数据迁移完成只是开始,可持续的运维体系才是保障业务稳定运行的基石。本文将深入探讨RustFS在生产环境的监控告警、性能优化、故障排查和容灾备份全流程,助您构建企业级的存储运维体系。
目录
一、运维体系架构:从监控到自愈的完整闭环
一个成熟的RustFS运维体系应该包含监控采集、分析告警、故障自愈三个核心层次,形成完整的运维闭环。
1.1 运维架构设计
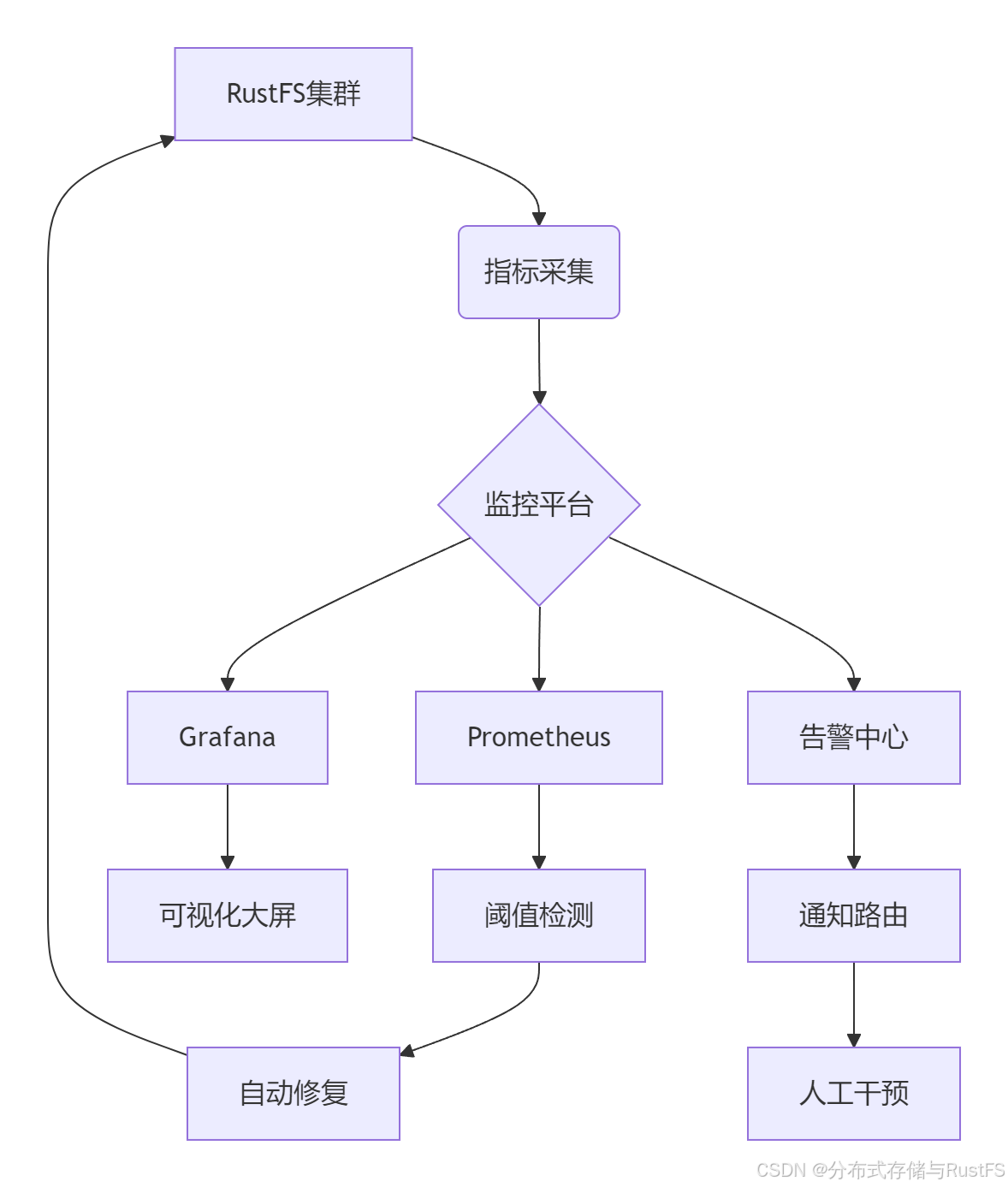
核心组件选型:
-
指标采集:Prometheus Exporters + 自定义指标
-
可视化:Grafana Dashboard + 业务定制视图
-
告警管理:Alertmanager + 多通道通知
-
日志分析:ELK Stack / Loki 分布式日志
-
自动化:Ansible / Kubernetes Operators
二、监控指标体系:全方位掌握集群健康状态
2.1 关键监控指标分类
根据RustFS的架构特点,监控指标应覆盖性能、容量、可用性、数据安全四个维度。
性能指标 - 反映系统处理能力
# prometheus/rustfs-performance.yml
performance_indicators:
throughput:
- rustfs_s3_put_throughput_bytes # 写入吞吐量
- rustfs_s3_get_throughput_bytes # 读取吞吐量
- rustfs_network_bytes_total # 网络总流量
latency:
- rustfs_s3_request_duration_seconds # 请求延迟分布
- rustfs_s3_first_byte_seconds # 首包时间
- rustfs_disk_io_latency_seconds # 磁盘IO延迟
concurrency:
- rustfs_s3_concurrent_requests # 并发请求数
- rustfs_connection_active # 活跃连接数
- rustfs_worker_threads_busy # 繁忙工作线程容量指标 - 资源使用情况
# 容量监控脚本示例
#!/bin/bash
# capacity_monitor.sh
# 存储容量使用率
STORAGE_USAGE=$(curl -s http://localhost:9000/minio/v2/metrics/cluster | grep rustfs_disk_used_bytes | awk '{print $2}')
STORAGE_TOTAL=$(curl -s http://localhost:9000/minio/v2/metrics/cluster | grep rustfs_disk_total_bytes | awk '{print $2}')
USAGE_PERCENT=$((STORAGE_USAGE * 100 / STORAGE_TOTAL))
# 对象数量统计
OBJECT_COUNT=$(curl -s http://localhost:9000/minio/v2/metrics/cluster | grep rustfs_s3_objects_total | awk '{print $2}')
echo "存储使用率: $USAGE_PERCENT%"
echo "对象总数: $OBJECT_COUNT"可用性指标 - 服务健康状态
-
节点在线状态:
rustfs_node_up{instance="$node"} -
API可用性:
rustfs_api_healthcheck -
数据一致性:
rustfs_data_consistency_check
数据安全指标 - 完整性保障
-
校验和错误:
rustfs_checksum_errors_total -
数据修复次数:
rustfs_healing_operations_total -
备份完整性:
rustfs_backup_verification_success
2.2 Prometheus监控配置实战
# prometheus.yml 配置示例
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'rustfs-cluster'
static_configs:
- targets: ['rustfs-node1:9000', 'rustfs-node2:9000', 'rustfs-node3:9000']
metrics_path: '/minio/v2/metrics/cluster'
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_timeout: 10s
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: instance
regex: '(.*):9000'
replacement: '${1}'
- job_name: 'rustfs-node-exporter'
static_configs:
- targets: ['node1:9100', 'node2:9100', 'node3:9100']
scrape_interval: 30s
# 告警规则配置
rule_files:
- "rustfs_alerts.yml"2.3 告警规则配置
基于生产经验的关键告警规则:
# rustfs_alerts.yml
groups:
- name: rustfs_critical
rules:
- alert: RustFSNodeDown
expr: up{job="rustfs-cluster"} == 0
for: 2m
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "RustFS节点下线 {{ $labels.instance }}"
description: "节点 {{ $labels.instance }} 已离线超过2分钟"
- alert: RustFSHighLatency
expr: histogram_quantile(0.95, rate(rustfs_s3_request_duration_seconds_bucket[5m])) > 1
for: 5m
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "RustFS请求延迟过高"
description: "P95延迟持续高于1秒,当前值: {{ $value }}s"
- alert: RustFSDiskSpaceCritical
expr: (rustfs_disk_used_bytes / rustfs_disk_total_bytes) > 0.85
for: 5m
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "RustFS磁盘空间不足 {{ $labels.instance }}"
description: "磁盘使用率超过85%,当前: {{ $value | humanizePercentage }}"
- alert: RustFSChecksumErrorRateHigh
expr: rate(rustfs_checksum_errors_total[10m]) > 0.01
for: 5m
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "RustFS校验和错误率过高"
description: "校验和错误率超过1%,可能存在数据损坏风险"三、日常运维操作:运维人员的实战手册
3.1 节点管理与扩缩容
节点添加流程:
#!/bin/bash
# add_node.sh
NODE_IP="192.168.1.100"
CLUSTER_ENDPOINT="http://rustfs-cluster:9000"
# 1. 准备新节点
ssh $NODE_IP "mkdir -p /data/rustfs/{data1,data2}"
ssh $NODE_IP "docker pull rustfs/rustfs:latest"
# 2. 加入集群
ssh $NODE_IP "docker run -d \
--name rustfs-node4 \
-p 9000:9000 \
-p 9001:9001 \
-v /data/rustfs/data1:/data1 \
-v /data/rustfs/data2:/data2 \
-e RUSTFS_CLUSTER_NODES=rustfs-node1,rustfs-node2,rustfs-node3,rustfs-node4 \
rustfs/rustfs:latest"
# 3. 验证节点状态
curl -s $CLUSTER_ENDPOINT/minio/v2/metrics/cluster | grep rustfs_node_status节点维护模式:
# 进入维护模式
curl -X POST http://localhost:9000/minio/v2/admin/mode?maintenance=true
# 检查维护状态
curl -s http://localhost:9000/minio/v2/metrics/cluster | grep maintenance_mode
# 退出维护模式
curl -X POST http://localhost:9000/minio/v2/admin/mode?maintenance=false3.2 存储桶策略管理
生命周期策略配置:
# lifecycle_manager.py
import boto3
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
def setup_lifecycle_policy(bucket_name):
"""配置存储桶生命周期策略"""
s3 = boto3.client('s3',
endpoint_url='http://rustfs-cluster:9000',
aws_access_key_id='admin',
aws_secret_access_key='password'
)
lifecycle_config = {
'Rules': [
{
'ID': 'MoveToColdStorage',
'Status': 'Enabled',
'Filter': {'Prefix': 'logs/'},
'Transitions': [
{
'Days': 30,
'StorageClass': 'COLD'
}
],
'Expiration': {'Days': 365}
},
{
'ID': 'DeleteTemporaryFiles',
'Status': 'Enabled',
'Filter': {'Prefix': 'temp/'},
'Expiration': {'Days': 7}
}
]
}
s3.put_bucket_lifecycle_configuration(
Bucket=bucket_name,
LifecycleConfiguration=lifecycle_config
)
print(f"存储桶 {bucket_name} 生命周期策略配置完成")3.3 日志分析与故障排查
日志收集配置:
# filebeat.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:
- /var/log/rustfs/*.log
fields:
service: rustfs
json.keys_under_root: true
json.add_error_key: true
output.logstash:
hosts: ["logstash:5044"]
# 日志解析规则
processors:
- decode_json_fields:
fields: ["message"]
target: "json"
- add_fields:
target: ""
fields:
environment: production
cluster: rustfs-main常见故障排查脚本:
#!/bin/bash
# rustfs_troubleshoot.sh
echo "=== RustFS故障排查工具 ==="
echo "1. 检查服务状态..."
systemctl status rustfs --no-pager -l
echo "2. 检查网络连接..."
netstat -tulpn | grep 9000
ping -c 3 rustfs-cluster
echo "3. 检查磁盘空间..."
df -h /data/rustfs
echo "4. 检查内存使用..."
free -h
echo "5. 检查最近错误日志..."
tail -100 /var/log/rustfs/error.log | grep -i error
echo "6. 检查节点间通信..."
curl -s http://localhost:9000/minio/v2/metrics/cluster | grep rustfs_node_communication四、性能优化:持续的性能调优策略
4.1 基于监控数据的性能分析
性能瓶颈识别:
# performance_analyzer.py
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def analyze_performance_bottleneck(metrics_data):
"""分析性能瓶颈"""
df = pd.DataFrame(metrics_data)
# 识别CPU瓶颈
cpu_bottleneck = df[df['cpu_usage'] > 80]['timestamp'].count() / len(df) > 0.1
# 识别内存瓶颈
memory_bottleneck = df[df['memory_usage'] > 90]['timestamp'].count() / len(df) > 0.05
# 识别磁盘瓶颈
disk_bottleneck = df[df['disk_iops'] > df['disk_iops_max'] * 0.8]['timestamp'].count() / len(df) > 0.1
# 识别网络瓶颈
network_bottleneck = df[df['network_throughput'] > df['network_capacity'] * 0.7]['timestamp'].count() / len(df) > 0.1
bottlenecks = {
'cpu': cpu_bottleneck,
'memory': memory_bottleneck,
'disk': disk_bottleneck,
'network': network_bottleneck
}
return bottlenecks
def generate_optimization_recommendations(bottlenecks):
"""生成优化建议"""
recommendations = []
if bottlenecks['cpu']:
recommendations.extend([
"增加CPU核心数或升级CPU",
"调整线程池大小: worker_threads = CPU核心数 * 2",
"启用CPU亲和性设置"
])
if bottlenecks['memory']:
recommendations.extend([
"增加物理内存",
"调整JVM内存参数: -Xmx -Xms",
"优化缓存策略,减少内存碎片"
])
if bottlenecks['disk']:
recommendations.extend([
"使用NVMe SSD替换SATA SSD",
"增加磁盘数量,使用RAID 0条带化",
"调整I/O调度算法: echo deadline > /sys/block/sda/queue/scheduler"
])
if bottlenecks['network']:
recommendations.extend([
"升级网络带宽至10G/25G",
"启用网络中断亲和性",
"调整TCP缓冲区大小"
])
return recommendations4.2 参数调优实战
根据业务负载特点的动态调优:
# 高性能场景配置
high_performance_config:
network:
tcp_keepalive_time: 300
tcp_keepalive_intvl: 30
tcp_keepalive_probes: 3
tcp_retries2: 5
storage:
max_io_workers: 64
io_queue_depth: 256
read_ahead_blocks: 32
write_back_blocks: 16
cache:
meta_cache_size: "8GB"
data_cache_size: "32GB"
cache_ttl: "24h"
cache_compression: "lz4"
erasure_coding:
data_shards: 6
parity_shards: 2
block_size: "4MB"
stream_buffer_size: "16MB"五、容灾与备份:数据安全的最后防线
5.1 多集群数据同步
跨集群复制配置:
# cross_cluster_replication.py
import boto3
from botocore.config import Config
def setup_cross_region_replication(source_bucket, destination_bucket):
"""配置跨集群数据复制"""
# 源集群客户端
source_client = boto3.client('s3',
endpoint_url='http://rustfs-primary:9000',
aws_access_key_id='primary_admin',
aws_secret_access_key='primary_password'
)
# 目标集群客户端
dest_client = boto3.client('s3',
endpoint_url='http://rustfs-dr:9000',
aws_access_key_id='dr_admin',
aws_secret_access_key='dr_password'
)
# 配置复制规则
replication_config = {
'Role': 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/replication-role',
'Rules': [
{
'ID': 'FullBucketReplication',
'Status': 'Enabled',
'Priority': 1,
'Filter': {'Prefix': ''},
'Destination': {
'Bucket': f'arn:aws:s3:::{destination_bucket}',
'StorageClass': 'STANDARD'
}
}
]
}
source_client.put_bucket_replication(
Bucket=source_bucket,
ReplicationConfiguration=replication_config
)
print(f"已配置 {source_bucket} -> {destination_bucket} 的跨集群复制")5.2 数据备份与恢复
全量备份策略:
#!/bin/bash
# rustfs_backup.sh
# 备份配置
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/rustfs"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d)
RETENTION_DAYS=30
# 创建备份目录
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR/$DATE
# 1. 备份元数据
echo "备份元数据..."
mc admin info rustfs-primary > $BACKUP_DIR/$DATE/metadata.info
# 2. 备份配置
docker exec rustfs-primary tar czf - /etc/rustfs > $BACKUP_DIR/$DATE/config.tar.gz
# 3. 增量备份数据
if [ -d "$BACKUP_DIR/last_backup" ]; then
echo "执行增量备份..."
mc mirror --overwrite rustfs-primary/backup-bucket $BACKUP_DIR/$DATE/incr-backup \
--older-than $(cat $BACKUP_DIR/last_backup/timestamp)
else
echo "执行全量备份..."
mc mirror --overwrite rustfs-primary/backup-bucket $BACKUP_DIR/$DATE/full-backup
fi
# 4. 更新最新备份标记
echo $DATE > $BACKUP_DIR/last_backup/timestamp
# 5. 清理旧备份
find $BACKUP_DIR -type d -mtime +$RETENTION_DAYS -exec rm -rf {} \;
echo "备份完成: $BACKUP_DIR/$DATE"数据恢复流程:
# disaster_recovery.py
import subprocess
import logging
class DisasterRecovery:
def __init__(self, primary_endpoint, backup_endpoint):
self.primary = primary_endpoint
self.backup = backup_endpoint
self.logger = self.setup_logger()
def restore_from_backup(self, backup_path, bucket_name):
"""从备份恢复数据"""
try:
self.logger.info(f"开始恢复存储桶 {bucket_name}")
# 1. 创建目标存储桶
subprocess.run([
'mc', 'mb', f'{self.primary}/{bucket_name}'
], check=True)
# 2. 恢复数据
subprocess.run([
'mc', 'mirror', '--overwrite',
backup_path, f'{self.primary}/{bucket_name}'
], check=True)
# 3. 验证数据完整性
verification_result = subprocess.run([
'mc', 'diff',
backup_path, f'{self.primary}/{bucket_name}'
], capture_output=True, text=True)
if verification_result.returncode == 0:
self.logger.info("数据恢复验证成功")
return True
else:
self.logger.error("数据恢复验证失败")
return False
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
self.logger.error(f"恢复过程出错: {str(e)}")
return False
def emergency_failover(self):
"""紧急故障切换"""
# 停止写入主集群
# 切换DNS或负载均衡配置
# 启用备份集群写入
# 验证业务连续性
pass六、运维自动化:提升效率的关键
6.1 自动化运维脚本集
健康检查自动化:
# health_check_automation.py
import requests
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MimeText
class RustFSAutomation:
def automated_health_check(self):
"""自动化健康检查"""
checks = [
self.check_node_connectivity,
self.check_disk_space,
self.check_memory_usage,
self.check_api_responsiveness,
self.check_data_consistency
]
results = []
for check in checks:
result = check()
results.append(result)
if not result['status']:
self.send_alert(f"健康检查失败: {result['check_name']}")
return results
def check_data_consistency(self):
"""数据一致性检查"""
try:
response = requests.get('http://rustfs-cluster:9000/minio/v2/metrics/cluster')
metrics = response.text
# 检查校验和错误
if 'rustfs_checksum_errors_total 0' not in metrics:
return {
'status': False,
'check_name': '数据一致性检查',
'details': '发现校验和错误'
}
return {
'status': True,
'check_name': '数据一致性检查',
'details': '所有数据校验通过'
}
except Exception as e:
return {
'status': False,
'check_name': '数据一致性检查',
'details': str(e)
}
def send_alert(self, message):
"""发送告警通知"""
# 实现邮件、短信、钉钉等告警通道
pass6.2 基于Kubernetes的运维自动化
Operator自动修复:
# rustfs-operator.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: rustfs-automatic-healing
spec:
schedule: "0 */6 * * *" # 每6小时执行一次
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: healing-agent
image: rustfs/healing-agent:latest
env:
- name: RUSTFS_ENDPOINT
value: "http://rustfs-service:9000"
- name: HEALING_THRESHOLD
value: "0.95"
command: ["/bin/healing-agent"]
restartPolicy: OnFailure总结:构建完善的RustFS运维体系
通过本文的运维指南,您可以建立起监控告警、日常运维、性能优化、容灾备份四位一体的完整运维体系。关键成功因素包括:
-
预防性监控:建立完善的监控指标体系,提前发现潜在问题
-
自动化运维:减少人工干预,提高运维效率和准确性
-
性能持续优化:基于业务负载特点动态调整配置参数
-
容灾备份保障:确保数据安全性和业务连续性
运维成熟度演进路径:
-
初级阶段:基础监控 + 手动运维
-
中级阶段:自动化脚本 + 预警机制
-
高级阶段:AIOps + 自愈能力 + 预测性维护
RustFS作为一个高性能的分布式存储系统,其运维工作同样需要专业性和系统性。希望本文能为您的RustFS运维实践提供有力支持。
扩展阅读:建议进一步探索RustFS与云原生生态的深度集成,如Kubernetes CSI驱动、服务网格等高级主题,构建面向未来的存储基础设施。
以下是深入学习 RustFS 的推荐资源:RustFS
官方文档: RustFS 官方文档- 提供架构、安装指南和 API 参考。
GitHub 仓库: GitHub 仓库 - 获取源代码、提交问题或贡献代码。
社区支持: GitHub Discussions- 与开发者交流经验和解决方案。





















 1030
1030










