第一题:带分数
问题描述
100 可以表示为带分数的形式:100 = 3 + 69258 / 714。
还可以表示为:100 = 82 + 3546 / 197。
注意特征:带分数中,数字1~9分别出现且只出现一次(不包含0)。
类似这样的带分数,100 有 11 种表示法。
输入格式
从标准输入读入一个正整数N (N<1000*1000)
输出格式
程序输出该数字用数码1~9不重复不遗漏地组成带分数表示的全部种数。
注意:不要求输出每个表示,只统计有多少表示法!
样例输入1
100
样例输出1
11
样例输入2
105
样例输出2
6
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int parse(const char* arr, int pos, int len) {
int ans = 0;
int t = 1;
for (int i = pos + len - 1; i >= pos; --i) {
ans += (arr[i] - '0') * t;
t *= 10;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
int n=0, ans = 0;
cin >> n;
string s = "123456789";
do {
const char* str = s.c_str();//c_str会返回一个const
for (int i = 1; i <= 7; ++i) {//+号前的串长度
int inta = parse(str, 0, i);
if (inta >= n) break;
for (int j = i; j <= 9 - i - 1; ++j) {//+/两个符号之间的串长度
int intb = parse(str, i, j);
int intc = parse(str, i + j, 9 - i - j);
if (intb % intc == 0 && inta + intb / intc == n) ans++;
}
}
} while (next_permutation(s.begin(), s.end()));
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
第二题:李白打酒
题目描述
话说大诗人李白,一生好饮。幸好他从不开车。
一天,他提着酒壶,从家里出来,酒壶中有酒2斗。他边走边唱:
无事街上走,提壶去打酒。
逢店加一倍,遇花喝一斗。
这一路上,他一共遇到店5次,遇到花10次,已知最后一次遇到的是花,他正好把酒喝光了。
请你计算李白遇到店和花的次序,可以把遇店记为a,遇花记为b。则:babaabbabbabbbb 就是合理的次序。像这样的答案一共有多少呢?请你计算出所有可能方案的个数(包含题目给出的)。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int time = 0;
int arr[15] = {-1,-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,-1, -1, 2 , 2 , 2 , 2, 2 };
do {
int n = 2;
for (int i = 0;i < 15;i++)
{
if (arr[i] == -1) {
n += arr[i];
}
else {
n *= arr[i];
}
}
if (arr[14] == -1 && n == 0)
time += 1;
} while (next_permutation(arr, arr + 15)); //全排列
cout << time<< endl;
return 0;
}
第三题:第39级台阶
题目描述:
小明刚刚看完电影《第39级台阶》,离开电影院的时候,他数了数礼堂前的台阶数,恰好是39级!
站在台阶前,他突然又想着一个问题:
如果我每一步只能迈上1个或2个台阶。先迈左脚,然后左右交替,最后一步是迈右脚,也就是说一共要走偶数步。那么,上完39级台阶,有多少种不同的上法呢?
输出格式:
输出一个整数
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int num = 0;
void fun(int m ,int step) {
if (m < 0) return;
if (m == 0) {
if (step % 2 == 0) num++;
return;
}
fun(m - 1, step + 1);
fun(m - 2, step + 1);
}
int main()
{
int step = 39;
fun(39, 0);
cout << num << endl;
return 0;
}
//答案:51167078
第四题:穿越雷区
题目描述
已知的地图是一个方阵,上面用字母标出了A,B区,其它区都标了正号或负号分别表示正负能量辐射区。
例如:
A + - + -
- + - - +
- + + + -
+ - + - +
B + - + -
坦克车只能水平或垂直方向上移动到相邻的区。
数据格式要求:
输入第一行是一个整数n,表示方阵的大小, 4<=n<100
接下来是n行,每行有n个数据,可能是A,B,+,-中的某一个,中间用空格分开。
A,B都只出现一次。
要求输出一个整数,表示坦克从A区到B区的最少移动步数。
如果没有方案,则输出-1
例如:
用户输入:
5
A + - + -
- + - - +
- + + + -
+ - + - +
B + - + -
则程序应该输出:
10
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int num = 0;
void search(char a[100][100], int n) {
int ai = 0, aj = 0, bi = 0, bj = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n;j++)
{
if (a[i][j] == 'A') {
ai = i;
aj = j;
}
if (a[i][j] == 'B') {
bi = i;
bj = j;
}
}
}
num = abs(ai - bi) + abs(aj - bj);
}
int main()
{
int n =4;
char a[100][100]{};
char m;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n;j++)
{
cin >> m;
}
}
search(a, n);
return 0;
}
第五题:迷宫
题目描述
下图给出了一个迷宫的平面图,其中标记为 1 的为障碍,标记为 0 的为可 以通行的地方。
010000
000100
001001
110000
迷宫的入口为左上角,出口为右下角,在迷宫中,只能从一个位置走到这 个它的上、下、左、右四个方向之一。 对于上面的迷宫,从入口开始,可以按DRRURRDDDR 的顺序通过迷宫, 一共 10 步。其中 D、U、L、R 分别表示向下、向上、向左、向右走。 对于下面这个更复杂的迷宫(30 行 50 列),请找出一种通过迷宫的方式, 其使用的步数最少,在步数最少的前提下,请找出字典序最小的一个作为答案。 请注意在字典序中D<L<R<U。(如果你把以下文字复制到文本文件中,请务 必检查复制的内容是否与文档中的一致。在试题目录下有一个文件 maze.txt, 内容与下面的文本相同)
答案提交
这是一道结果填空的题,你只需要算出结果后提交即可。本题的结果为一 个字符串,包含四种字母 D、U、L、R,在提交答案时只填写这个字符串,填 写多余的内容将无法得分
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define PI 3.1415927
#define M(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int dir[30][50] = { {1,0},{0,-1},{0,1},{-1,0} }, vis[30][50];
string S = "DLRU";
char mazz[30][50];
struct node {
int x, y, step;
string str;
node(int x1, int y1, string s1, int st1)
{
x = x1, y = y1, str = s1, step = st1;
}
};
int test(int x, int y)
{
return mazz[x][y] == '1' || x < 0 || x >= 30 || y < 0 || y >= 50 || vis[x][y] == 1 ? 0 : 1;
}
void bfs(int x, int y, string s, int step)
{
queue<node> q;
q.push(node(x, y, s, step));
while (!q.empty())
{
node top = q.front();
q.pop();
if (top.x == 29 && top.y == 49)
{
cout << top.str << top.step;
return;
}
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++)
{
int tx = top.x + dir[i][0];
int ty = top.y + dir[i][1];
if (test(tx, ty))
{
q.push(node(tx, ty, top.str + S[i], top.step + 1));
vis[tx][ty] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0;i < 30;i++)
cin >> mazz[i];
bfs(0, 0, "", 0);
return 0;
}
第六题:跳马
题目描述:
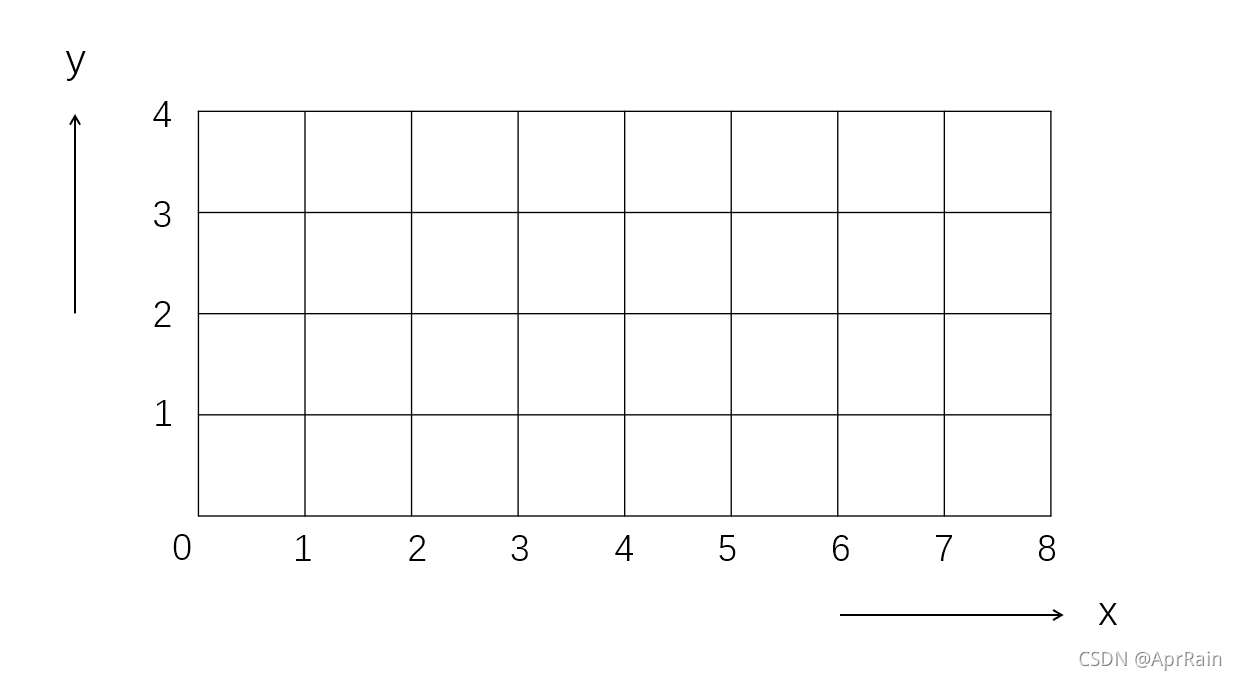
在半张中国象棋的棋盘上,一匹马从左下角跳到右上角,只允许往右跳,不允许往左跳,问有多少种方案。
中国象棋的棋盘是 8×8 格规模大小,半张棋盘就是 8×4 格规模大小,如图所示。由题意得棋子要从 (0,0) 位置走到 (8,4) 位置。取值范围 0≤x≤8,0≤y≤4。
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int ax[9], ay[9];
int dir[4][2] = { {1,2},{1,-2},{2,1},{2,-1} };
int c = 0;
bool inMap(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x <= 8 && y >= 0 && y <= 4;
}
void output(int n) {
cout << "0 0";
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
cout << " → " << ax[i] << " " << ay[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
void findRoad(int n) {
int x1 = ax[n], y1 = ay[n];
if (x1 == 8) {
if (y1 == 4) {
output(n);
c ++;
}
}
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++) {
int x2 = x1 + dir[i][0];
int y2 = y1 + dir[i][1];
if (inMap(x2, y2)) {
ax[n + 1] = x2;
ay[n + 1] = y2;
findRoad(n + 1);
}
}
}
int main() {
findRoad(0);
cout << "共有" << c << "种方案!" << endl;
return 0;
}
第七题:路径之谜
题目描述:
小明冒充X星球的骑士,进入了一个奇怪的城堡。
城堡里边什么都没有,只有方形石头铺成的地面。
假设城堡地面是 n x n 个方格。【如图1.png】所示。
按习俗,骑士要从西北角走到东南角。
可以横向或纵向移动,但不能斜着走,也不能跳跃。
每走到一个新方格,就要向正北方和正西方各射一箭。
(城堡的西墙和北墙内各有 n 个靶子)
同一个方格只允许经过一次。但不必做完所有的方格。
如果只给出靶子上箭的数目,你能推断出骑士的行走路线吗?
有时是可以的,比如图1.png中的例子。
本题的要求就是已知箭靶数字,求骑士的行走路径(测试数据保证路径唯一)
输入:
第一行一个整数N(0<N<20),表示地面有 N x N 个方格
第二行N个整数,空格分开,表示北边的箭靶上的数字(自西向东)
第三行N个整数,空格分开,表示西边的箭靶上的数字(自北向南)
输出:
一行若干个整数,表示骑士路径。
为了方便表示,我们约定每个小格子用一个数字代表,从西北角开始编号: 0,1,2,3....
比如,图1.png中的方块编号为:
0 1 2 3
4 5 6 7
8 9 10 11
12 13 14 15
示例:
用户输入:
4
2 4 3 4
4 3 3 3
程序应该输出:
0 4 5 1 2 3 7 11 10 9 13 14 15
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int north[25], west[20], mp[25][25], mark[25][25];
int n;
int d[4][2] = { {0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0} };
vector<int> way;
void dfs(int x, int y)
{
if (x == n - 1 && y == n - 1)//如果到达终点
{
int cntX[25], cntY[25];
memset(cntX, 0, sizeof(cntX));
memset(cntY, 0, sizeof(cntY));
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
for (int j = 0;j < n;j++)
{
cntX[i] += mark[i][j];
cntY[j] += mark[i][j];
}
int flag = true;
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
if (cntX[i] != west[i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
if (cntY[i] != north[i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag)
{
for (int i = 0;i < way.size();i++)
{
if (i == 0)
cout << way[i];
else
cout << " " << way[i];
}
}
}
int tx, ty;
for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++)
{
tx = x + d[i][0];
ty = y + d[i][1];
if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < n && mark[tx][ty] == 0)
{
mark[tx][ty] = 1;
way.push_back(mp[tx][ty]);
dfs(tx, ty);
mark[tx][ty] = 0;
way.pop_back();
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
cin >> north[i];
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
cin >> west[i];
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
for (int j = 0;j < n;j++)
mp[i][j] = t++;//给格子编码
mark[0][0] = 1;
way.push_back(0);
dfs(0, 0);
}
//样例输入:
//4
//2 4 3 4
//4 3 3 3
//样例输出:
// 0 4 5 1 2 3 7 11 10 9 13 14 15
第八题:未名湖边的烦恼
问题描述:
每年冬天,北大未名湖上都是滑冰的好地方。北大体育组准备了许多冰鞋,可是人太多了,每天下午收工后,常常一双冰鞋都不剩。
每天早上,租鞋窗口都会排起长龙,假设有还鞋的m个,有需要租鞋的n个。现在的问题是,这些人有多少种排法,可以避免出现体育组没有冰鞋可租的尴尬场面。(两个同样需求的人(比如都是租鞋或都是还鞋)交换位置是同一种排法)
输入格式
两个整数,表示m和n
输出格式
一个整数,表示队伍的排法的方案数。
样例输入
3 2
样例输出
5
数据规模和约定
m,n∈[0,18]
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fun(int m, int n) {
if (m < n) return 0;
else if (n == 0) return 1;
else return fun(m - 1, n) + fun(m, n - 1);
}
int main()
{
int m= 0, n=0;
cin >> m >> n;
cout << fun(m, n);
return 0;
}
第十题:2n皇后问题
题目描述:
给定一个n*n的棋盘,棋盘中有一些位置不能放皇后。现在要向棋盘中放入n个黑皇后
和n个白皇后,使任意的两个黑皇后都不在同一行、同一列或同一条对角线上,任意的两
个白皇后都不在同一行、同一列或同一条对角线上。问总共有多少种放法?n小于等于8。
输入格式:
输入的第一行为一个整数n,表示棋盘的大小。
接下来n行,每行n个0或1的整数,如果一个整数为1,表示对应的位置可以放皇后,
如果一个整数为0,表示对应的位置不可以放皇后。
输出格式:
输出一个整数,表示总共有多少种放法。
案例输入
No.1
4
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
No.2
4
1 0 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
案例输出
No.1
2
No.2
0
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int n ,ans;
int a[10][10];//棋盘
int white[10], black[10];
int valid_white(int row, int conlumn)
{
for (int i = 1;i < row; i++)
if (conlumn == white[i] || abs(row - i) == abs(conlumn - white[i]))
return 0;
return 1;
}
int valid_black(int row, int conlumn) {
for (int i = 1;i < row;i++) {
if (conlumn == black[i] || abs(row - i) == abs(conlumn - black[i]))
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void queen_black(int row) {
if (row == n + 1) {
ans++;
}
else {
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
if (a[row][i] == 0 || i == white[row])
continue;
else if (valid_black(row, i)) {
black[row] = i;
queen_black(row + 1);
}
}
}
void queen_white(int row) {
if (row == n + 1) {
queen_black(1);
return;
}
else {
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
if (a[row][i] == 0 )
continue;
else if (valid_white(row, i)) {
white[row] = i;
queen_white(row + 1);
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
for (int j = 1;j <= n;j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
queen_white(1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}








 本文解析了一系列算法挑战赛题目,包括带分数表示法、李白打酒、第39级台阶等,涉及递归、搜索、组合数学等算法知识。
本文解析了一系列算法挑战赛题目,包括带分数表示法、李白打酒、第39级台阶等,涉及递归、搜索、组合数学等算法知识。
















 1257
1257

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








