一、简单工厂模式
定义:简单工厂模式是一种创建型模式,也被称为静态工厂方法模式,它属于类创建型模式。在简单工厂模式中,一个工厂对象决定创建
出哪一种产品类的实例。
优点:
-
只需要传入正确的参数,就可以获取需要的对象,无需知道创建细节。
-
工厂类中有必要的判断逻辑,可以决定根据当前的参数创建对应的产品实例,客户端可以免除直接创建产品对象的责任。
-
通过该模式,实现了对创建实例和使用实例的责任分割。
-
提供专门的工厂类用于创建对象,客户端无需知道所创建的产品类的类名,只需要知道对应产品类的参数即可创建对象实例。
缺点:
-
工厂类职责过重,当有新的产品类型时,必须要修改工厂的创建逻辑,对系统的维护和扩展非常不利。
-
违背了高内聚的责任分配原则,工厂集中了全部的创建逻辑,当工厂出现问题系统会崩溃。
适用场景:
-
创建对象少,工厂类负责创建的对象比较少。
-
不关心创建过程,客户端只知道传入工厂类的参数。
类图:

代码:
public interface TV {
void play();
}
public class HaierTV implements TV{
public void play(){
System.out.println("海尔电视ing");
}
}
public class MiTV implements TV{
public void play(){
System.out.println("小米电视ing");
}
}
public class TVFactory {
public static TV produceTV(String brand){
if(brand.equals("Haier")){
System.out.println("生产海尔电视机");
return new HaierTV();
}
else if(brand.equals("Mi")){
System.out.println("生产小米电视机");
return new MiTV();
}
else{
System.out.println("暂时不能生产该品牌的电视");
return null;
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv=TVFactory.produceTV("Haier");
tv.play();
}
}
二、工厂方法模式
定义:工厂方法模式是一种设计模式,它定义了一个创建对象的接口,让实现这个接口的子类决定实例化哪个类。工厂方法将类的实例化
推迟到子类中进行。
优点:
-
用户只需要知道具体工厂的名称就可得到所要的产品,无须知道产品的具体创建过程。
-
在系统增加新的产品时只需要添加具体产品类和对应的具体工厂类,无须对原工厂进行任何修改,满足开闭原则。
-
屏蔽产品的具体实现,调用者只关心产品的接口。
缺点:
每增加一个产品就要增加一个具体产品类和一个对应的具体工厂类,这增加了系统的复杂度。
适用场景:
-
当一个类不知道它所需要的对象的类时。
-
当一个类希望通过其子类来指定创建对象时。
-
将创建对象的任务委托给多个工厂子类中的某一个,客户端在使用时可以无须关心是哪一个工厂子类创建产品子类,需要时再动态指
定,可将具体工厂类的类名存储在配置文件或数据库中。
类图:
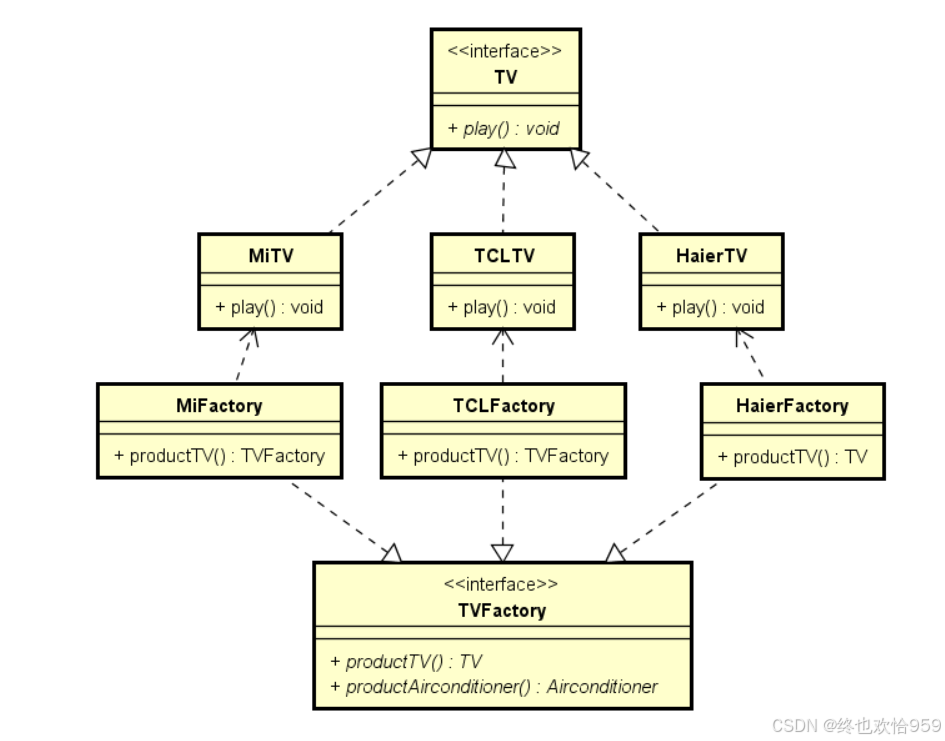
代码:
public interface TV {
void play();
}
public interface TVFactory {
TV produceTV();
}
public class HaierTV implements TV {
public void play(){
System.out.println("海尔电视播放中。。。");
}
}
public class TclTV implements TV{
public void play(){
System.out.println("TCL电视播放中。。。");
}
}
public class MiTV implements TV {
public void play(){
System.out.println("小米电视播放中。。。");
}
}
class HaierTVFactory implements TVFactory{
public TV produceTV(){
System.out.println("海尔工厂生产海尔电视");
return new HaierTV();
}
}
class TclTVFactory implements TVFactory{
public TV produceTV(){
System.out.println("TCL工厂生产TCL电视");
return new TclTV();
}
}
public class MiTVFactory implements TVFactory{
public TV produceTV(){
System.out.println("小米工厂生产小米电视");
return new MiTV();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv;
TVFactory haierfactory=new HaierTVFactory();
tv=haierfactory.produceTV();
tv.play();
TVFactory tclfactory=new TclTVFactory();
tv=tclfactory.produceTV();
tv.play();
}
}三、抽象工厂模式
定义:抽象工厂模式是一种创建型设计模式,它为创建一组相关或者相互依赖的对象提供了一个接口,而不需要指定他们的具体类。
优点:
-
良好的封装性和低耦合:抽象工厂模式将对象的创建和使用封装在工厂类中,使得客户端可以更加专注于其自身的业务逻辑,而无需
关心对象的创建过程,降低了系统各部分之间的耦合度。
-
产品族内具有约束性,且为非公开状态:抽象工厂模式中,工厂类负责创建具有相同约束的对象族,这样可以确保对象族的正确使
用。同时,由于工厂类的实现是私有的,外部无法直接访问,从而保证了对象族的安全性。
缺点:
-
工厂类职责过重,当有新的产品类型时,必须要修改工厂的创建逻辑,对系统的维护和扩展非常不利。
-
违背了高内聚的责任分配原则,工厂集中了全部的创建逻辑,当工厂出现问题系统会崩溃。
适用场景:
-
一个系统需要使用多个产品族时:如果一个系统需要使用多个产品族,例如,同时使用多个数据库实现或同时使用多个第三方库,那
么可以使用抽象工厂模式来提供一个统一的接口,用于获取这些产品族的对象。
-
产品的依赖关系需要封装时:如果一个系统中,不同产品族之间的依赖关系需要封装起来,不希望被外部直接访问,那么可以使用抽
象工厂模式来提供一个统一的接口,用于获取这些产品族的对象。
类图:

代码:
public interface TV {
void play();
}
public class TclTV implements TV {
public void play(){
System.out.println("TCL电视播放中。。。");
}
}
public class HaierTV implements TV {
public void play(){
System.out.println("海尔电视播放中。。。");
}
}
public class MiTV implements TV {
public void play(){
System.out.println("小米电视播放中。。。");
}
}
public interface Airconditioner {
void changeTemperature();
}
public class HaierAirconditioner implements Airconditioner {
public void changeTemperature(){
System.out.println("海尔空调调节温度。。。");
}
}
public class MiAirconditioner implements Airconditioner {
public void changeTemperature(){
System.out.println("小米空调调节温度。。。");
}
}
public class TCLAirconditioner implements Airconditioner {
public void changeTemperature(){
System.out.println("TCL空调调节温度。。。");
}
}
public interface ProductFactory {
TV produceTV();
Airconditioner produceAirconditioner();
}
class HaierFactory implements ProductFactory {
public TV produceTV(){
System.out.println("海尔工厂生产海尔电视");
return new HaierTV();
}
public Airconditioner produceAirconditioner(){
System.out.println("海尔工厂生产海尔空调");
return new HaierAirconditioner();
}
}
public class MiFactory implements ProductFactory {
public TV produceTV(){
System.out.println("小米工厂生产小米电视");
return new MiTV();
}
public Airconditioner produceAirconditioner(){
System.out.println("小米工厂生产小米电视");
return new MiAirconditioner();
}
}
public class TclFactory implements ProductFactory {
public TV produceTV(){
System.out.println("TCL工厂生产TCL电视");
return new TclTV();
}
public Airconditioner produceAirconditioner(){
System.out.println("TCL工厂生产TCL空调");
return new TCLAirconditioner();
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv;
Airconditioner ac;
ProductFactory haierFactory=new HaierFactory();
tv=haierFactory.produceTV();
tv.play();
ac=haierFactory.produceAirconditioner();
ac.changeTemperature();
}
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








