异常
异常是指在程序的运行过程中所发生的不正常的事件,它会中断正在运行的程序
程序运行-异常-中断程序
异常处理
Java编程语言使用异常处理机制为程序提供了错误处理的能力
1、程序中预先设置好 对付异常的处理办法
2、程序运行
3、异常
4、对异常进行处理
5、处理完毕,程序继续运行
异常分类
Throwable:所以异常和错误的根类
Error:编译异常或会导致程序中断的错误
Exception:所以异常类的根类
RuntimeException:运行时异常,在程序的运行期间可能发生的异常
CheckedException:必须被处理的异常,在编译器会显式报错,只有try处理后才不会报错
常见异常
ArithmeticException:算术异常
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组越界异常
IndexOutOfBoundsException:下标越界异常
NullPointerException:空指针异常
InputMismatchException:输入不匹配异常
ClassCastException:类型转换异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
try{//可能出现异常的代码
int a =input.nextInt();
int b =input.nextInt();
System.out.println(a / b);
}catch(ArithmeticException e){//捕获异常
// e.printStackTrace();//打印堆栈信息
System.err.println(e.getMessage());//打印堆栈信息中一部分
// System.out.println("分母为0不合法");//自定义打印错误信息
}catch (InputMismatchException e){
e.printStackTrace();
// System.out.println("输入类型不匹配");
}
System.out.println("程序结束!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: -2
// int[] a={};
// System.out.println(a[-2]);
//NullPointerException 对象为空 用对象调用属性和方法
String s=null;
try {
//只有这种强行中断程序才会不运行finally
if (null==s) {
System.exit(-1);
}
String rst=s.toString();
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {//catch和finally 必须有一个
//无论系统是否异常或是捕获,finally块的代码都会运行
System.out.println("最终块");
}
System.out.println("...");
//IO Exception
//SQLException
}
IOException:输入输出异常
SQLException:数据库异常
ClassNotFoundException:类型未找到异常
异常处理结构
try-catch
try-finally
try-catch-finally
异常处理的三种情况
1、程序未发生异常,try块走完,不进入catch块,进入finally块,同时继续运行
2、程序发生异常并被捕获,try块走到发生异常的位置后,进入catch块,进入finally块,同时继续向下运行
3、程序发生异常但未被捕获,try块走到发生异常的位置后,进入finally块,同时不会继续往下运行
在catch中处理异常
1、自定义异常
System.err.println("");
2、打印出错堆栈信息
e.printStackTrace();
catch块捕获时会同时新开堆栈信心继续运行
所以会出现打印堆栈信息和其他打印信息顺序不正常
3、返回异常类型后的具体异常信息
e.getMessage();
有return的finally块走势
1、无返回值:catch中如果有return,会在finally快中运行完再运行catch中的return
public void test(){
int i=1;
try{
int a=1/0;
i++;//这个是不会执行的
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("进入catch");
i++;
return ;
}finally {
System.out.println("进入finally");
i++;
}
System.out.println(i);//这个是不会执行的
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo3 d= new Demo3();
d.test();
//System.out.println(d.testA());
}

2、有返回值:catch块的return会正常运行,finally快会运行完再回到catch的return处,但不会再次运行
public int testA(){
int i=1;
try{
int a=1/0;
i++;
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("进入catch");
i++;
return i;
}finally {
System.out.println("进入finally");
i++;
//return i;
}
return i;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo3 d= new Demo3();
// d.test();
System.out.println(d.testA());
}

如果finally块中也有return,则会覆盖catch的return
public int testA(){
int i=1;
try{
int a=1/0;
i++;
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("进入catch");
i++;
return i;
}finally {
System.out.println("进入finally");
i++;
return i;
}
//return i;
}

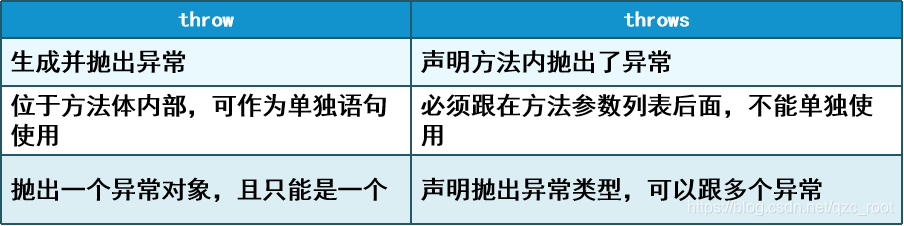
throw与throws
public class Demo5 {
private int age;
public void setAge(int age){
if (age>=1&&age<=100){
this.age=age;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("年龄必须在1-100之间");
}
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int age=input.nextInt();
Demo5 d= new Demo5();
try{
d.setAge(age);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
自定义异常
1、定义异常类,继承Throwable、Exception、RuntimeException
2、编写构造方法继承父类的实现
3、实例化自定义异常对象
4、使用throw抛出
public class WrongAgeException extends RuntimeException {
public WrongAgeException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
class User{
private int age;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age>100||age<0){
throw new WrongAgeException("当前年龄输入错误");
}
this.age = age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
User u=new User();
try {
u.setAge(180);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(u.getAge());
}
}




















 470
470

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








