思维题
当你认为这道题很难的时候你就输了,对于思维题我们可以考虑从数据下手,或者缩减情况,从特殊再到一般
D. Harder Problem
题目:


思路:
我们可以知道,如果任意两个数字数字出现次数相同,那么肯定可以当作这个序列的模,也就是说对于一个数列1~n,其中任意一个数字都可以当作这个序列的模,因为他们都只出现过一次,所以我们可以构造一个排列,由于数组长度刚好是n,所以满足每个元素都可出现过一次
于是可以根据bi来构造了,我们可以按bi中数字出现的顺序把数字都放在前面,没出现过的数字直接排在后面即可,详见代码
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl
#define no cout << "NO" << endl
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a;
set<int> has;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
if (!has.count(x))
{
a.push_back(x);
}
has.insert(x);
}
set<int> dnthas;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!has.count(i))
dnthas.insert(i);
}
for (auto x : a)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
for (auto d : dnthas)
{
cout << d << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
// cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1971/D
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1971/D
D. Binary Cut
题目:


思路:
题目要求我们将字符串最后排成000...01111..11的形式,那么显然我们肯定要将所有连续段落拆开,但是我们观察题目给的样例发现,它只切了3份,这其实也是一个提示,我们可以将一个01有拼接的串合成一整块,这样就能少切一刀,同时有且仅有少切一次,因为01 和 01是无法直接拼起来的
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl
#define no cout << "NO" << endl
void solve()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
int tag = 0;
int cnt = 1;
char now = s[0];
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++)
{
if (s[i] != now)
{
now = s[i];
cnt++;
}
if (s[i] == '1' && s[i-1] == '0')
{
tag = 1;
}
}
cout << cnt - tag << endl;
}
int main()
{
// cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}C. Assembly via Remainders
题目:


思路:
我们可以观察一下数据范围,居然只有500!那我们就可以想到可以用一个很大的数来构造这个数列了,对于a1,我们可以选501,这样即使x是500,我们的余数也是500(500 / 501 = 0 ... 500)
所以后面的同理,我们就可以使a2 = a1 + x1,总之每次都是前一个数+当前的X,因为除数大于大于被除数,所以最后肯定的余数肯定是被除数
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl
#define no cout << "NO" << endl
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
n--;
int a = 501;
cout << a << ' ';
while (n--)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
a += x;
cout << a << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
int main()
{
// cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. Olya and Game with Arrays
题目:



思路:
对于这道题,我们肯定可以先想到对每队排好序,那观察题目给的条件,我们可以知道其实最后的答案取决与每个数组的最小值和次小值,那么贪心的想,我们肯定全选次小值是最好的,但是由于每次都要将最小值移走,所以我们肯定要用一个数组来装其他数组的最小值,很显然,我们要装的数组就是次小值最小的数组上,这样就能牺牲最小而得到最大
注意,当我们把其他数组的最小值移走后,那个次小值最小的数组的最小值可能会发生变化,所以还得维护所有数组最小值中的最小值
于是答案就是 次小值的和 + 最小值的最小值 - 次小值的最小值
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl
#define no cout << "NO" << endl
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<int>> a(n);
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int m;
cin >> m;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
int x; cin >> x;
a[i].push_back(x);
}
sort(a[i].begin(), a[i].end());
ans += a[i][1];
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), [](vector<int> a, vector<int> b) {
return a[0] < b[0]; });
int minf = 1e9;
int ming = 1e9;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
minf = min(minf, a[i][0]);
ming = min(ming, a[i][1]);
}
cout << ans + minf - ming << endl;
}
int main()
{
// cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}C. Yet Another Permutation Problem
题目:


思路:
其实我们可以观察发现,最后的答案一定是[n/2],为什么呢?
对于n,我们只需要找到n/2,这样就能有gcd(n,n/2) = n/2这个答案了
同理对于其他 n-1,n-2...,我们都能找到对于的数字,直到1,同时可以确保每个gcd都不相同,因为每次gcd都是n/2,而每次取得n都不一样,所以这个方法肯定是最优得
所以我们每次都可以用x去寻找2*x,同时每次找不到后都让x+2,为什么呢?
因为偶数都被x=2找过了,所以接下来我们只需要找奇数就行了
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl
#define no cout << "NO" << endl
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
int cur = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i += 2) {
for (int j = i; j <= n; j *= 2) {
a[cur++] = j;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << '\n';
}
int main()
{
//cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. Split Sort
题目:


思路:
这是一个比较考直觉得思维题,对于任意一个x,如果x+1在x前面,那我们肯定只能用x+1来使x到x+1前,所以我们只需要找有多少个这种情况即可
官方题解也没证明,我只能说观察力惊人(
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl
#define no cout << "NO" << endl
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
int t, n, a[maxn], ans, x[maxn];
void solve()
{
ans = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
x[a[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
ans += (x[i] > x[i + 1]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
// cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}C. MEX Repetition
题目:

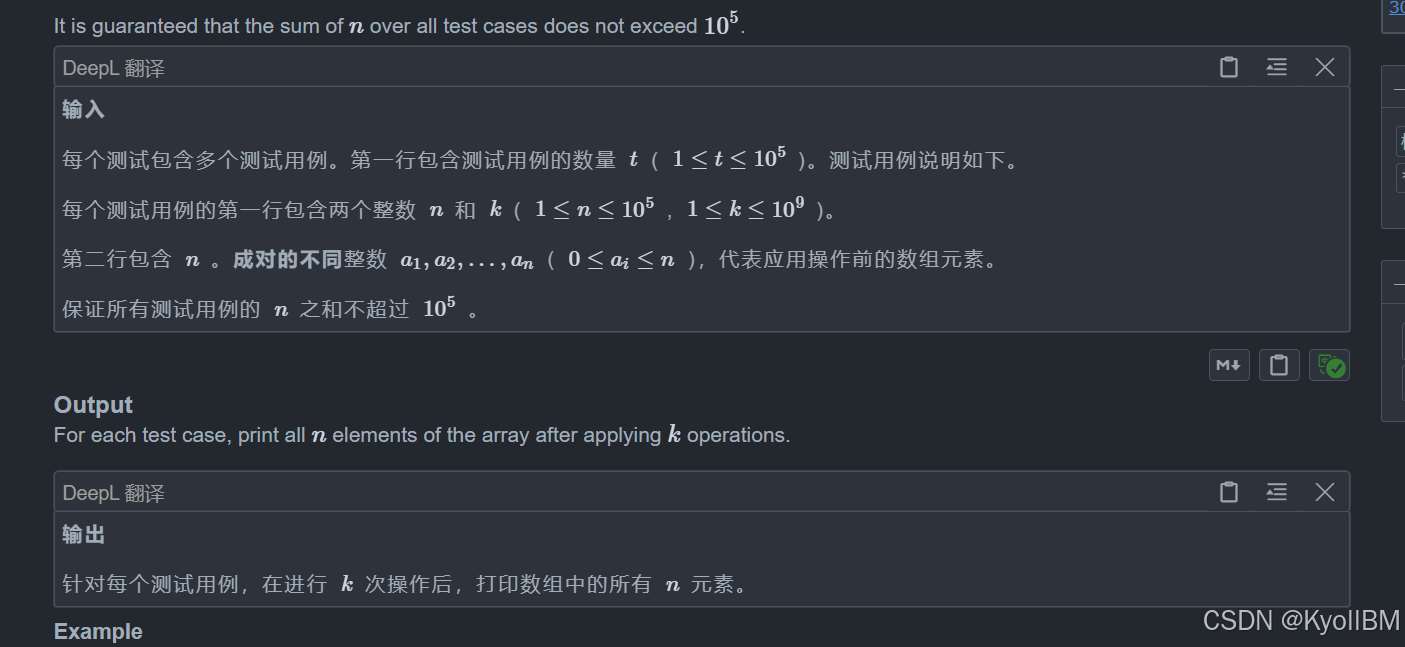
思路:
观察题目给的数据,k足足有1e9,那么就算模拟来做,最后肯定也是超时,所以我们就要来找规律,对于这种大数据得题目,我们第一眼肯定要往循环情况上找
观察样例 1 2 3 4 5,我们接下来把每次操作一开始的MEX写下来
1. 1 2 3 4 5 | 0
2. 0 1 2 3 4 | 5
3. 5 0 1 2 3 | 4
4. 4 5 0 1 2 | 3
5. 3 4 5 0 1 | 2
6. 2 3 4 5 0 | 1
7. 1 2 3 4 5 | 0
这时我们发现进入了循环,且循环的周期T = n+1
同时我们再观察一下,我们可以发现每次都是在改变循环的起点和终点的位置
比如2.就是将起点从0开始终点以4结束,那我们就只需要计算这个区间即可
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl
#define no cout << "NO" << endl
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n;
int a[N];
int cnt[N];
void init()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
cnt[i] = 0;
}
}
void solve()
{
int k;
cin >> n >> k;
init();
int mex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
cnt[a[i]]++;//记录每个数字是否出现
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!cnt[i])
{
mex = i;//找到当前的MEX
break;
}
}
a[n + 1] = mex;
k = k % (n + 1);
for (int i = n + 1 - k + 1; i <= n + 1; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n - k; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
// cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}






















 294
294

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








