一、导入依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
二、自定义一个注解
@Target({ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface AuthorityAnnotation {
String value() default "";
}
三、定义好需要执行的方法
打上注解,并在注解中定义好需要的权限code
将该类需要交给spring管理
@Service
public class MyMethode {
@AuthorityAnnotation(value = "delete")
public void delete() {
System.out.println("已删除");
}
@AuthorityAnnotation(value = "update")
public void update() {
System.out.println("已添加");
}
}
四、使用aop拦截打有注解的方法
这里使用的是环绕通知,也可以使用其他方式
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAop {
@Pointcut("@annotation(cn.ly.service.aop.AuthorityAnnotation)")
public void point(){};
@Around("point() && @annotation(authorityAnnotation)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, AuthorityAnnotation authorityAnnotation) {
try {
/*获取用户权限code 这里写死了2个权限*/
List<String> codes = Arrays.asList("delete", "add");
/*判断用户权限是否具备该权限,不具备则抛出异常*/
if (!codes.contains(authorityAnnotation.value())) {
throw new RuntimeException("没有权限进行此操作");
}
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
五、使用测试类进行测试
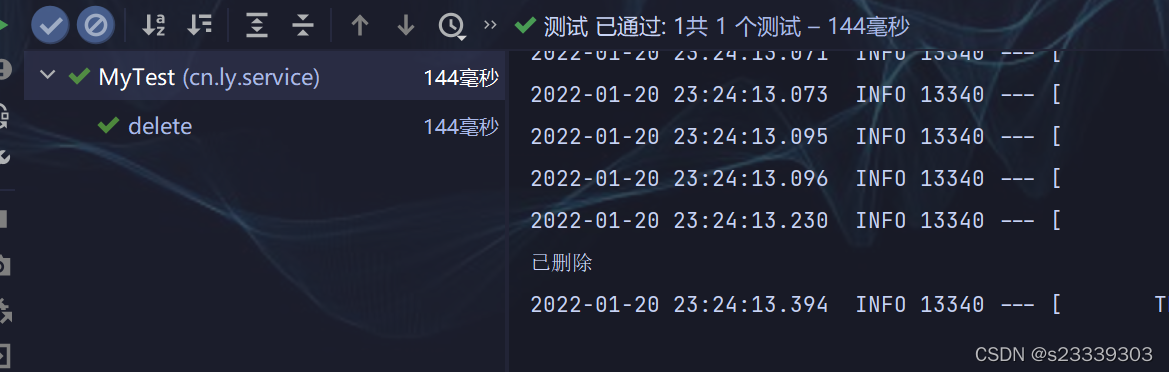
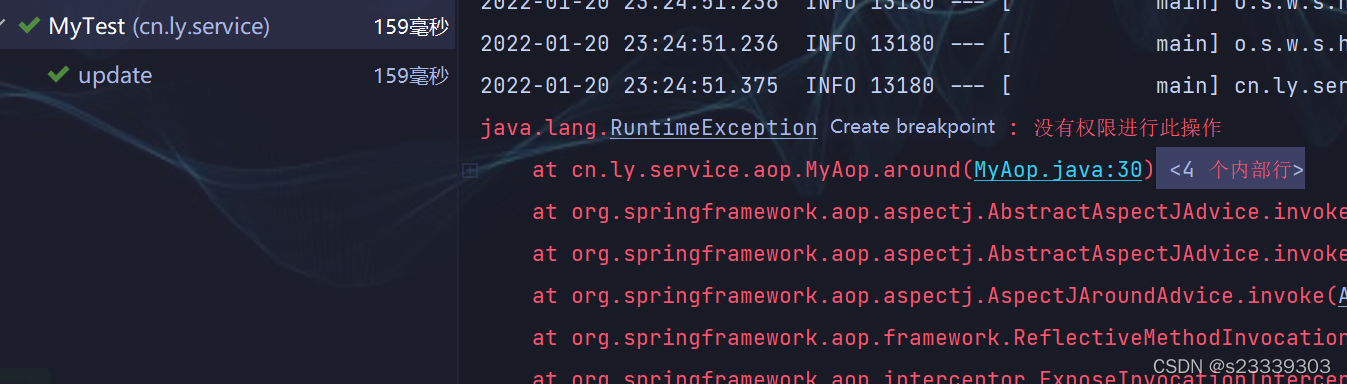
使用springboot测试 测试结果:
因为该用户只有删除和添加的权限,所以访问删除方法成功,访问更新方法失败
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = App.class)
public class MyTest {
@Autowired
MyMethode myMethode;
@Test
public void delete() {
myMethode.delete();
}
@Test
public void update() {
myMethode.update();
}
}







 本文介绍如何在Spring Boot项目中实现基于注解的权限管理。通过自定义注解、AOP切面及测试类,实现对特定方法的权限验证。
本文介绍如何在Spring Boot项目中实现基于注解的权限管理。通过自定义注解、AOP切面及测试类,实现对特定方法的权限验证。
















 1541
1541

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








