|
1、串口概述 linux中的串口设备文件存放于/dev目录下,其中串口一,串口二对应设备名依次为“/dev/ttyS0”、“/dev/ttyS1”。在linux下操作串口与操作文件相同。
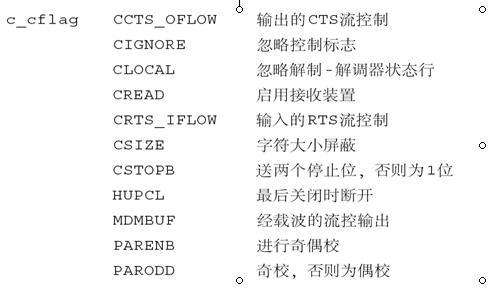
串口设置由下面结构体实现: Struct termios { 该结构中c_cflag最为重要,可设置波特率、数据位、校验位、停止位。在设置波特率时需在数字前加上‘B’,如B9600或B19200。使用其需通过“与”“或”操作方式。
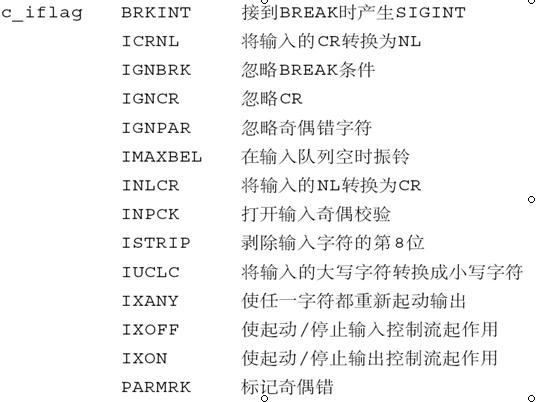
输入模式c_iflag成员控制端口接收端的字符输入处理。
Tcgetattr 取属性(termios结构) 2.1 串口配置流程 struct termios newtio,oldtio; 2. 激活选项有CLOCAL和CREAD,用于本地连接和接收使能。 newtio.c_cflag | = CLOCAL | CREAD; 3. 设置波特率,使用cfsetispeed和cfsetospeed函数。 cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200); 4. 设置数据位,需使用掩码设置。 newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; 5. 设置奇偶校验位,使用c_cflag和c_iflag。 newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB; 设置偶校验: newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP); 6. 设置停止位,通过激活c_cflag中的CSTOPB实现。若停止位为1,则清除CSTOPB,若停止位为2,则激活CSTOPB。 newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; 7. 设置最少字符和等待时间,对于接收字符和等待时间没有特别要求时,可设为0。 newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
tcflush函数刷清输入缓存(终端驱动程序已接收到,但用户程序尚未读)或输出缓存(用户程序已经写,但尚未发送)。 int tcflush(int filedes, int queue ) queue参数应当是下列三个常数之一: • TCIFLUSH 刷清输入队列。 9. 激活配置。在完成配置后,需激活配置使其生效。使用tcsettattr()函数。原型: int tcgetattr(int filedes, struct termios * termptr); tcsetattr的参数opt使我们可以指定在什么时候新的终端属性才起作用。opt可以指定为下列常数中的一个: • TCSANOW 更改立即发生。
在配置完串口的相关属性后,就可对串口进行打开,读写操作了。其使用方式与文件操作一样,区别在于串口是一个终端设备。 3.1 打开串口 fd = open( "/dev/ttyS0",O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_NDELAY); fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0); 接着,测试打开的文件描述府是否引用一个终端设备,以进一步确认串口是否正确打开。 isatty(STDIN_FILENO);
read(fd,buff,8);
Example:seri.c #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <errno.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <termios.h> #include <stdlib.h>
int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop) { struct termios newtio,oldtio; if ( tcgetattr( fd,&oldtio) != 0) { perror("SetupSerial 1"); return -1; } bzero( &newtio, sizeof( newtio ) ); newtio.c_cflag |= CLOCAL | CREAD; newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch( nBits ) { case 7: newtio.c_cflag |= CS7; break; case 8: newtio.c_cflag |= CS8; break; }
switch( nEvent ) { case 'O': newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB; newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD; newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP); break; case 'E': newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP); newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB; newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD; break; case 'N': newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; break; }
switch( nSpeed ) { case 2400: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2400); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2400); break; case 4800: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4800); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4800); break; case 9600: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600); break; case 115200: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B115200); break; default: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600); break; } if( nStop == 1 ) newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; else if ( nStop == 2 ) newtio.c_cflag |= CSTOPB; newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0; newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 0; tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH); if((tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio))!=0) { perror("com set error"); return -1; } printf("set done!/n"); return 0; }
int open_port(int fd,int comport) { char *dev[]={"/dev/ttyS0","/dev/ttyS1","/dev/ttyS2"}; long vdisable; if (comport==1) { fd = open( "/dev/ttyS0", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_NDELAY); if (-1 == fd){ perror("Can't Open Serial Port"); return(-1); } else printf("open ttyS0 ...../n"); } else if(comport==2) { fd = open( "/dev/ttyS1", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_NDELAY); if (-1 == fd){ perror("Can't Open Serial Port"); return(-1); } else printf("open ttyS1 ...../n"); } else if (comport==3) { fd = open( "/dev/ttyS2", O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_NDELAY); if (-1 == fd){ perror("Can't Open Serial Port"); return(-1); } else printf("open ttyS2 ...../n"); } if(fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0)<0) printf("fcntl failed!/n"); else printf("fcntl=%d/n",fcntl(fd, F_SETFL,0)); if(isatty(STDIN_FILENO)==0) printf("standard input is not a terminal device/n"); else printf("isatty success!/n"); printf("fd-open=%d/n",fd); return fd; }
int main(void) { int fd; int nread,i; char buff[]="Hello/n";
if((fd=open_port(fd,1))<0){ perror("open_port error"); return; } if((i=set_opt(fd,115200,8,'N',1))<0){ perror("set_opt error"); return; } printf("fd=%d/n",fd); // fd=3; nread=read(fd,buff,8); printf("nread=%d,%s/n",nread,buff); close(fd); |
linux串口应用开发
最新推荐文章于 2025-10-24 22:58:55 发布
linux串口应用开发
2009年10月20日 星期二 14:16




















 152
152

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








