CyclicBarrier简介
CyclicBarrier是一个同步辅助类,允许一组线程互相等待,直到到达某个公共屏障点 (common barrier point)。因为该 barrier 在释放等待线程后可以重用,所以称它为循环 的 barrier。
CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier的对比:
①CountDownLatch的作用是允许1或N个线程等待其他线程完成执行;而CyclicBarrier则是允许N个线程相互等待。
②CountDownLatch的计数器无法被重置;CyclicBarrier的计数器可以被重置后使用,因此它被称为是循环的barrier。
CyclicBarrier方法列表
CyclicBarrier(int parties)//创建一个新的 CyclicBarrier,它将在给定数量的参与者(线程)处于等待状态时启动,但它不会在启动 barrier 时执行预定义的操作
CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction)//创建一个新的 CyclicBarrier,它将在给定数量的参与者(线程)处于等待状态时启动,并在启动 barrier 时执行给定的屏障操作,该操作由最后一个进入 barrier 的线程执行
int await()//在所有参与者都已经在此 barrier 上调用 await 方法之前,将一直等待
int await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)//在所有参与者都已经在此屏障上调用 await 方法之前将一直等待,或者超出了指定的等待时间
int getNumberWaiting()//返回当前在屏障处等待的参与者数目
int getParties()//返回要求启动此 barrier 的参与者数目
boolean isBroken()//查询此屏障是否处于损坏状态
void reset()//将屏障重置为其初始状态
CyclicBarrier数据结构
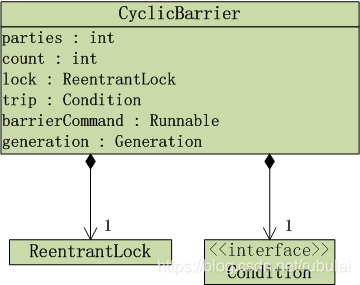
CyclicBarrier包含了"ReentrantLock对象lock"和"Condition对象trip",它是通过独占锁实现的。
CyclicBarrier源码分析
public class CyclicBarrier {
/**
* Each use of the barrier is represented as a generation instance.
* The generation changes whenever the barrier is tripped, or
* is reset. There can be many generations associated with threads
* using the barrier - due to the non-deterministic way the lock
* may be allocated to waiting threads - but only one of these
* can be active at a time (the one to which <tt>count</tt> applies)
* and all the rest are either broken or tripped.
* There need not be an active generation if there has been a break
* but no subsequent reset.
*/
private static class Generation {
boolean broken = false;
}
/** The lock for guarding barrier entry */
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Condition to wait on until tripped */
private final Condition trip = lock.newCondition();
/** The number of parties */
private final int parties;
/* The command to run when tripped */
private final Runnable barrierCommand;
/** The current generation */
private Generation generation = new Generation();
/**
* Number of parties still waiting. Counts down from parties to 0
* on each generation. It is reset to parties on each new
* generation or when broken.
*/
private int count;
/**
* Updates state on barrier trip and wakes up everyone.
* Called only while holding lock.
*/
private void nextGeneration() {
// signal completion of last generation
trip.signalAll();
// set up next generation
count = parties;
generation = new Generation();
}
/**
* Sets current barrier generation as broken and wakes up everyone.
* Called only while holding lock.
*/
private void breakBarrier() {
generation.broken = true;
count = parties;
trip.signalAll();
}
/**
* Main barrier code, covering the various policies.
*/
private int dowait(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException,
TimeoutException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
final Generation g = generation;
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
breakBarrier();
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int index = --count;
if (index == 0) { // tripped
boolean ranAction = false;
try {
final Runnable command = barrierCommand;
if (command != null)
command.run();
ranAction = true;
nextGeneration();
return 0;
} finally {
if (!ranAction)
breakBarrier();
}
}
// loop until tripped, broken, interrupted, or timed out
for (;;) {
try {
if (!timed)
trip.await();
else if (nanos > 0L)
nanos = trip.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
if (g == generation && ! g.broken) {
breakBarrier();
throw ie;
} else {
// We're about to finish waiting even if we had not
// been interrupted, so this interrupt is deemed to
// "belong" to subsequent execution.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
if (g != generation)
return index;
if (timed && nanos <= 0L) {
breakBarrier();
throw new TimeoutException();
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Creates a new <tt>CyclicBarrier</tt> that will trip when the
* given number of parties (threads) are waiting upon it, and which
* will execute the given barrier action when the barrier is tripped,
* performed by the last thread entering the barrier.
*
* @param parties the number of threads that must invoke {@link #await}
* before the barrier is tripped
* @param barrierAction the command to execute when the barrier is
* tripped, or {@code null} if there is no action
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code parties} is less than 1
*/
public CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction) {
if (parties <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.parties = parties;
this.count = parties;
this.barrierCommand = barrierAction;
}
/**
* Creates a new <tt>CyclicBarrier</tt> that will trip when the
* given number of parties (threads) are waiting upon it, and
* does not perform a predefined action when the barrier is tripped.
*
* @param parties the number of threads that must invoke {@link #await}
* before the barrier is tripped
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code parties} is less than 1
*/
public CyclicBarrier(int parties) {
this(parties, null);
}
/**
* Returns the number of parties required to trip this barrier.
*
* @return the number of parties required to trip this barrier
*/
public int getParties() {
return parties;
}
/**
* Waits until all {@linkplain #getParties parties} have invoked
* <tt>await</tt> on this barrier.
*
* <p>If the current thread is not the last to arrive then it is
* disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies dormant until
* one of the following things happens:
* <ul>
* <li>The last thread arrives; or
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread; or
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* one of the other waiting threads; or
* <li>Some other thread times out while waiting for barrier; or
* <li>Some other thread invokes {@link #reset} on this barrier.
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the current thread:
* <ul>
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting
* </ul>
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's
* interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>If the barrier is {@link #reset} while any thread is waiting,
* or if the barrier {@linkplain #isBroken is broken} when
* <tt>await</tt> is invoked, or while any thread is waiting, then
* {@link BrokenBarrierException} is thrown.
*
* <p>If any thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting,
* then all other waiting threads will throw
* {@link BrokenBarrierException} and the barrier is placed in the broken
* state.
*
* <p>If the current thread is the last thread to arrive, and a
* non-null barrier action was supplied in the constructor, then the
* current thread runs the action before allowing the other threads to
* continue.
* If an exception occurs during the barrier action then that exception
* will be propagated in the current thread and the barrier is placed in
* the broken state.
*
* @return the arrival index of the current thread, where index
* <tt>{@link #getParties()} - 1</tt> indicates the first
* to arrive and zero indicates the last to arrive
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
* @throws BrokenBarrierException if <em>another</em> thread was
* interrupted or timed out while the current thread was
* waiting, or the barrier was reset, or the barrier was
* broken when {@code await} was called, or the barrier
* action (if present) failed due an exception.
*/
public int await() throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException {
try {
return dowait(false, 0L);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new Error(toe); // cannot happen;
}
}
/**
* Waits until all {@linkplain #getParties parties} have invoked
* <tt>await</tt> on this barrier, or the specified waiting time elapses.
*
* <p>If the current thread is not the last to arrive then it is
* disabled for thread scheduling purposes and lies dormant until
* one of the following things happens:
* <ul>
* <li>The last thread arrives; or
* <li>The specified timeout elapses; or
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* the current thread; or
* <li>Some other thread {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupts}
* one of the other waiting threads; or
* <li>Some other thread times out while waiting for barrier; or
* <li>Some other thread invokes {@link #reset} on this barrier.
* </ul>
*
* <p>If the current thread:
* <ul>
* <li>has its interrupted status set on entry to this method; or
* <li>is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while waiting
* </ul>
* then {@link InterruptedException} is thrown and the current thread's
* interrupted status is cleared.
*
* <p>If the specified waiting time elapses then {@link TimeoutException}
* is thrown. If the time is less than or equal to zero, the
* method will not wait at all.
*
* <p>If the barrier is {@link #reset} while any thread is waiting,
* or if the barrier {@linkplain #isBroken is broken} when
* <tt>await</tt> is invoked, or while any thread is waiting, then
* {@link BrokenBarrierException} is thrown.
*
* <p>If any thread is {@linkplain Thread#interrupt interrupted} while
* waiting, then all other waiting threads will throw {@link
* BrokenBarrierException} and the barrier is placed in the broken
* state.
*
* <p>If the current thread is the last thread to arrive, and a
* non-null barrier action was supplied in the constructor, then the
* current thread runs the action before allowing the other threads to
* continue.
* If an exception occurs during the barrier action then that exception
* will be propagated in the current thread and the barrier is placed in
* the broken state.
*
* @param timeout the time to wait for the barrier
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout parameter
* @return the arrival index of the current thread, where index
* <tt>{@link #getParties()} - 1</tt> indicates the first
* to arrive and zero indicates the last to arrive
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
* @throws TimeoutException if the specified timeout elapses
* @throws BrokenBarrierException if <em>another</em> thread was
* interrupted or timed out while the current thread was
* waiting, or the barrier was reset, or the barrier was broken
* when {@code await} was called, or the barrier action (if
* present) failed due an exception
*/
public int await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException,
BrokenBarrierException,
TimeoutException {
return dowait(true, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
/**
* Queries if this barrier is in a broken state.
*
* @return {@code true} if one or more parties broke out of this
* barrier due to interruption or timeout since
* construction or the last reset, or a barrier action
* failed due to an exception; {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public boolean isBroken() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return generation.broken;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Resets the barrier to its initial state. If any parties are
* currently waiting at the barrier, they will return with a
* {@link BrokenBarrierException}. Note that resets <em>after</em>
* a breakage has occurred for other reasons can be complicated to
* carry out; threads need to re-synchronize in some other way,
* and choose one to perform the reset. It may be preferable to
* instead create a new barrier for subsequent use.
*/
public void reset() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
breakBarrier(); // break the current generation
nextGeneration(); // start a new generation
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns the number of parties currently waiting at the barrier.
* This method is primarily useful for debugging and assertions.
*
* @return the number of parties currently blocked in {@link #await}
*/
public int getNumberWaiting() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return parties - count;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
CyclicBarrier是通过ReentrantLock(独占锁)和Condition来实现的。下面,分析一下CyclicBarrier中核心函数: 构造函数和等待函数。
1、构造函数
CyclicBarrier的构造函数共2个:CyclicBarrier 和 CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction)。第1个构造函数是调用第2个构造函数来实现的,第2个构造函数的源码:
public CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction) {
if (parties <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// parties表示“必须同时到达barrier的线程个数”
this.parties = parties;
// count表示“处在等待状态的线程个数”
this.count = parties;
// barrierCommand表示“parties个线程到达barrier时,会执行的动作”
this.barrierCommand = barrierAction;
}
2、等待函数
CyclicBarrier.java中await()方法如下:
public int await() throws InterruptedException,BrokenBarrierException {
try {
return dowait(false, 0L);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new Error(toe); // cannot happen;
}
}
说明:await()是通过dowait()实现的
private int dowait(boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException,TimeoutException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 获取“独占锁(lock)”
lock.lock();
try {
// 保存“当前的generation”
final Generation g = generation;
// 若“当前generation已损坏”,则抛出异常
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
// 如果当前线程被中断,则通过breakBarrier()终止CyclicBarrier,唤醒CyclicBarrier中所有等待线程
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
breakBarrier();
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 将“count计数器”-1
int index = --count;
// 如果index=0,则意味着“有parties个线程到达barrier”
if (index == 0) { // tripped
boolean ranAction = false;
try {
// 如果barrierCommand不为null,则执行该动作
final Runnable command = barrierCommand;
if (command != null)
command.run();
ranAction = true;
// 唤醒所有等待线程,并更新generation
nextGeneration();
return 0;
} finally {
if (!ranAction)
breakBarrier();
}
}
// 当前线程一直阻塞,直到“有parties个线程到达barrier” 或 “当前线程被中断” 或 “超时”这3者之一发生,当前线程才继续执行。
for (;;) {
try {
// 如果不是“超时等待”,则调用awati()进行等待;否则,调用awaitNanos()进行等待
if (!timed)
trip.await();
else if (nanos > 0L)
nanos = trip.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
// 如果等待过程中,线程被中断,则执行下面的函数
if (g == generation && ! g.broken) {
breakBarrier();
throw ie;
} else {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
// 如果“当前generation已经损坏”,则抛出异常
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
// 如果“generation已经换代”,则返回index
if (g != generation)
return index;
// 如果是“超时等待”,并且时间已到,则通过breakBarrier()终止CyclicBarrier,唤醒CyclicBarrier中所有等待线程
if (timed && nanos <= 0L) {
breakBarrier();
throw new TimeoutException();
}
}
} finally {
// 释放“独占锁(lock)”
lock.unlock();
}
}
说明:dowait()的作用就是让当前线程阻塞,直到“有parties个线程到达barrier” 或 “当前线程被中断” 或 “超时”这3者之一发生,当前线程才继续执行。
① generation是CyclicBarrier的一个成员属性,它的定义如下:
private Generation generation = new Generation();
private static class Generation {
boolean broken = false;
}
在CyclicBarrier中,同一批的线程属于同一代,即同一个Generation;CyclicBarrier中通过generation对象,记录属于哪一代。当有parties个线程到达barrier,generation就会被更新换代;
②如果当前线程被中断,即Thread.interrupted()为true;则通过breakBarrier()终止CyclicBarrier。breakBarrier()的源码如下:
private void breakBarrier() {
generation.broken = true;
count = parties;
trip.signalAll();
}
breakBarrier()会设置当前中断标记broken为true,意味着“将该Generation中断”;同时,设置count=parties,即重新初始化count;最后,通过signalAll()唤醒CyclicBarrier上所有的等待线程;
③将“count计数器”-1,即–count;然后判断是不是“有parties个线程到达barrier”,即index是不是为0。当index=0时,如果barrierCommand不为null,则执行该barrierCommand,barrierCommand就是我们创建CyclicBarrier时,传入的Runnable对象。然后,调用nextGeneration()进行换代工作,nextGeneration()的源码如下:
private void nextGeneration() {
trip.signalAll();
count = parties;
generation = new Generation();
}
首先,它会调用signalAll()唤醒CyclicBarrier上所有的等待线程;接着,重新初始化count;最后,更新generation的值;
④在for(;;)循环中,timed是用来表示当前是不是“超时等待”线程。如果不是,则通过trip.await()进行等待;否则,调用awaitNanos()进行超时等待。
CyclicBarrier的使用示例
示例1:新建5个线程,这5个线程达到一定的条件时,它们才继续往后运行
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
public class CyclicBarrierTest1 {
private static int SIZE = 5;
private static CyclicBarrier cb;
public static void main(String[] args) {
cb = new CyclicBarrier(SIZE);
// 新建5个任务
for(int i=0; i<SIZE; i++)
new InnerThread().start();
}
static class InnerThread extends Thread{
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " wait for CyclicBarrier.");
// 将cb的参与者数量加1
cb.await();
// cb的参与者数量等于5时,才继续往后执行
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " continued.");
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//结果
Thread-1 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-2 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-3 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-4 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-0 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-0 continued.
Thread-4 continued.
Thread-2 continued.
Thread-3 continued.
Thread-1 continued.
结果说明:主线程中新建了5个线程,所有的这些线程都调用cb.await()而被阻塞等待。这些线程一直等待,直到cb中所有线程都到达barrier(barrier满)时,这些线程才继续运行(类似于水坝当水位上升至一个危险高度时,才开闸放水)。
示例2:新建5个线程,当这5个线程达到一定的条件时,执行某项任务
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
public class CyclicBarrierTest2 {
private static int SIZE = 5;
private static CyclicBarrier cb;
public static void main(String[] args) {
cb = new CyclicBarrier(SIZE, new Runnable () {
public void run() {
System.out.println("CyclicBarrier's parties is: "+ cb.getParties());
}
});
// 新建5个任务
for(int i=0; i<SIZE; i++)
new InnerThread().start();
}
static class InnerThread extends Thread{
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " wait for CyclicBarrier.");
// 将cb的参与者数量加1
cb.await();
// cb的参与者数量等于5时,才继续往后执行
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " continued.");
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//结果
Thread-1 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-2 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-3 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-4 wait for CyclicBarrier.
Thread-0 wait for CyclicBarrier.
CyclicBarrier's parties is: 5
Thread-0 continued.
Thread-4 continued.
Thread-2 continued.
Thread-3 continued.
Thread-1 continued.
结果说明:主线程中新建了5个线程,所有的这些线程都调用cb.await()等待。所有这些线程一直等待,直到cb中所有线程都达到barrier时,先执行新建cb时注册的Runnable任务,然后接着执行各个线程中的任务。


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








