目录
事务

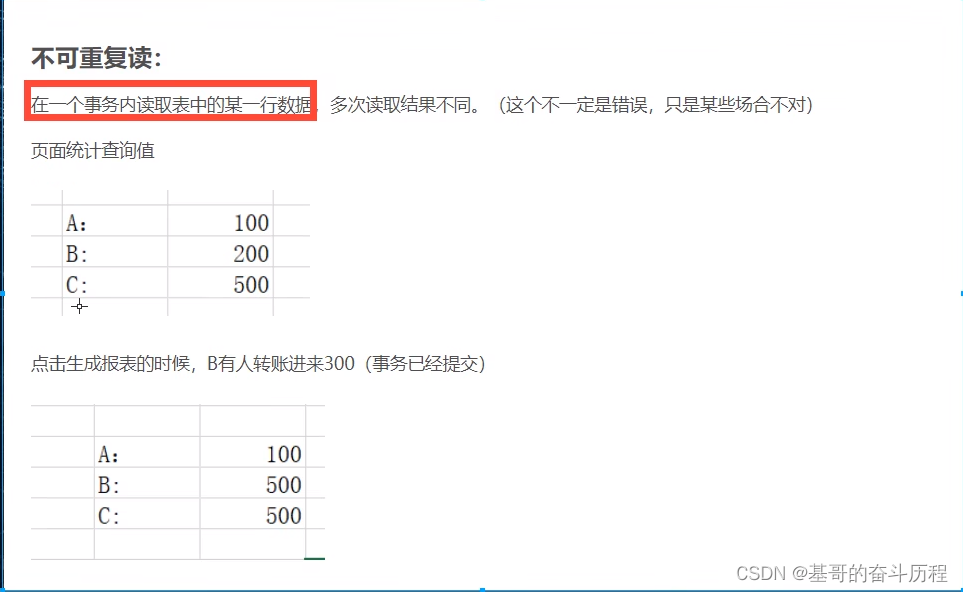


事务操作

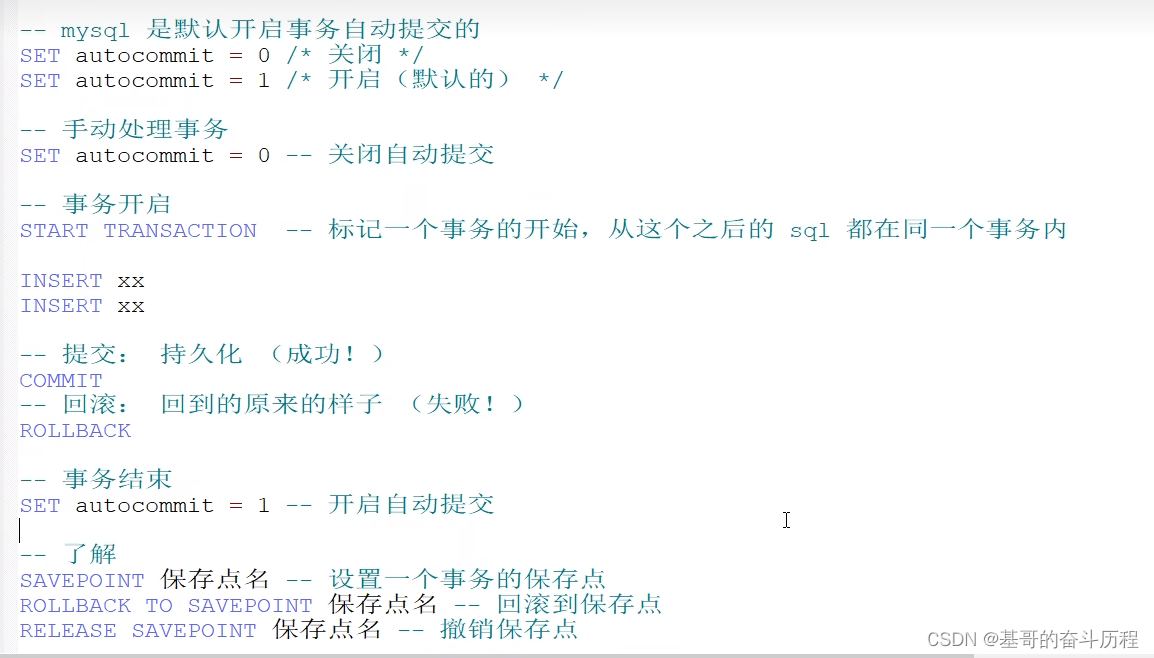
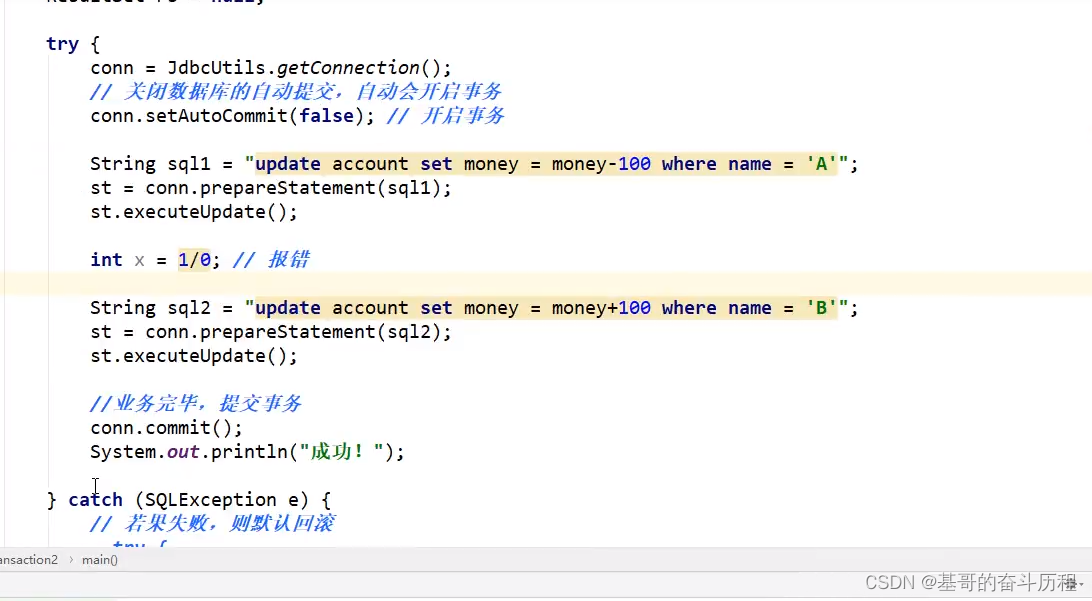
--模拟转账:事务
SET autocommit = 0;--关闭自动提交
START TRANSACTION --开启事务(一组事务)
UPDATE account SET money=money-100 WHERE `name`='A' --A少100
UPDATE account SET money=money+500 WHERE `name`='B' --B加500
COMMIT; --提交事务
ROLLBACK; --如果失败回滚
SET autocommit = 1;--开启自动提交索引
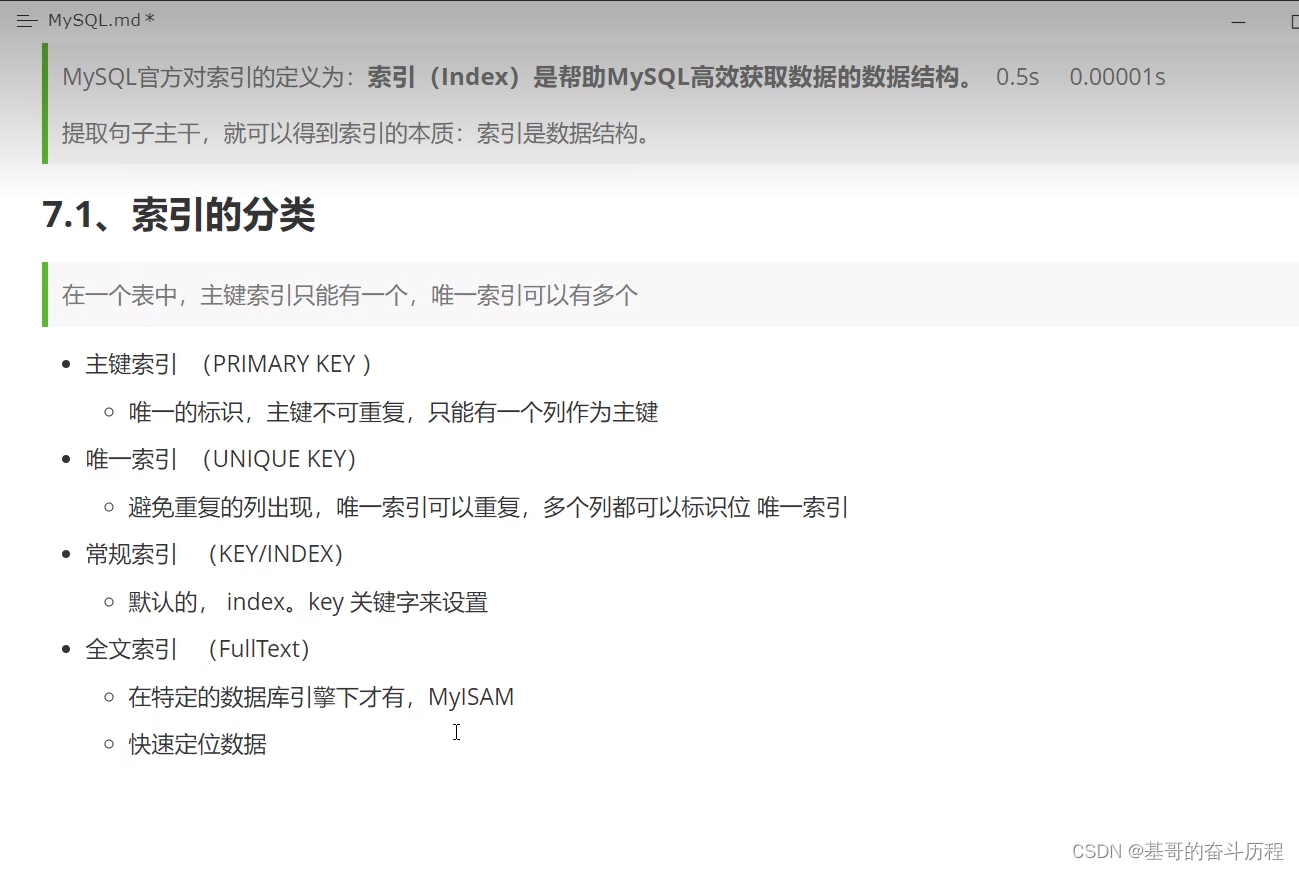
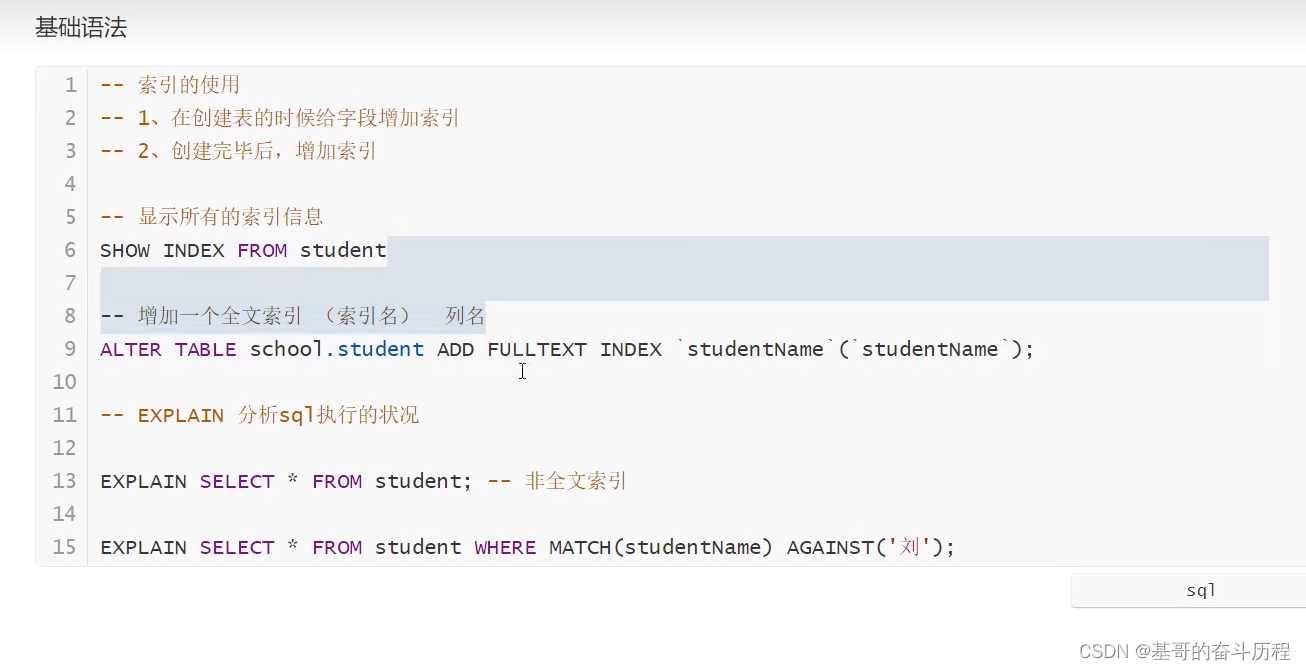





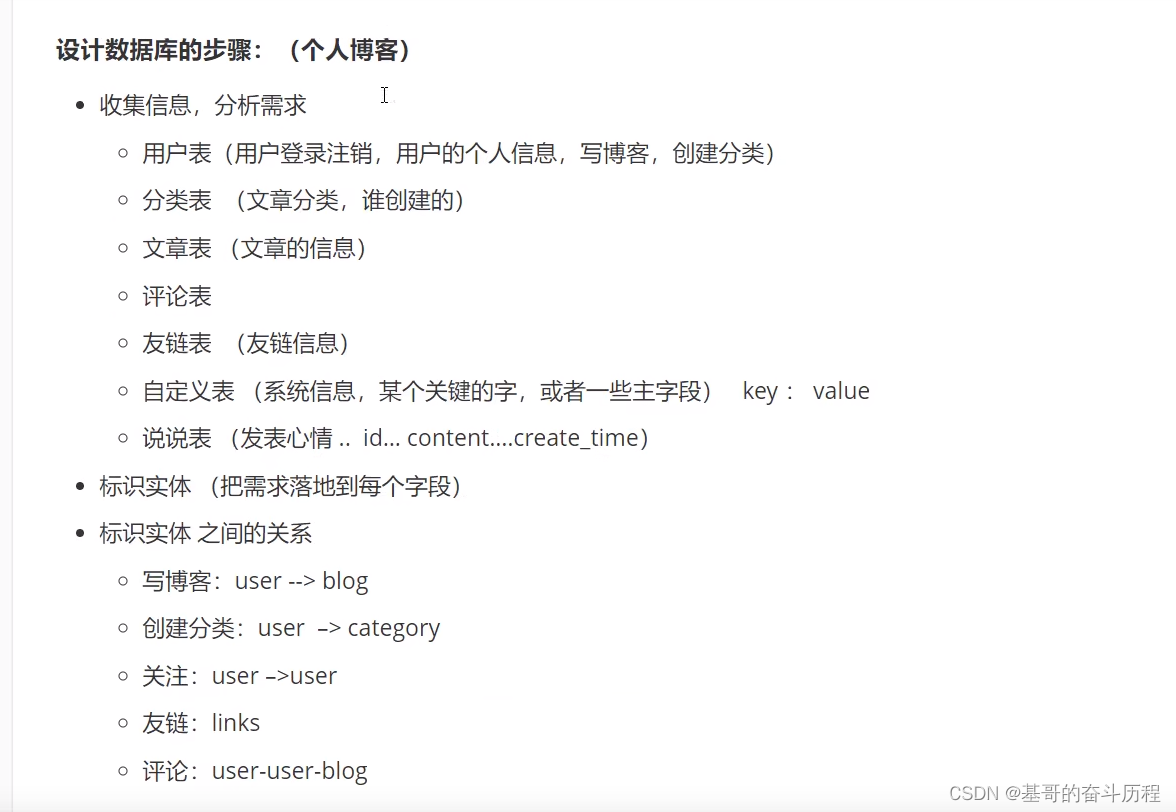
如何创建一个好的数据库

三大范式

第一范式

第二范式
第三范式


JDBC
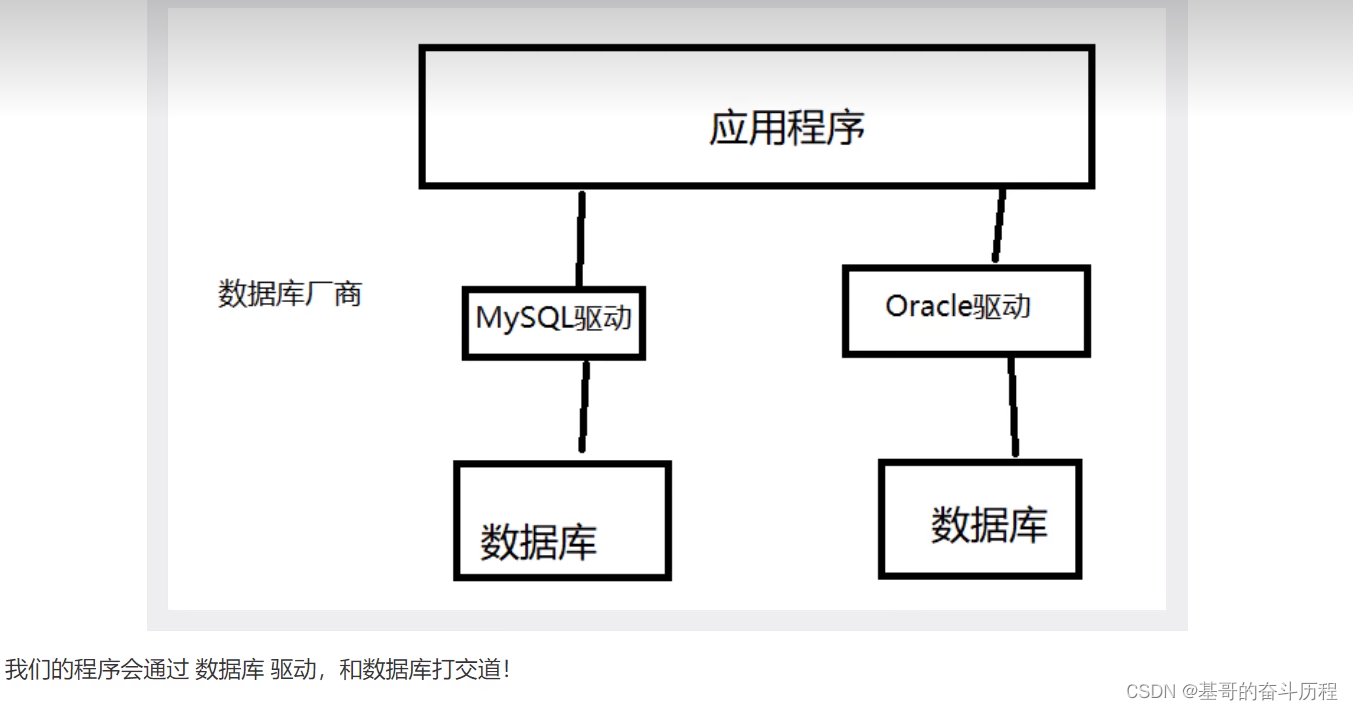
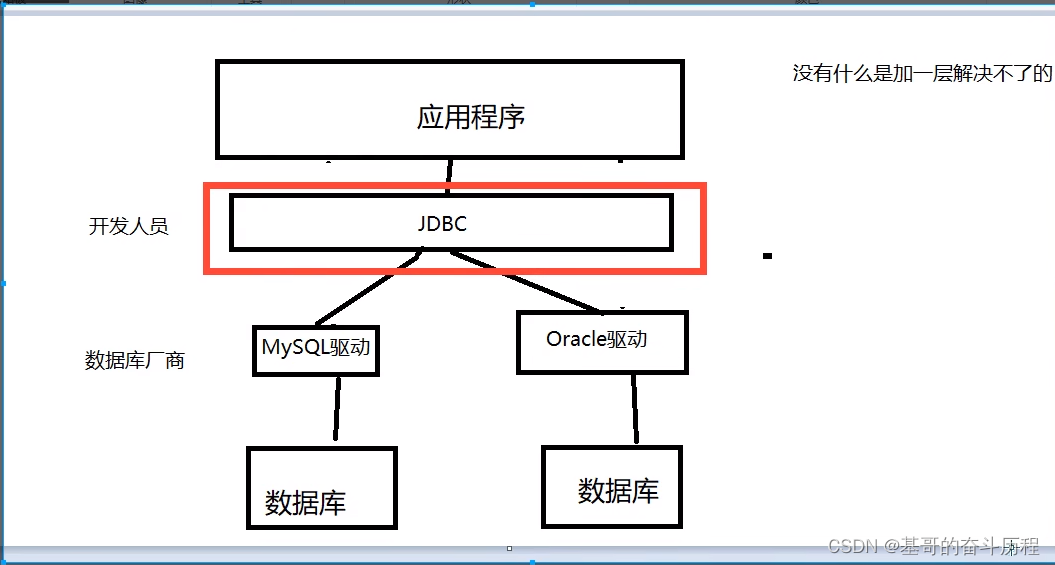
第一个JDBC程序
package com.kuangshen.lesson01;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
import java.sql.*;
//我的第一个JDBC程序
public class JdbcFirstDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//固定写法,加载驱动
//2.用户信息和url
//1.支持中文编码 2.设置字符集为utf-8 3.用安全的连接
String url ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String usename = "root";
String password = "2001";
//3.连接成功。数据库对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, usename, password);
//4.执行SQL对象 Statement执行SQL的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5.执行SQL对象,执行SQL
String sql="SELECT * FROM `users`";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);//返回的结果集,结果集 中封装了我们全部的查询出来的结果
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.print("id="+resultSet.getObject("id")+" ");
System.out.print("name="+resultSet.getObject("NAME")+" ");
System.out.print("pwd="+resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD")+" ");
System.out.print("eml="+resultSet.getObject("email")+" ");
System.out.println("birth="+resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println("=================");
}
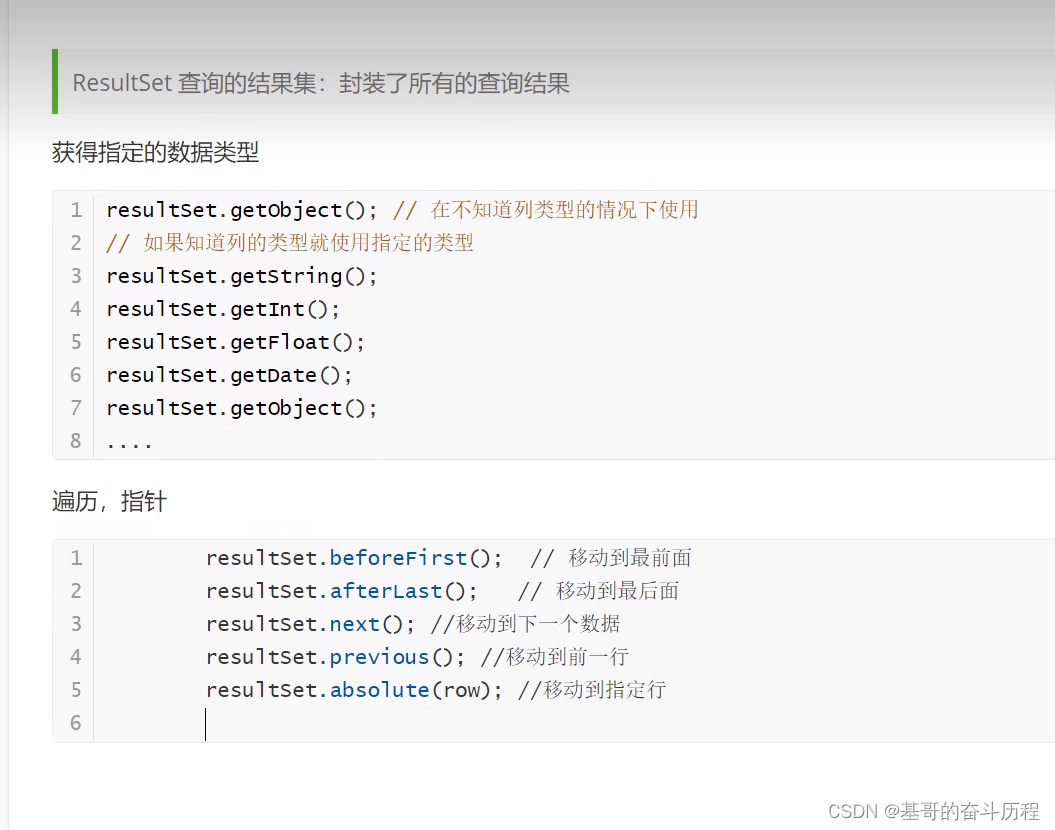
//6.释放连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}

JDBC对象解释
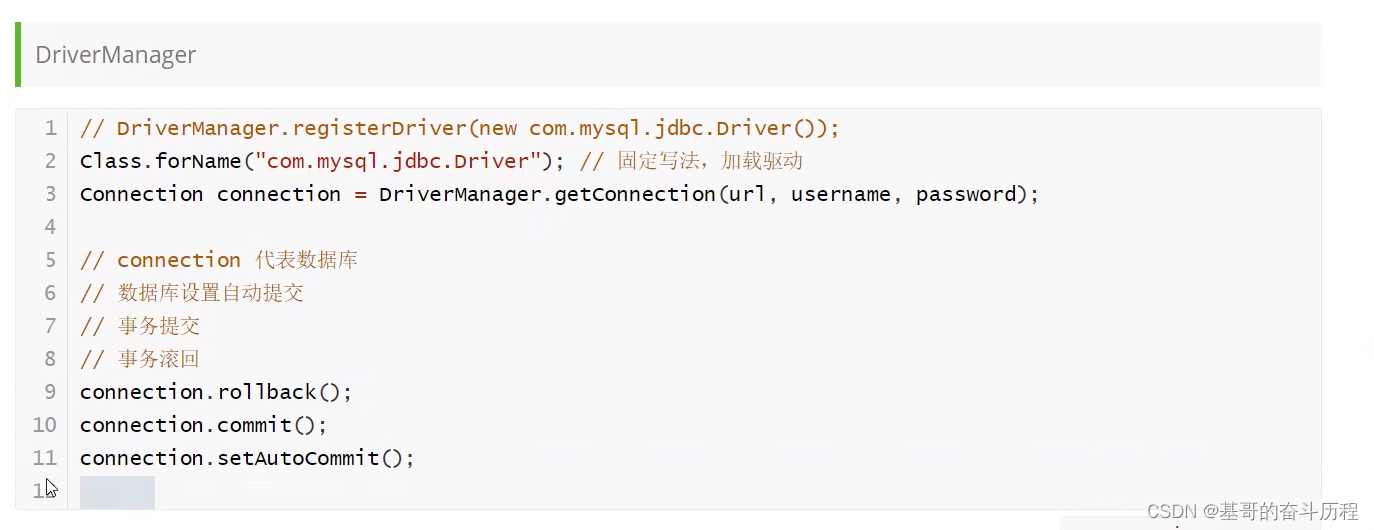

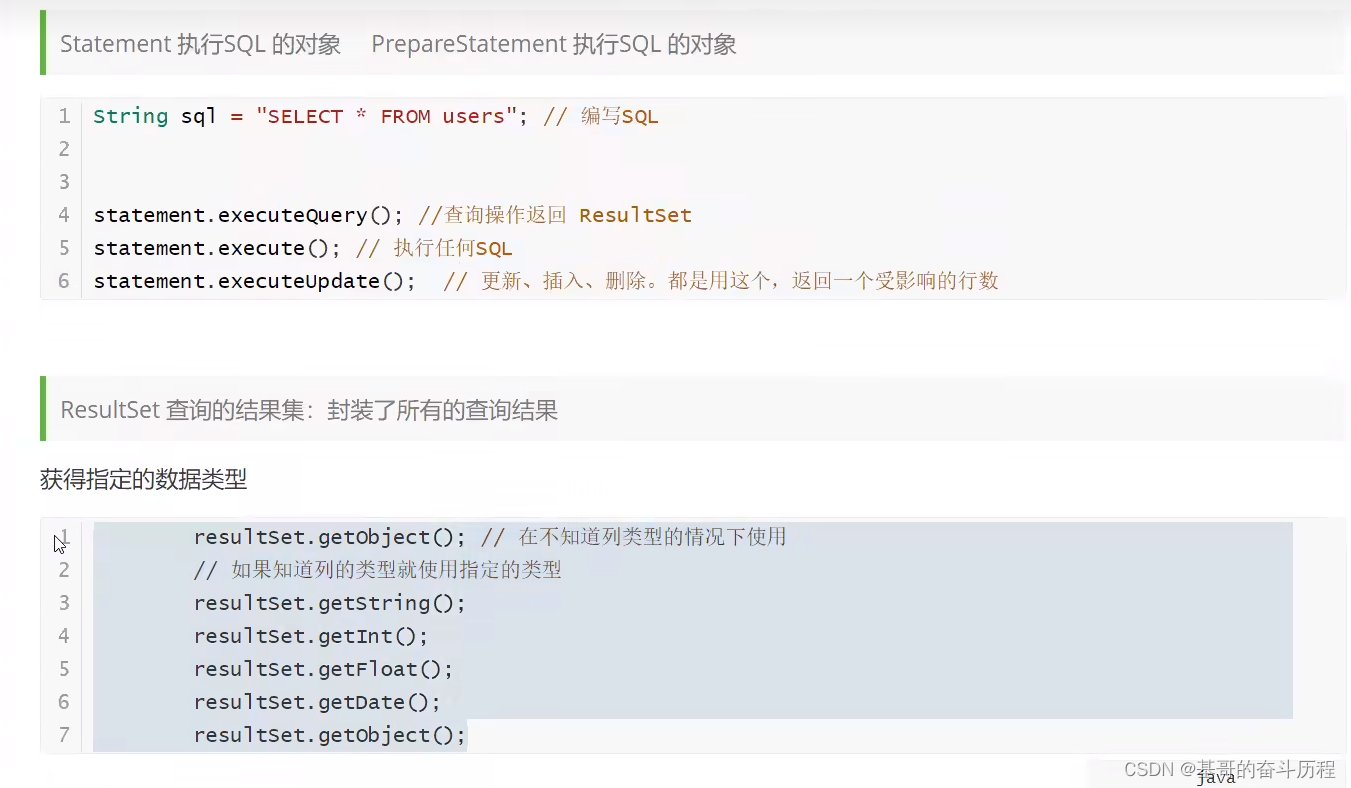
关闭对象
这里是通过类获取反射对象,然后获取反射对象的类加载器,调用类加载器的获取资源的方法。一步一步来的
各位,这里是反射的类加载器+集合的map子接口Properties类的知识,别被前面的误导了
前面的,这哪里是IO流的properties类的知识啊?你这不乱引导人么?
我就说看这个Properties类很熟悉,但是IO流没学到过啊。
package com.kuangshen.lesson02.utils;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driver =null;
private static String url =null;
private static String username =null;
private static String password =null;
static {
try {
InputStream in = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dp.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver= properties.getProperty("driver");
url= properties.getProperty("url");
username= properties.getProperty("username");
password= properties.getProperty("password");
//1.驱动只用加载一次
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
//释放连接资源
public static void release(Connection con, Statement st, ResultSet rs){
if (con!=null) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (st != null) {
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}}}
package com.kuangshen.lesson02;
import com.kuangshen.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestInsert {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection conn=null;
Statement st =null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try {
conn= JdbcUtils.getConnection();//获取数据库连接
st=conn.createStatement();//获得SQL的执行对象
String sql="INSERT INTO users(`id`,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`)" +
"VALUES('4','jiji','213123','123123@qq.com','20010301')";
int i=st.executeUpdate(sql);
if (i>0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,rs);
}
}
}
package com.kuangshen.lesson02;
import com.kuangshen.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestSelect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
Statement st=null;
ResultSet RS=null;
try {
conn= JdbcUtils.getConnection();
st =conn.createStatement();
String sql ="SELECT * FROM users where id = 1";
RS=st.executeQuery(sql);
while (RS.next()){
System.out.println("name="+RS.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,RS);
}
}
}
SQL注入问题

![]()
PreparedStatement对象
1.preparedStatement可以防止SQL注入,效率更高

1.新增
package com.kuangshen.lesson03;
import com.kuangshen.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestInsert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement st=null;
try {
conn= JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别
//使用?占位符代替参数
String sql= "INSERT INTO users(`id`,`NAME`,`PASSWORD`,`email`,`birthday`) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";
st= conn.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译,先写SQL,不执行
st.setInt(1,5);
st.setString(2,"铭基");
st.setString(3,"231");
st.setString(4,"139z@qq,com");
//注意点:util.Date java
// sql.Date 数据库 new Date().getTime()获得时间戳 java.sql.Date()通过它转化为数据库的时间
st.setDate(5,new java.sql.Date(new Date().getTime()));
//执行
int i= st.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}else {
System.out.println("插入失败");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,null);
}
}
}
2.删除
package com.kuangshen.lesson03;
import com.kuangshen.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement st=null;
try {
conn= JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别
//使用?占位符代替参数
String sql= "DELETE FROM users where id =?";
st= conn.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译,先写SQL,不执行
st.setInt(1,4);
//执行
int i= st.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("删除成功,共影响"+i+"行");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,null);
}
}
}
3.修改
package com.kuangshen.lesson03;
import com.kuangshen.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestUpdate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement st=null;
try {
conn= JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别
//使用?占位符代替参数
String sql= "Update users set NAME =? where id=?";
st= conn.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译,先写SQL,不执行
st.setString(1,"基基");
st.setInt(2,1);
//执行
int i= st.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("修改成功,共影响"+i+"行");
}else {
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,null);
}
}
}
4.查询
package com.kuangshen.lesson03;
import com.kuangshen.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestSelect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement st=null;
ResultSet rs =null;
try {
conn= JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别
//使用?占位符代替参数
String sql= "SELECT `NAME` from users where id =?";
st= conn.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译,先写SQL,不执行
st.setInt(1,1);
//执行
rs= st.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString("NAME"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn,st,null);
}
}
}
防止SQL注入
preparedStatement
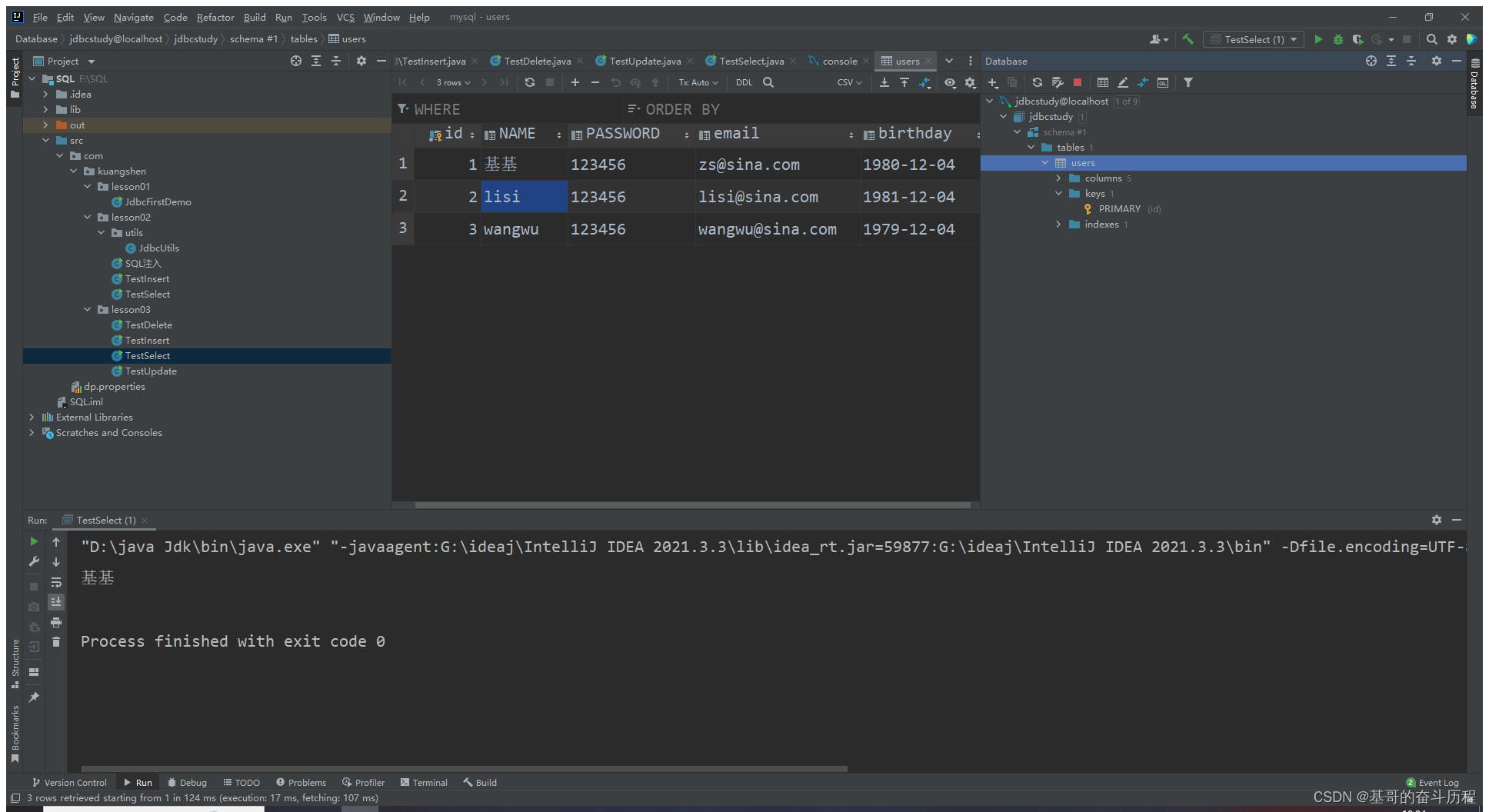
使用IDEA连接数据库

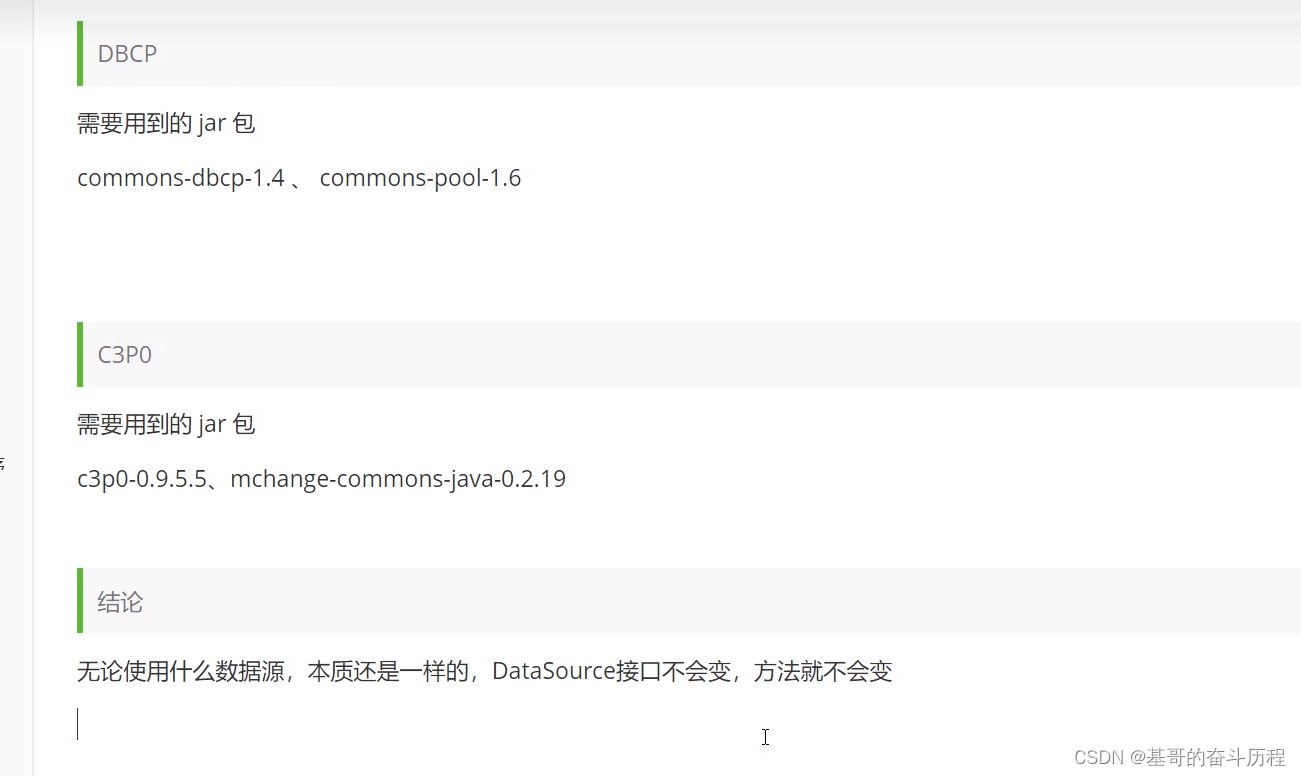
数据库连接池

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








