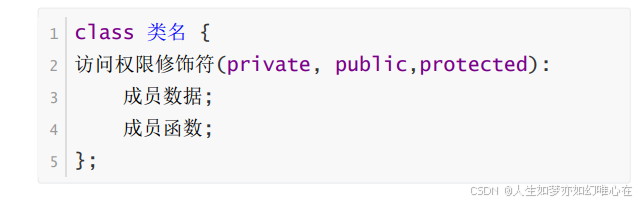
类与对象
类的语法
案列:定时器
功能:
- 设置倒计时:分,秒
- tick() 走 1 秒
- 读取当前剩余:分,秒
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 定时器的定义
class Timer
{
public:
void set(int min,int sec);
void tick();
int get_min();
int get_sec();
private:
int min;
int sec;
};
////// 定时器的实现
void Timer::set(int m, int s)
{
min = m;
sec = s;
}
// 走1秒
void Timer::tick()
{
if(sec>0){
sec--;
}else if(min>0){
min--;
sec = 59;
}
if(min==0 && sec==0)cout << "beep ... beep ... " <<endl;
}
// 读取时间
int Timer::get_min() { return min; }
int Timer::get_sec() { return sec; }
int main()
{
Timer a;
a.set(1,15);
a.tick();
cout << a.get_min() << "," << a.get_sec() <<
endl;
for(int i=0; i<80; i++) a.tick();
return 0;
}

对象初始化
如果不对对象进行初始化,则成员变量值不确定 初始化途径:
- 定义成员变量时给初始值 创建对象时,
- 用 { } 语法
- 构造函数(构造子)
![]()
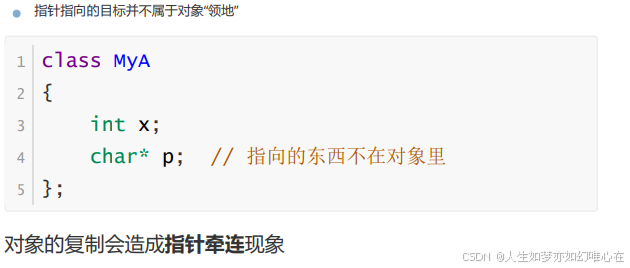
对象与指针
对象内部的指针
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
char* get_p(){
return p;
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA a;
a.set("zhangsan",10);
MyA b=a;
b.set("zha",10);
cout << a.get_p() << endl;
return 0;
}


==内存泄漏==过程示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA a;
a.set("zhangsan", 10);
cout << sizeof(MyA) << endl;
return 0;
}

修正:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
void finish(){
delete [] p;
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA a;
a.set("zhangsan", 10);
a.finish();
cout << sizeof(MyA) << endl;
return 0;
}

指向对象的指针
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
void finish(){
delete [] p;
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA* p=new MyA();
p->set("zhangsan",10);
p[0].finish();
delete p;
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA
{
public:
void set(char* name, int age){
x = age;
p = new char [strlen(name)+1];
strcpy(p,name);
}
char* get_p(){
return p;
}
void finish(){
delete [] p;
}
private:
int x;
char* p;
};
int main()
{
MyA* p=new MyA();
p->set("zhangsan",10);
p[1].finish();
cout << p->get_p() << endl;
delete p;
return 0;
}


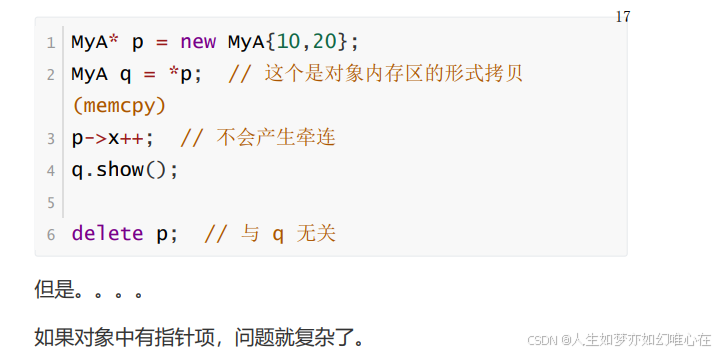
指针赋值与对象拷贝
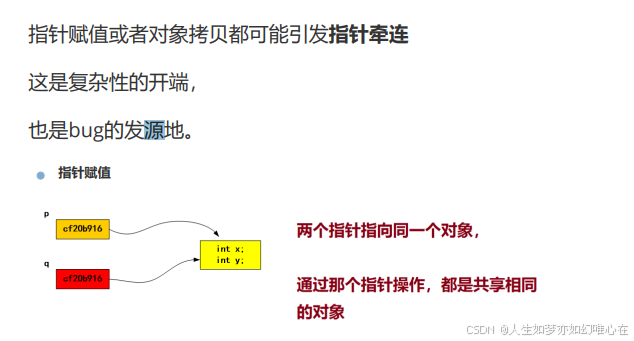

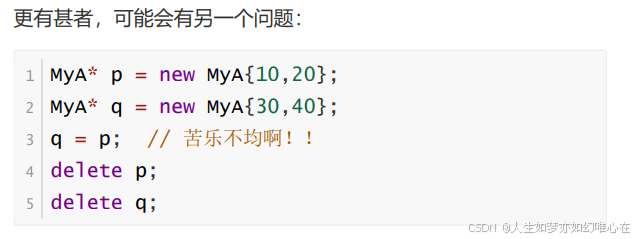
对象赋值(对象拷贝)




注意:
属性在public中能用{}初始化对象,在private中就用不了。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class MyA{
public:
int x;
int y;
void show(){
printf("(%d,%d)\n", x, y);
}
};
int main()
{
MyA p={1,2};
MyA* b=new MyA{1,2};
return 0;
}
MyA* p = new MyA{10,20}; 和 MyA p = {10,20}; 区别



浅拷贝与深拷贝
浅拷贝
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class LinkNode{
public:
int data;
LinkNode* next;
void add(LinkNode* it){
it->next = next;
next = it;
}
void clear(){
if(next==NULL) return;
next->clear();
delete next;
next = NULL;
}
void show(){
cout << data << " ";
if(next) next->show();
}
};
int main()
{
LinkNode a = {-1,NULL};
for(int i=9; i>=1; i--) a.add(new
LinkNode{i,NULL});
LinkNode b = a;
b.show();
cout << endl;
a.clear();
b.show(); cout << endl;
return 0;
}
a调用clear方法,影响b的值。

深拷贝
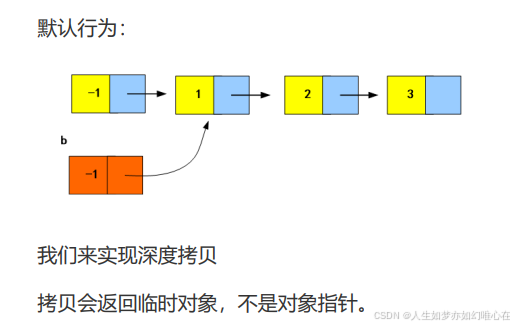
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class LinkNode{
public:
int data;
LinkNode* next;
void add(LinkNode* it){
it->next = next;
next = it;
}
void clear(){
if(next) next->clear();
delete next;
next = NULL;
}
void show(){
cout << data << " ";
if(next) next->show();
}
LinkNode copy(); // 深度拷贝
};
LinkNode LinkNode::copy()
{
LinkNode t = {data, NULL};
LinkNode* p = next;
LinkNode* q = &t;
while(p){
q->next = new LinkNode{p->data,NULL};
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
LinkNode a = {-1,NULL};
for(int i=9; i>=1; i--) a.add(new
LinkNode{i,NULL});
LinkNode b = a.copy();
b.show(); cout << endl;
a.clear();
b.show(); cout << endl;
return 0;
}

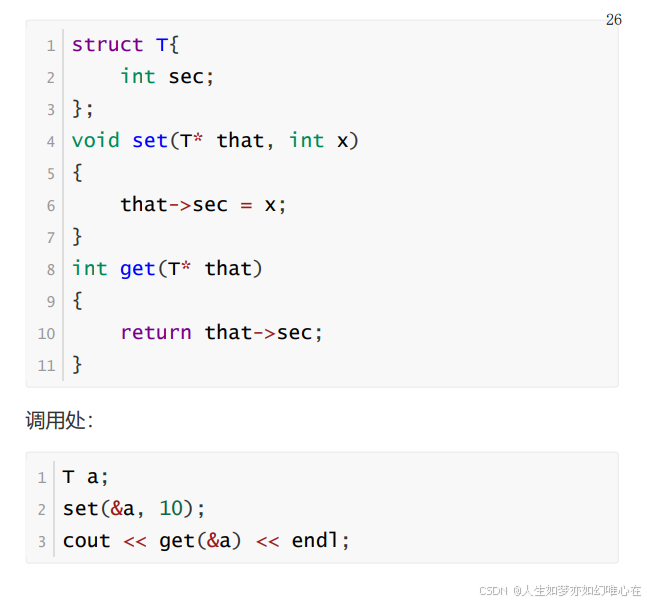
成员函数与this指针



构造子与析构子

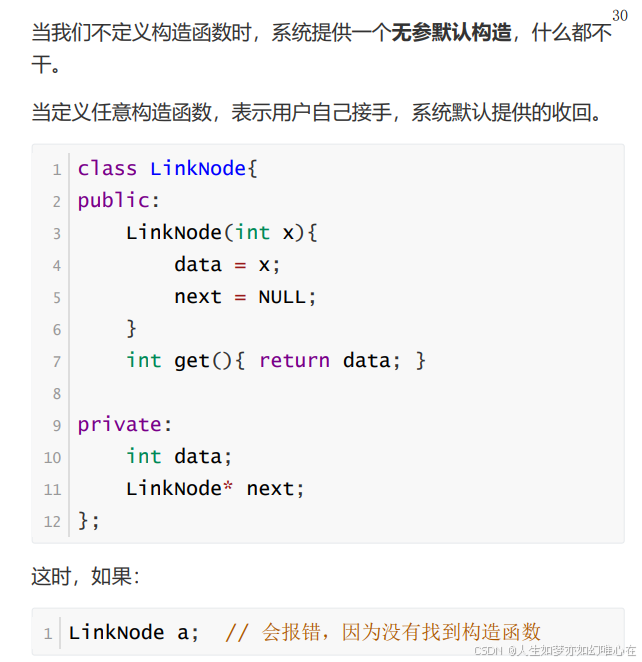


#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class LinkNode
{
public:
LinkNode(int x){
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
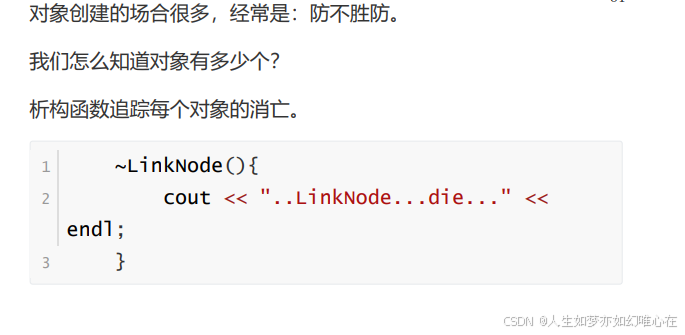
~LinkNode(){
cout << "destroy... " << endl;
if(next) delete next;
next = NULL;
}
LinkNode& add(int x){
LinkNode* p = new LinkNode(x);
p->next = next;
next = p;
return *p;
}
void show(){
LinkNode* p = this;
while(p){
cout << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
int data;
LinkNode* next;
};
int main()
{
LinkNode head(-1);
head.add(1).add(2).add(3);
head.show();
return 0;
}

构造函数重载

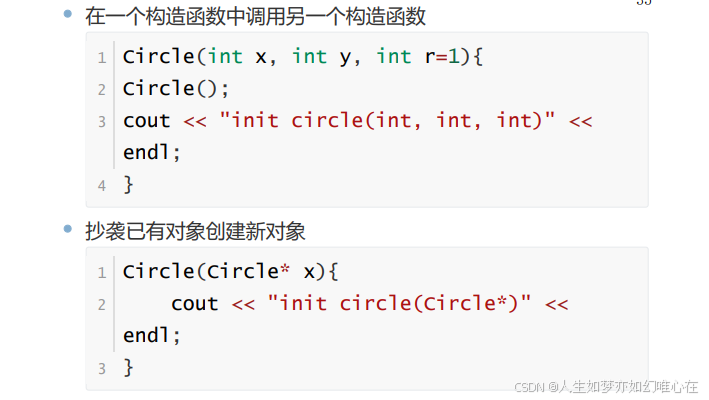
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Circle{
public:
Circle(){
cout << "init Circle()" << endl;
}
Circle(int x, int y, int r=1){
cout << "init circle(int, int,int)" << endl;
}
private:
int x;
int y;
int r;
};
int main()
{
Circle a;
Circle b={1,2,3};
return 0;
}


#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
Point() {
cout << "init point()" << endl;
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
Point(int x, int y){
cout << "init point(x, y)" << endl;
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void set(int x, int y){
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
int getx() { return x; }
int gety() { return y; }
private:
int x;
int y;
};
class Circle
{
public:
Circle(){
cout << "init circle()" << endl;
pt.set(0,0);
r = 1;
}
Circle(int r){
cout << "init circle(int)" << endl;
Circle();
this->r = r;
}
void show(){
printf("circle: (%d,%d)%d\n",pt.getx(),pt.gety(),r);
}
private:
Point pt; // 圆心
int r; // 半径
};
int main()
{
//Circle a; //此时,Point对象初始化几次?
Circle a(10); // Point对象初始化时机和次数?
//a.show();
return 0;
}

注意:会重复创建Point对象

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
Point() {
cout << "init point()" << endl;
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
Point(int x, int y){
cout << "init point(x, y)" << endl;
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
void set(int x, int y){
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
int getx() { return x; }
int gety() { return y; }
private:
int x;
int y;
};
class Circle
{
public:
Circle():pt(1,1),r(10){
cout << "init circle()" << endl;
// pt.set(0,0);
// r = 1;
}
Circle(int r):Circle(){
cout << "init circle(int)" << endl;
//Circle();
this->r = r;
}
void show(){
printf("circle: (%d,%d)%d\n",pt.getx(),pt.gety(),r);
}
private:
Point pt; // 圆心
int r; // 半径
};
int main()
{
//Circle a; //此时,Point对象初始化几次?
Circle a(10); // Point对象初始化时机和次数?
//a.show();
return 0;
}
对象的生存期
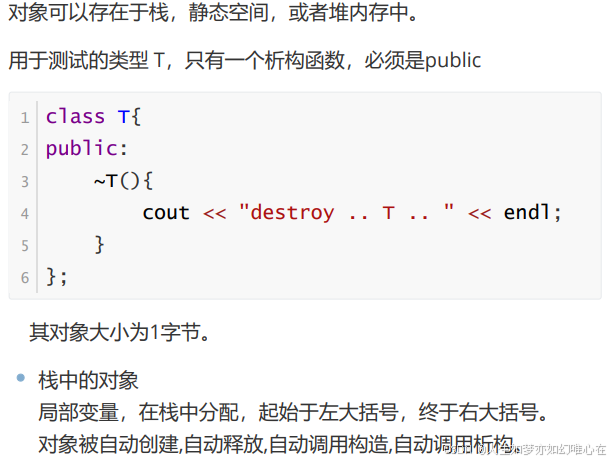



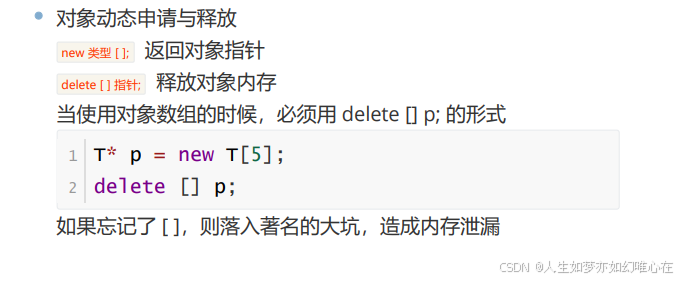
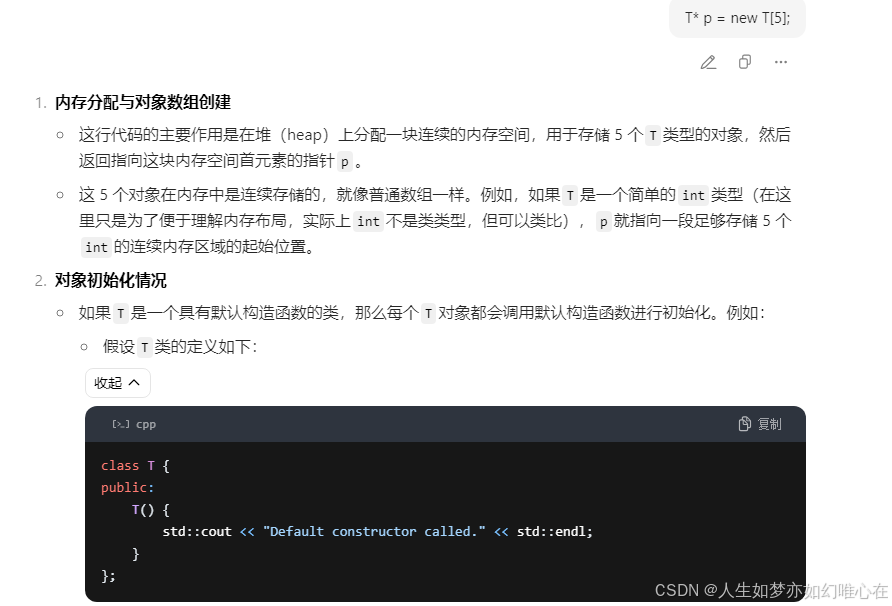

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
T a; //不能T a();
cout << "end" <<endl;
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
void f(T x){}
int main()
{
T a; //不能T a();
f(a);
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
void f(T x){}
int main()
{
T{};//立即数
f(T{});
cout << "111" << endl;
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
T f(T x){
return T{};
}
int main()
{
T a;
f(a);
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T
{
public:
~T(){
cout << "destroy .. T .. " << endl;
}
};
T f(T x){
return T{};
}
int main()
{
T* p=new T();//也可以用 T* p=new T{};
return 0;
}
T* p=new T();和 T* p=new T{}; 区别


C++创建数组的方式:



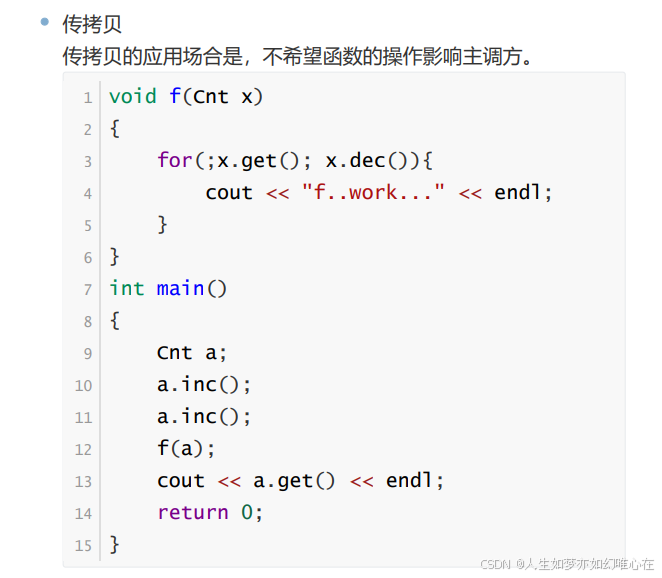
对象的传递

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){ x = 0; }
~Cnt() { cout << "destroy .. counter ..." << x << endl; }
void inc() { x++; }
void dec() { x--; }
int get() { return x; }
private:
int x;
};
int main()
{
Cnt a;
a.inc();
a.inc();
cout << a.get() << endl;
return 0;
}



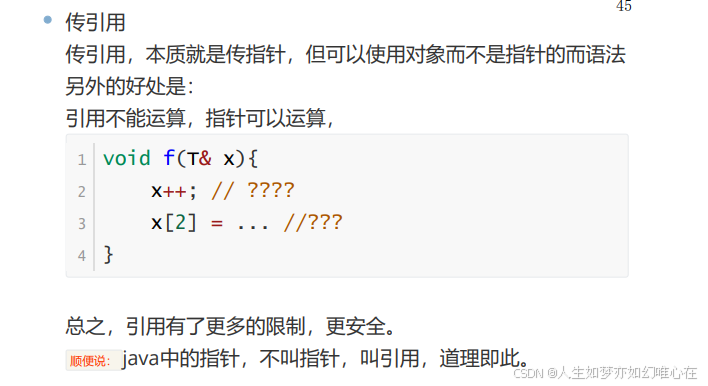
指针和引用的区别


引用不能运算,指针可以运算


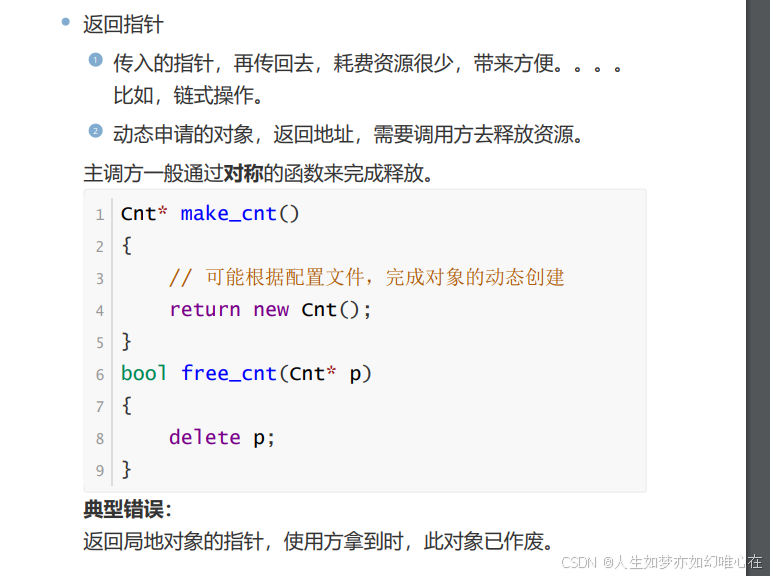

静态成员函数

静态成员函数的常见使用场景

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Cnt{
public:
Cnt(){
x = 0;
}
Cnt& inc(){ x++; return *this; }
Cnt& dec(){ x--; return *this; }
void show() { cout << x << endl; }
void add(Cnt& t){ // t 的值并入 我自己
x += t.x;
}
static Cnt add(Cnt& a, Cnt& b){ // a,b都不变,返回新的
Cnt t;
t.x = a.x + b.x;
return t;
}
private:
int x;
};
int main()
{
Cnt a;
a.inc().inc();
Cnt b;
b.inc();
a.add(b);
a.show();
//Cnt c=a.add(a,b); 看起来不简便
Cnt c=Cnt::add(a,b);
c.show();
return 0;
}



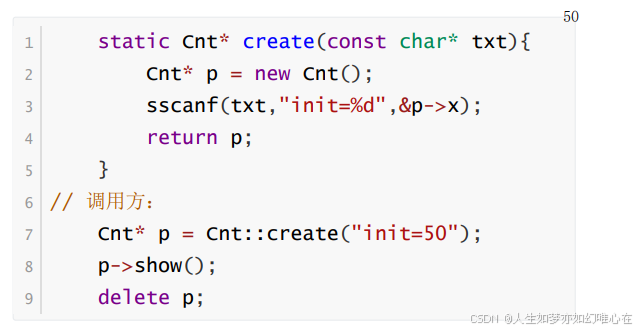

静态成员变量


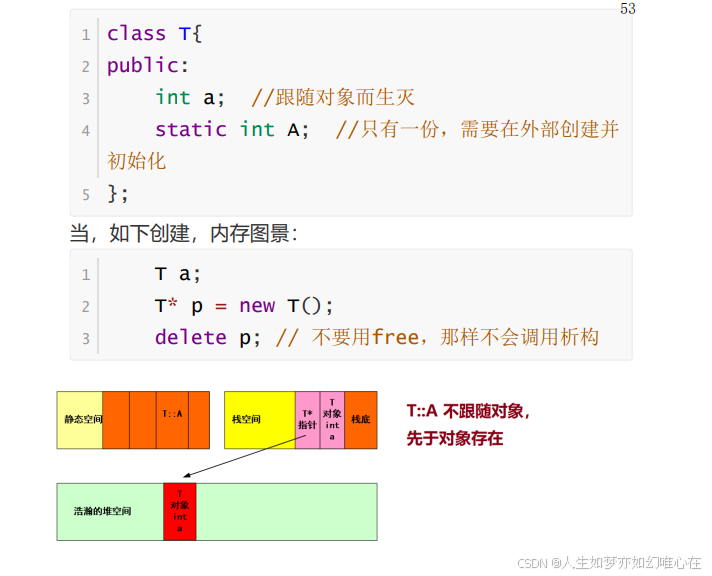

#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T{
public:
T(){ A++; }
~T(){ A--; }
int x;
static int A;
};
int T::A=0;
int main()
{
T a;
T b;
cout << T::A << endl;
return 0;
}


#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class T{
public:
static T* get_instance(){
if(pObj==NULL) pObj = new T();
return pObj;
}
static void free(){
if(pObj){
delete pObj;
pObj = NULL;
}
}
private:
T(){}
~T(){}
static T* pObj;
};
T* T::pObj = NULL; // 不要忘记真正创建变量
int main()
{
T* p1 = T::get_instance();
T* p2 = T::get_instance();
cout << (p1 == p2) << endl;
return 0;
}

对象的状态

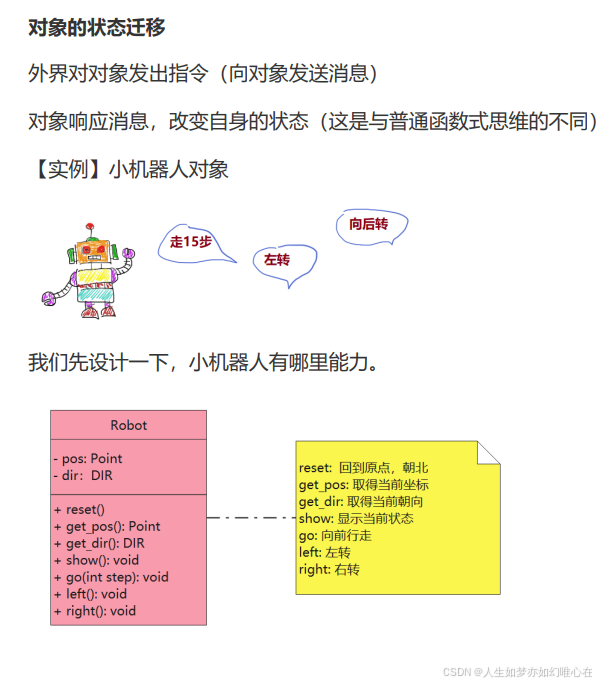

最后,实现小机器人类:
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
enum DIR{
NORTH, EAST, SOUTH, WEST
};
struct Point{
int x;
int y;
Point(){
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
void show(){
printf("(%d,%d)", x, y);
}
};
class Robot{
public:
Robot(){
dir = NORTH;
}
Robot& go(int step){
switch (dir) {
case NORTH:
pt.y += step;
break;
case EAST:
pt.x += step;
break;
case SOUTH:
pt.y -= step;
break;
case WEST:
pt.x -= step;
break;
}
return *this;
}
Robot& left(){
dir = (DIR)((dir-1+4)%4);
return *this;
}
Robot& right(){
dir = (DIR)((dir+1)%4);
return *this;
}
void show() {
pt.show(); cout << " ";
switch (dir) {
case NORTH:
cout << "north";
break;
case EAST:
cout << "east";
break;
case SOUTH:
cout << "south";
break;
case WEST:
cout << "west";
}
cout << endl;
}
void reset(){
pt.x = 0; pt.y = 0;
dir = NORTH;
}
private:
Point pt; //当前坐标
DIR dir; // 朝向
};
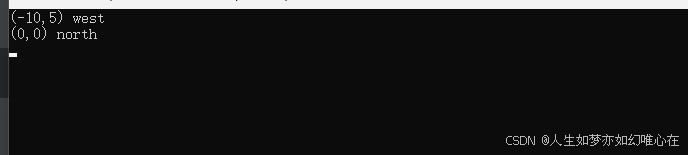
int main()
{
Robot a;
a.go(5);
a.right();
a.go(10);
a.left().left().go(20); //需要支持链式
a.show();
a.reset();
a.show();
return 0;
}








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 865
865

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










