一:异常的处理:抓抛处理
过程一:"抛":程序在正常执行的过程中,一旦出现异常,就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象
并将此对象抛出
一旦抛出对象以后,其后的代码不再执行
过程二:"抓":可以理解为异常的处理方式:
① try - catch - finally
② throws
二:try-catch-finally的使用
try{
//可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类型1 变量名1){
//处理异常的方式1
}catch(异常类型2 变量名2){
//处理异常的方式2
}
....
finally{
//一定会执行的代码
}举例:
public class ExceptionTest1 {
@Test
public void test1(){
String str = "123";
str = "abc";
int num = 0;
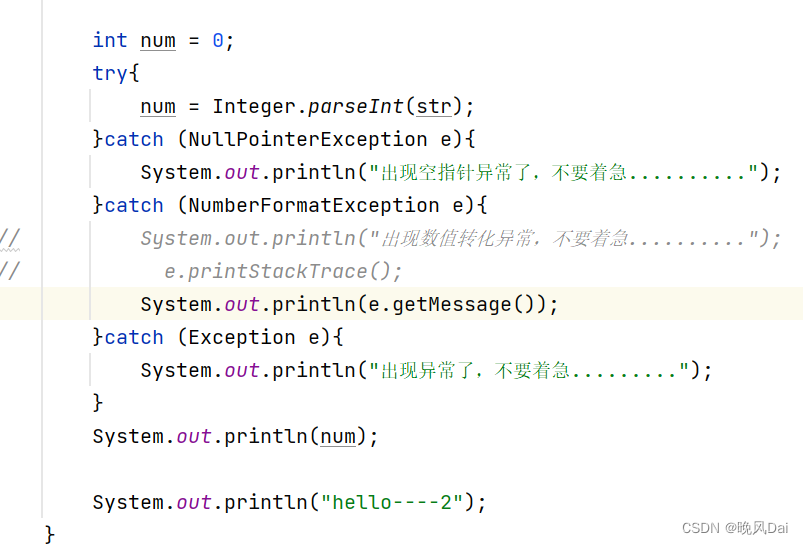
try{
num = Integer.parseInt(str);
}catch (NumberFormatException e){
System.out.println("出现数值转化异常,不要着急..........");
}catch (NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("出现空指针异常了,不要着急..........");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("出现异常了,不要着急.........");
}
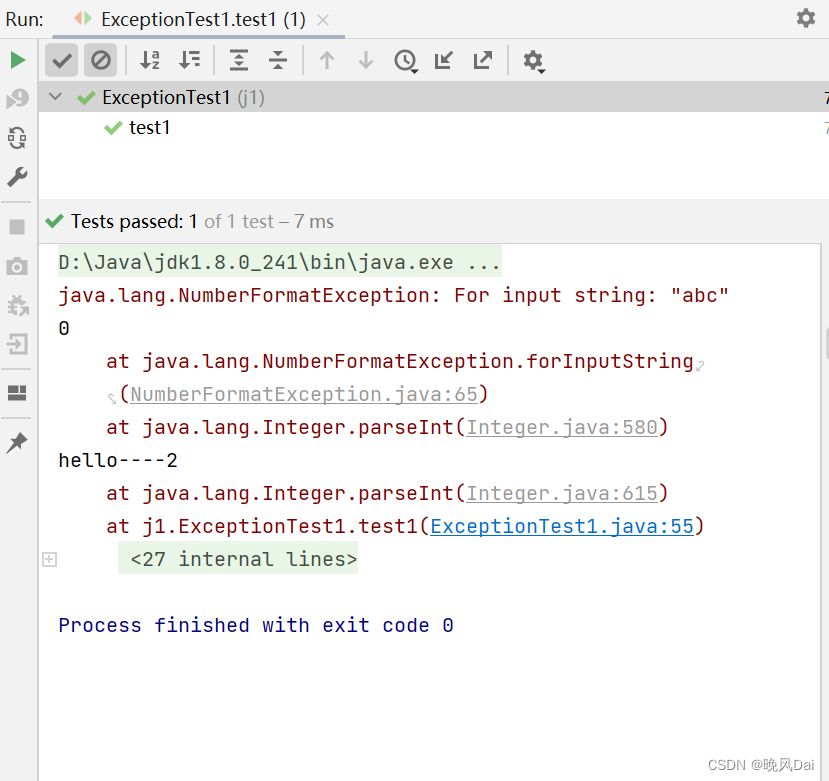
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println("hello----2");
}
}
运行结果如下:

还有两种常见的异常处理方式:
e.printStackTrace();
public class ExceptionTest1 {
@Test
public void test1(){
String str = "123";
str = "abc";
int num = 0;
try{
num = Integer.parseInt(str);
}catch (NumberFormatException e){
// System.out.println("出现数值转化异常,不要着急..........");
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("出现空指针异常了,不要着急..........");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("出现异常了,不要着急.........");
}
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println("hello----2");
}
}运行结果:
e.getMessage() ----->返回一个字符串
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
public class ExceptionTest1 {
@Test
public void test1(){
String str = "123";
str = "abc";
int num = 0;
try{
num = Integer.parseInt(str);
}catch (NumberFormatException e){
// System.out.println("出现数值转化异常,不要着急..........");
// e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}catch (NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("出现空指针异常了,不要着急..........");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("出现异常了,不要着急.........");
}
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println("hello----2");
}
}
运行结果:

注意:catch中的异常类型声明的顺序
举例:将上文代码的catch的异常顺序交换

综上所述 :catch中的异常类型如果没有子父类关系,则谁声明在上,谁声明在下无所谓catch中的异常类型如果满足子父类关系,则要求子类一定声明在父类的上面,否则报错
=================================我是分割线=============================================
总结:
1.finally是可选的
2.使用try将可能出现异常代码包装起来,在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会生成一个异常类的对象根据此对象的类型,去catch中进行匹配
3.一旦try中的异常对象匹配到某一个catch时,就会进入catch中进行异常处理一旦处理完成,就跳出当前的try—catch结构(在没有写finally的情况)继续执行其后的代码
4.catch中的异常类型如果没有子父类关系,则谁声明在上,谁声明在下无所谓catch中的异常类型如果满足子父类关系,则要求子类一定声明在父类的上面,否则报错
5.常用的异常对象处理的方式:
① String getMessage()
② printStackTrace()
6.在try结构中声明的变量,再出了try结构以后,就不能别调用了
体会:使用try-catch-finally处理编译时异常,使得程序在编译就不在报错,但是运行时任可能报错
先当与我们使用try-catch-finally将一个编译时可能出现异常,延迟到运行时出现
感谢观看!!!




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








