一、目的
文件的存储与导出java对象,文件格式包括xml、txt、xlxs三种文件格式
二、准备
Student 类
/**
* 学生的信息(学号、姓名、电话、邮箱信息)
*
* @ClassName Student
* @Description TODO
* @Author Mr_X
* @Date 2022/5/6 8:07
* @Version 1.0
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlRootElement(name = "Student")
@XmlType(propOrder = {
"sno",
"name",
"phone",
"email",
})
public class Student implements Serializable, Comparable<Student> {
private String sno;
private String name;
private String phone;
private String email;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String sno, String name, String phone, String email) {
this.sno = sno;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.email = email;
}
public String getSno() {
return sno;
}
public void setSno(String sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("%-10s%-15s%-25s%-15s",sno,name,phone,email);
}
/**
* 学号是判断对象是否相等的唯一依据,学号是主键,equal方法不应该与compareTo方法产生歧义
*
* @description:
* @param: o
* @return: boolean
* @author MR_X
* @date: 17:13 2022/5/6
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return sno != null ? sno.equals(student.sno) : student.sno == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = sno != null ? sno.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + (name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (phone != null ? phone.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (email != null ? email.hashCode() : 0);
return result;
}
/**
* 重写比较方法,便于排序,按照学号
*
* @description:
* @param: o
* @return: int
* @author
* @date: 17:16 2022/5/6
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return sno.compareTo(o.sno);
}
}
School类
/**
* @ClassName School
* @Description TODO
* @Author Mr_X
* @Date 2022/5/6 8:49
* @Version 1.0
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlRootElement(name = "School")
@XmlType(propOrder = {"students"})
public class School implements Serializable {
private Set<Student> students = new TreeSet<>();
public School() {
}
public School(Set<Student> students) {
this.students = students;
}
public Set<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
public void setStudents(Set<Student> students) {
this.students = students;
}
}
三、实现
3.1、 java对象与xml文件
详情请参考–>:玩转Java对象和XML相互转换
工具类
public class XmlStorageUtils {
/**
* 将对象存储到xml文件之中,形参传入路径s
*
* @description:
* @param: obj path
* @return: void
* @author
* @date: 8:17 2022/5/6
*/
public static void convertToXml(Object obj, String path) {
try {
// 利用jdk中自带的转换类实现
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(obj.getClass());
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
// 格式化xml输出的格式
marshaller.setProperty(Marshaller.JAXB_FORMATTED_OUTPUT,
Boolean.TRUE);
// 将对象转换成输出流形式的xml
// 创建输出流
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(path);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
marshaller.marshal(obj, fw);
} catch (JAXBException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 将file类型的xml转换成对象
*
* @description:
* @param: clazz xmlPath
* @return: java.lang.Object
* @author
* @date: 8:20 2022/5/6
*/
public static Object convertXmlFileToObject(Class clazz, String xmlPath) {
Object xmlObject = null;
try {
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(clazz);
Unmarshaller unmarshaller = context.createUnmarshaller();
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(xmlPath);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
xmlObject = unmarshaller.unmarshal(fr);
} catch (JAXBException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return xmlObject;
}
}
测试存进xml类
public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Student> set = new TreeSet<Student>();
Student student = new Student("001", "sandy", "1238127824", "sandy@163.com");
Student student1 = new Student("002", "tom", "1238113855", "tom@qq.com");
Student student2 = new Student("003", "amy", "1238437827", "amy@qq.com");
Student student3 = new Student("004", "jack", "1228127824", "jack@qq.com");
Student student4 = new Student("005", "eric", "1238127567", "eric@qq.com");
Student student5 = new Student("006", "hello", "1238127567", "hello@qq.com");
Student student6 = new Student("007", "who", "1238127567", "who@qq.com");
Student student7 = new Student("008", "are", "1238345567", "are@qq.com");
Student student8 = new Student("009", "you", "1238127567", "you@qq.com");
Student student9 = new Student("010", "there", "1238127447", "there@qq.com");
Student studentA = new Student("011", "are", "1238127227", "are@qq.com");
Student studentB = new Student("012", "fried", "1038127567", "fried@qq.com");
Student studentC = new Student("013", "mike", "1238155567", "mike@qq.com");
Student studentD = new Student("014", "then", "1231234567", "then@qq.com");
Student studentE = new Student("015", "louse", "1245237567", "louse@qq.com");
Student studentF = new Student("016", "jerry", "1333127567", "jerry@qq.com");
Student studentG = new Student("017", "petter", "1998127567", "petter@qq.com");
Student studentH = new Student("018", "grey", "1668127567", "grey@qq.com");
Student studentI = new Student("019", "yell", "1238127999", "yell@qq.com");
set.add(student);
set.add(student1);
set.add(student2);
set.add(student3);
set.add(student4);
set.add(student5);
set.add(student6);
set.add(student7);
set.add(student8);
set.add(student9);
set.add(studentA);
set.add(studentB);
set.add(studentC);
set.add(studentD);
set.add(studentE);
set.add(studentF);
set.add(studentG);
set.add(studentH);
set.add(studentI);
School school = new School(set);
//如果希望存进src文件夹下,可以代码中这样写,当然你也可以直接输入 String path = 指定的绝对路径;
String path = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("question_1/resource").getPath() + "/students.xml";
XmlStorageUtils.convertToXml(school, path);
}
}
写入文件展示
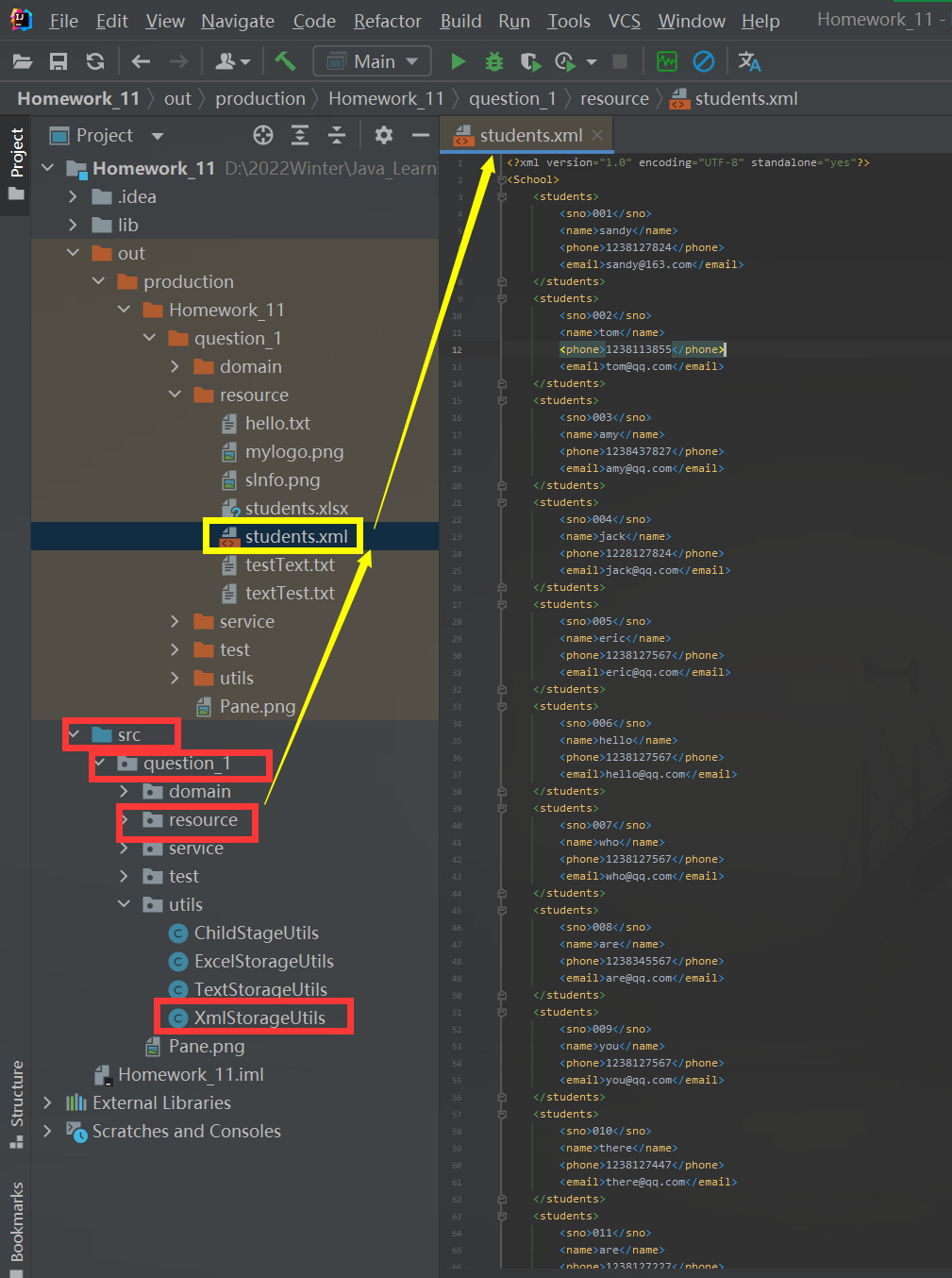
测试读取文件类
public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String path = 写绝对路径也行
String path = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("question_1/resource").getPath() + "/students.xml";
//强转一下
School school = (School) XmlStorageUtils.convertXmlFileToObject(School.class, path);
//lambda表达式
school.getStudents().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-CNABVht0-1652107247454)(https://wx1.sinaimg.cn/mw2000/008rcJvVly1h22gx5fp3wj31fy0sy1ay.jpg)]
3.2、java对象与xlxs即Excel文件
参考视频学习:
Java教程使用POI读取excel文档_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
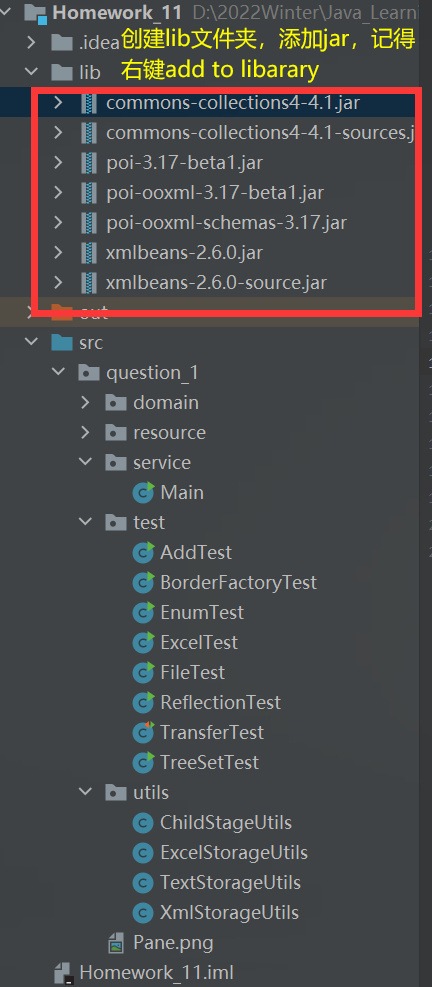
3.2.1、导入jar包
-
(推荐)百度网盘
poi的jar包链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1qKAzA9xGvJP6HI-YoKkA4A
提取码:26kj解压得到的jar包添加到库,省得去配置Maven。
工具类
public class ExcelStorageUtils {
/**
* 将程序数据存入磁盘中的excel文件中
*
* @description:
* @param: list tClass path
* @return: void
* @author
* @date: 22:36 2022/5/6
*/
public static <T> boolean exportExcel(List<T> list, Class<T> tClass, String path) throws Exception {
if (list == null || list.size() == 0) {
return false;
}
Field[] declaredFields = tClass.getDeclaredFields();
int columNum = declaredFields.length;
int rowLastIndex = list.size();
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet(tClass.getSimpleName());
//写入文件的关键代码
for (int i = 0; i <= rowLastIndex; i++) {
XSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(i);
//先给第一行附上属性名称
if (i == 0) {
for (int j = 0; j < columNum; j++) {
row.createCell(j).setCellValue(declaredFields[j].getName());
}
continue;
}
T t = list.get(i - 1);
for (int j = 0; j < columNum; j++) {
Field declaredField = declaredFields[j];
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
String value = (String) declaredField.get(t);
row.createCell(j).setCellValue(value);
}
}
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(path);
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.flush();
workbook.close();
return true;
}
/**
* 从excel文件中读取数据实例化对象,并返回由实例化对象生成的List集合
* 需要注意的是,要确保Excel文件的第一行(rowIndex=0 处的属性数据应该与要实例化的Class属性一致,否则无法通过反射创建对象)
*
* @description:
* @param: tClass path
* @return: java.util.List<T>
* @author
* @date: 0:20 2022/5/7
*/
public static <T> List<T> importExcel(Class<T> testClass, String path) throws Exception {
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
//获得工作本
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(path);
//获得表,默认是第一张表
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//获取sheet的行数,是以0开始的
int lastRowIndex = sheet.getLastRowNum();
//获取对应的属性及属性的个数
XSSFRow fieldRow = sheet.getRow(0);
short cellCount = fieldRow.getLastCellNum();
for (int i = 1; i <= lastRowIndex; i++) {
T t = testClass.newInstance();
XSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cellCount; j++) {
String filedName = fieldRow.getCell(j).getStringCellValue();
Field declaredField = testClass.getDeclaredField(filedName);
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
//根据反射赋值
String value = row.getCell(j).getStringCellValue();
declaredField.set(t, value);
}
list.add(t);
}
return list;
}
}
测试类
public class ExcelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TreeSet<Student> set = new TreeSet<Student>();
// Student student = new Student("123", "Mr_X", "123456", "qweq@163.com");
// Student student1 = new Student("456", "XXR", "12e456", "xxr@qq.com");
// Student student2 = new Student("789", "SLL", "12389123", "sll@qq.com");
// Student student3 = new Student("007", "NPY", "12389123", "sll@qq.com");
//
// boolean add = set.add(student);
// boolean add1 = set.add(student1);
// boolean add2 = set.add(student2);
// boolean add3 = set.add(student3);
//
// ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
// students.addAll(set);
String path = "D:\\TempResource\\students.xlsx";
// try {
// ExcelStorageUtils.exportExcel(students,Student.class,path);
// } catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
try {
List<Student> students = ExcelStorageUtils.importExcel(Student.class, path);
students.forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
效果
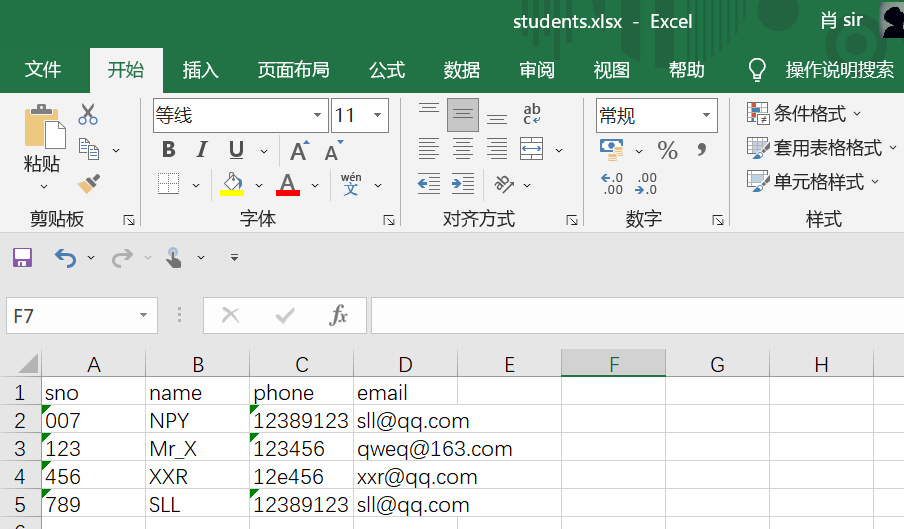
3.3、java与txt文件
TextStorageUtils工具类
public class TextStorageUtils {
/**
* 将list对象存进文本文件中
*
* @description:
* @param: list testClass path
* @return: void
* @author
* @date: 19:25 2022/5/9
*/
public static <T> boolean exportText(List<T> list, Class<T> testClass, String path) throws Exception {
if (list == null || list.size() == 0 || testClass == null || path == null || path.length() == 0) {
return false;
}
Field[] declaredFields = testClass.getDeclaredFields();
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(path);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) {
declaredFields[i].setAccessible(true);
String filedName = declaredFields[i].getName();
stringBuffer.append(filedName + "\t");
}
stringBuffer.append("\n");
for (T t : list) {
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) {
String filed = (String) declaredFields[i].get(t);
//这是细节,如果该属性值为空,则改为null
filed = filed == null ? "null" : filed;
stringBuffer.append(filed).append("\t");
}
stringBuffer.append("\n");
}
bw.write(stringBuffer.toString());
bw.close();
return true;
}
/**
将数据对象集合写入文本文件中
*/
public static <T> List<T> importText(Class<T> testClass, String path) throws Exception {
if (testClass == null || path == null || path.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
//作为返回的list
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
//创造节点流和缓冲流
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(path);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
Field[] declaredFields = testClass.getDeclaredFields();
int length = declaredFields.length;
String line;
int lineIndex = 0;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] infos = line.split("[\t]+");
//是第一行,则是属性信息行,更新属性数组,如果不是第一行则利用反射将构造对象
if (lineIndex == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.println(infos.length);
declaredFields[i] = testClass.getDeclaredField(infos[i]);
declaredFields[i].setAccessible(true);
}
} else {
T t = testClass.newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
declaredFields[i].set(t, infos[i]);
}
list.add(t);
}
//取出line
lineIndex++;
}
br.close();
return list;
}
}
测试类
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("question_1/resource").getPath()+"/textTest.txt";
// TreeSet<Student> set = new TreeSet<Student>();
// Student student = new Student("001", "sandy", "1238127824", "sandy@163.com");
// Student student1 = new Student("002", "tom", "1238113855", "tom@qq.com");
// Student student2 = new Student("003", "amy", "1238437827", "amy@qq.com");
// Student student3 = new Student("004", "jack", "1228127824", "jack@qq.com");
// Student student4 = new Student("005", "eric", "1238127567", "eric@qq.com");
// Student student5 = new Student("006", "hello", "1238127567", "hello@qq.com");
// Student student6 = new Student("007", "who", "1238127567", "who@qq.com");
// Student student7 = new Student("008", "are", "1238345567", "are@qq.com");
// Student student8 = new Student("009", "you", "1238127567", "you@qq.com");
// Student student9 = new Student("010", "there", "1238127447", "there@qq.com");
// Student studentA = new Student("011", "are", "1238127227", "are@qq.com");
// Student studentB = new Student("012", "fried", "1038127567", "fried@qq.com");
// Student studentC = new Student("013", "mike", "1238155567", "mike@qq.com");
// Student studentD = new Student("014", "then", "1231234567", "then@qq.com");
// Student studentE = new Student("015", "louse", "1245237567", "louse@qq.com");
// Student studentF = new Student("016", "jerry", "1333127567", "jerry@qq.com");
// Student studentG = new Student("017", "petter", "1998127567", "petter@qq.com");
// Student studentH = new Student("018", "grey", "1668127567", "grey@qq.com");
// Student studentI = new Student("019", "yell", "1238127999", "yell@qq.com");
//
// set.add(student);
// set.add(student1);
// set.add(student2);
// set.add(student3);
// set.add(student4);
// set.add(student5);
// set.add(student6);
// set.add(student7);
// set.add(student8);
// set.add(student9);
// set.add(studentA);
// set.add(studentB);
// set.add(studentC);
// set.add(studentD);
// set.add(studentE);
// set.add(studentF);
// set.add(studentG);
// set.add(studentH);
// set.add(studentI);
//
// ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>(set);
// try {
// boolean isDone = TextStorageUtils.exportText(list, Student.class, path);
// System.out.println(isDone);
// System.out.println(path);
// } catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
try {
List<Student> students = TextStorageUtils.importText(Student.class, path);
students.forEach(System.out::println);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
效果展示
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-SvkzBjG2-1652107247458)(https://wx2.sinaimg.cn/mw2000/008rcJvVly1h22hnzr7r3j316p0q07m0.jpg)]
四、综合可视化实现(JavaFX)
-
设计图形用户界面,用顺序存取文件方式分别完成新增、删除、修改、查询、显示功能:
新增:让用户能输入学生的信息(学号、姓名、电话、邮箱信息),检查无误后将数据存入文本文件;
删除:删除正在显示的学生信息;
修改:修改正在显示的一条学生信息,修改后可保存至文本文件;
查询:让用户输入姓名,一条条显示查询到的学生信息(借助“下一条”、“上一条”按钮查看下一条和上一条数据)。
显示:显示文件中存储的所有学生信息(借助“下一条”、“上一条”按钮查看下一条和上一条数据)。
-
修改1中程序,改用随机存取文件存取。
-
修改1中程序,将信息存储在xml文件中(其它功能不变)
-
修改1中程序,将信息存储在Excel文件中

提供工程的压缩包,有兴趣的可以看一下:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1vHDh7uizEejwCrrspelC0w
提取码:1g7u
运行效果:
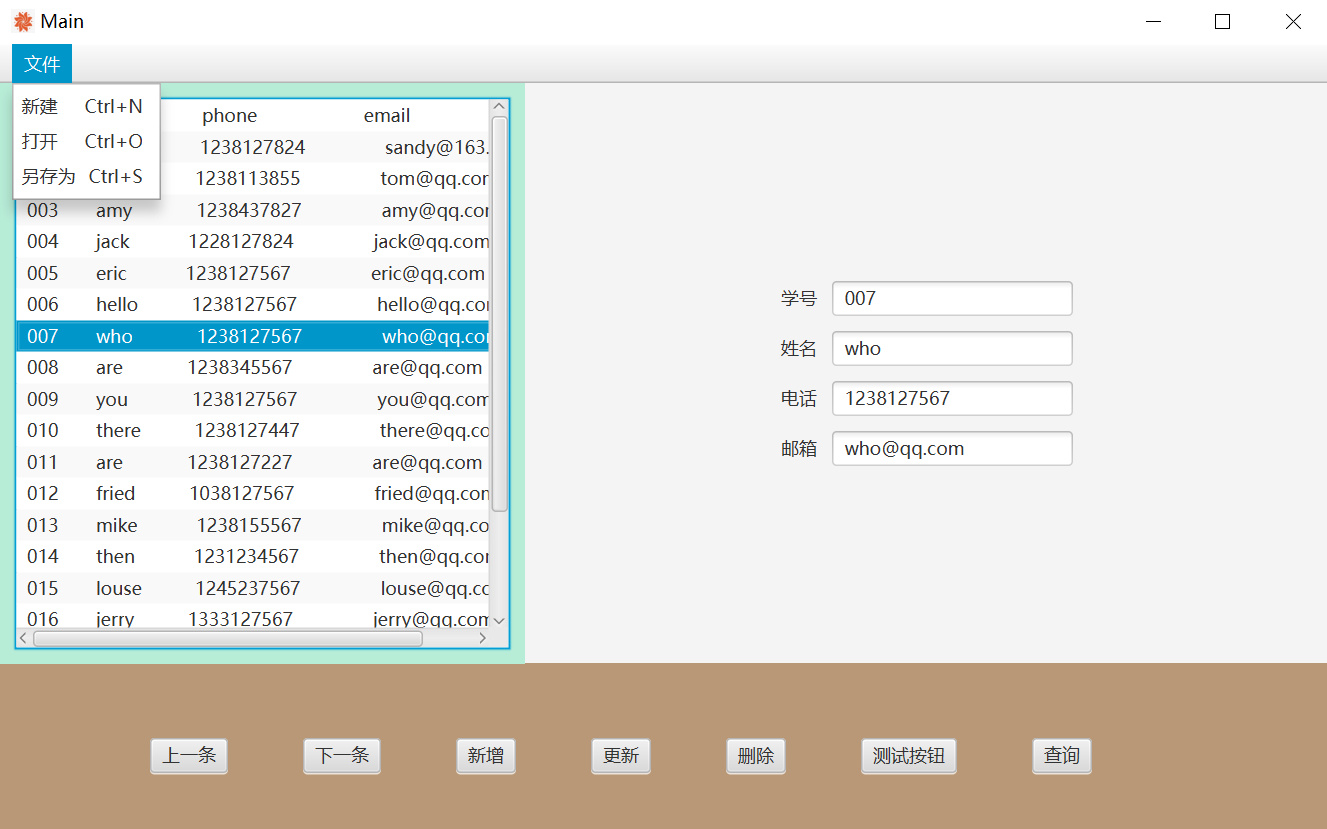
环境:IDEA
JDK版本:jdk8
好像jdk17后javafx得另外配置哈。
五、说明
- xml的解析与读取还可以采用dom4j来解析,请参见 dom4j解析xml_JavaWeb_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
- 所提供的工具类包括读入和导出,文件格式比较固定,要读取的数据文件格式请遵循工具类导出文件的相应格式,不然会发生错误。
- 这些工具类是为了应付学校作业写的,笔者能力水平有限,如有需要,请读者自行优化代码,希望看官不吝赐教,欢迎点赞~








 本文介绍了如何使用Java将Student和School类的对象存储为XML、Excel(XLSX)和TXT文件,包括了JAXB和POI库的应用,以及如何通过JavaFX实现基本的文件操作界面。
本文介绍了如何使用Java将Student和School类的对象存储为XML、Excel(XLSX)和TXT文件,包括了JAXB和POI库的应用,以及如何通过JavaFX实现基本的文件操作界面。
















 131
131

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








