1,两数之和

class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
hashmap = {}
for index, num in enumerate(nums):
another_num = target - num
if another_num in hashmap:
return [hashmap[another_num], index]
hashmap[num] = index
return None
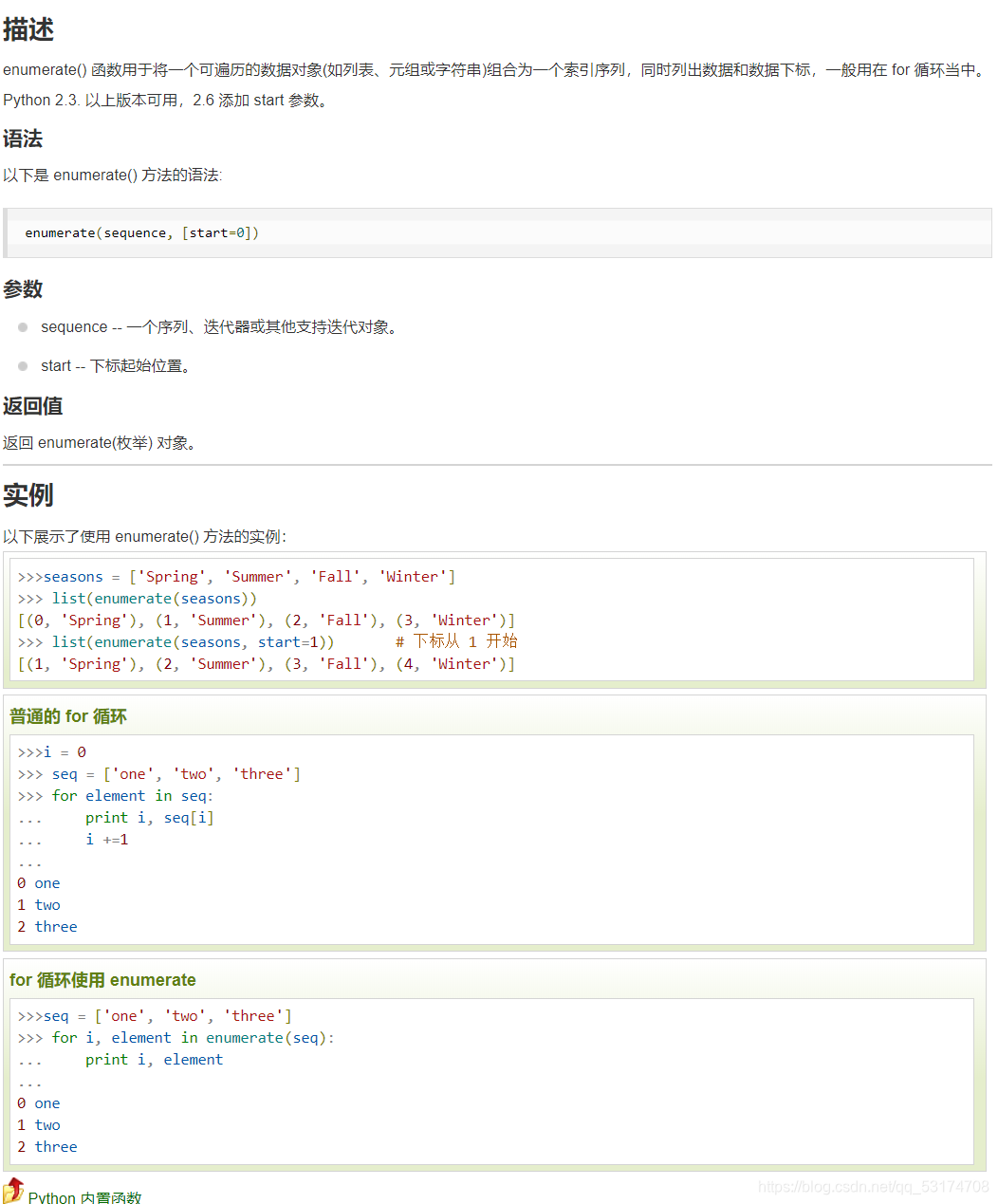
看了一下,这道题,快的都是用的哈希表。
下面是C语言暴力破解,还不错。
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize){
int i,j;
int *result=NULL;
for(i=0;i<numsSize-1;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<numsSize;j++)
{
if(nums[i]+nums[j]==target)
{
result=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*2);
result[0]=i;
result[1]=j;
*returnSize=2;
return result;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
#c++写法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<nums.size()-1;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<nums.size();j++)
{
if(nums[i]+nums[j]==target)
{
return {i,j};
}
}
}
return {i,j};
};
};
2,两数相加
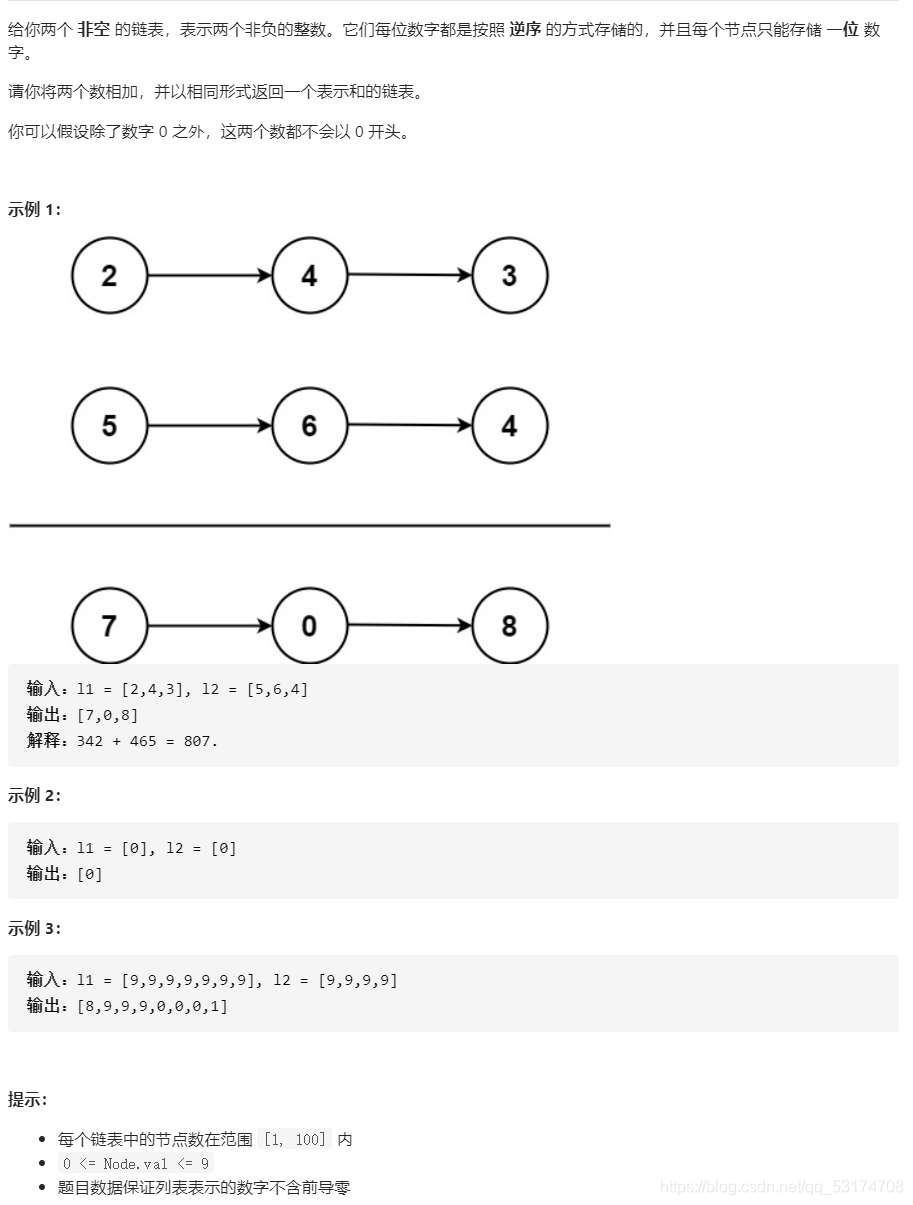
c艹
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
int len1=1;
int len2=1;
ListNode *p=l1;
ListNode *q=l2;
while(p->next!=NULL)
{
len1++;
p=p->next;
}
while(q->next!=NULL)
{
len2++;
q=q->next;
}
if(len1>len2)
{
for(int i=1;i<len1-len2;i++)
{
p->next=new ListNode(0);
p=p->next;
}
}
else
{
for(int j=0;j<len2-len1;j++)
{
q->next=new ListNode(0);
q=q->next;
}
}
p=l1;
q=l2;
ListNode *l3=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode*w=l3;
bool count=false;
int i=0;
while(p!=NULL&&q!=NULL)
{
i=count+p->val+q->val;
w->next=new ListNode(i%10);
count=i>=10?true:false;
w=w->next;
p=p->next;
q=q->next;
}
if(count)//若最后还有进位
{
w->next=new ListNode(1);
w=w->next;
}
return l3->next;
}
};




















 298
298










