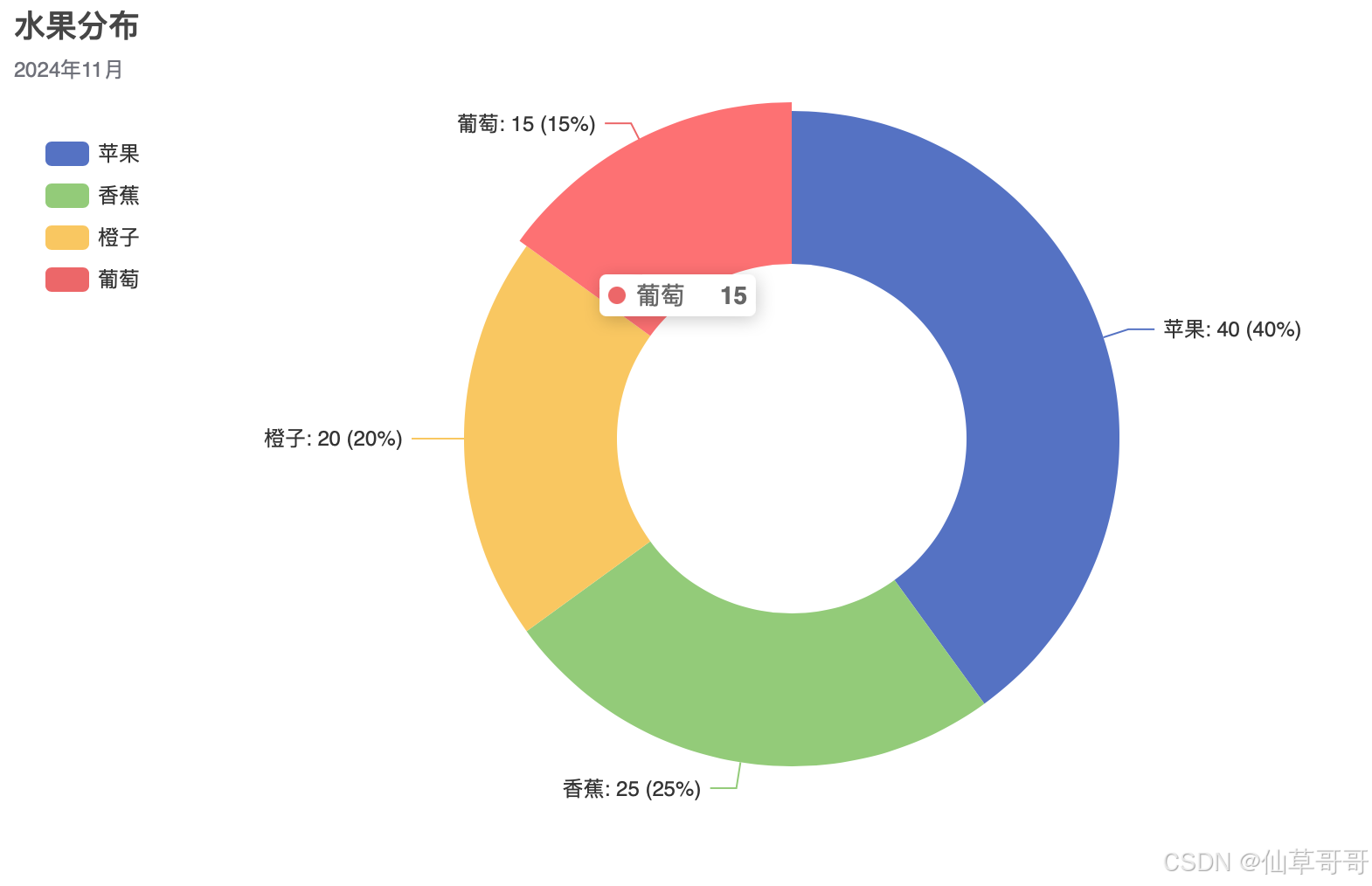
折线图
from pyecharts.charts import Line
from pyecharts import options as opts
x_data = ["周一", "周二", "周三", "周四", "周五", "周六", "周日"]
y_data = [10, 22, 31, 44, 28, 35, 20]
line = (
Line()
.add_xaxis(x_data)
.add_yaxis(
series_name="销量",
y_axis=y_data,
is_smooth=True,
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=True),
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="销量趋势", subtitle="一周数据折线图"),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(trigger="axis"),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(type_="category", boundary_gap=False),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(type_="value"),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(pos_top="5%"),
)
)
line.render("line_chart.html")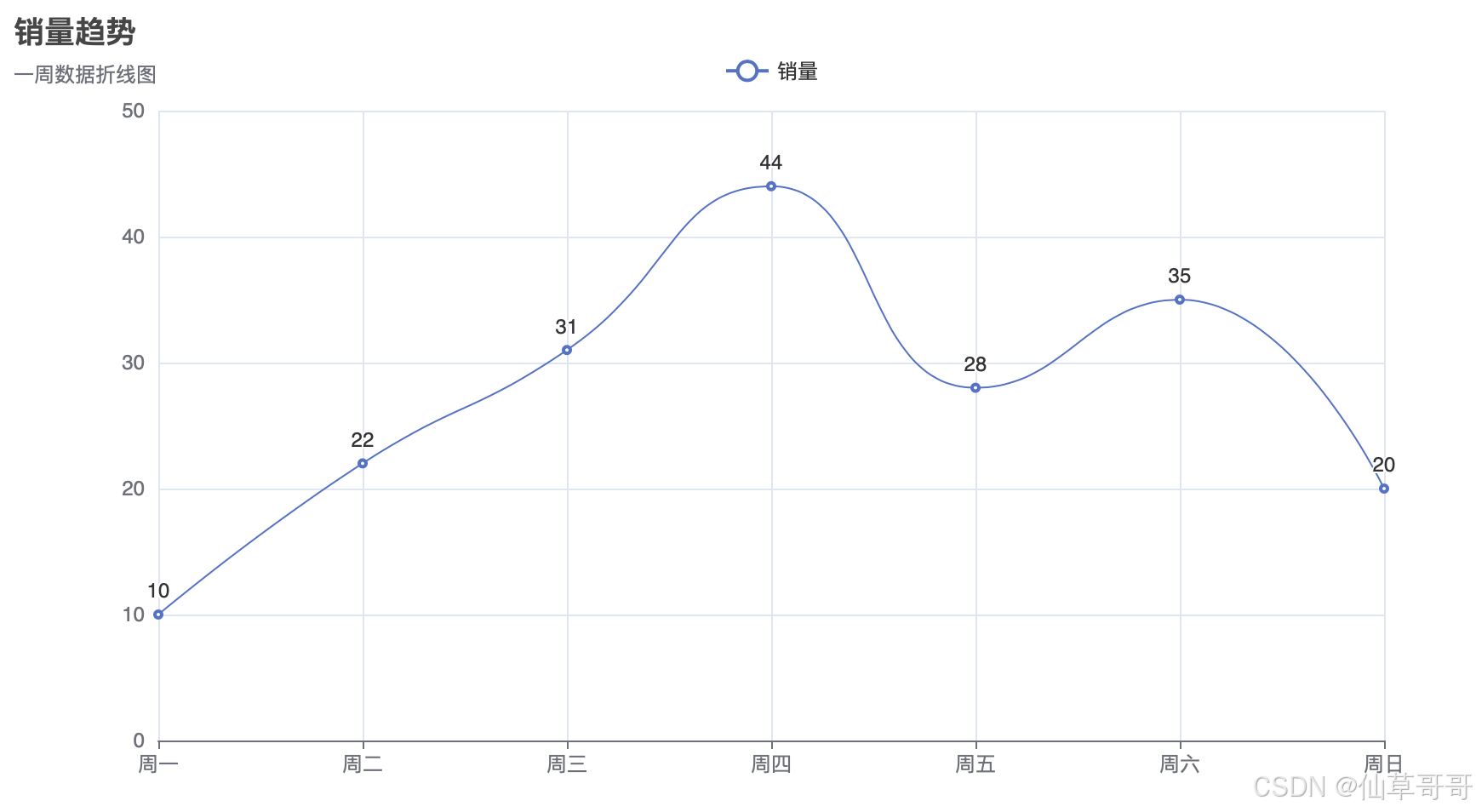
地图
from pyecharts.charts import Geo
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.globals import ChartType
geo = Geo()
geo.add_schema(maptype="美国")
geo.add_coordinate("Los Angeles", -118.2437, 34.0522)
geo.add_coordinate("New York", -74.0060, 40.7128)
geo.add_coordinate("Chicago", -87.6298, 41.8781)
geo.add_coordinate("Houston", -95.3698, 29.7604)
geo.add_coordinate("Phoenix", -112.0740, 33.4484)
data = [
("Los Angeles", 120),
("New York", 100),
("Chicago", 90),
("Houston", 80),
("Phoenix", 70),
]
geo.add(
series_name="城市数据",
data_pair=data,
type_=ChartType.EFFECT_SCATTER,
)
geo.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="美国城市分布地图"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=150),
)
geo.render("usa_geo_map.html")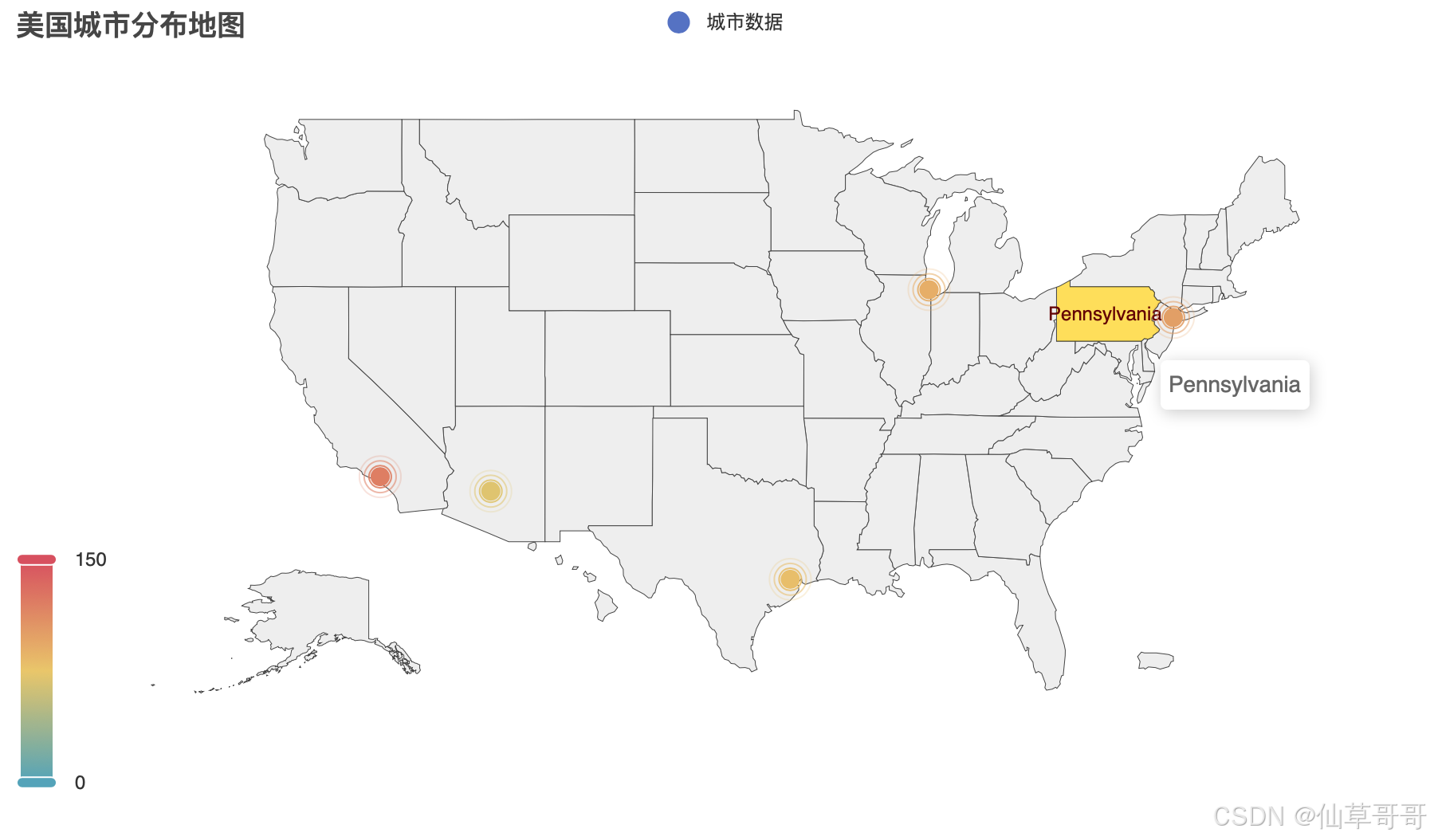
更多图表
需要更多图表样例,可以参考pyecharts官方文档
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








