C/C++支持最基本的三种程序运行结构:顺序结构,选择结构,循环结构
(1)顺序结构:程序按顺序执行,不发生跳转
(2)选择结构:依据条件是否满足,有选择的执行相应功能
(3)循环结构:依据条件是否满足,循环多次执行某段代码
4.1 选择结构
if语句:执行满足条件的语句;
if语句的三种形式
(1)单行格式if语句
(2)多行格式if语句
(3)多条件的if语句
1.单行格式if语句:if(条件)(条件满足执行的语句)
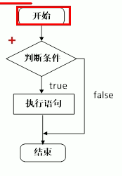
2.多行格式if语句:if(条件)(条件满足执行语句)else(条件不满足执行的语句);
3.多条件的if语句:if(条件1)(条件满足执行的语句)else if(条件2)(条件2满足执行的语句)…else(都不满足执行的语句)

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入一个分数:" << endl;
cin >> score;
cout << "您输入的分数为:" << score << endl;
if(score > 90){
cout << "优秀" << endl;
}else if((score > 60) && (score < 90)){
cout << "及格" << endl;
}else{
cout << "不及格" << endl;
}
}
4.1.2 三目运算符
作用:通过三目运算符实现简单的判断
语法:表达式1 ? 表达式2 :表达式3
(1)如果表达式1位真,执行表达式2,并返回表达式2的结果
(2)表达式1为假,执行表达式3,返回表达式3的结果
int re = (score > math ? score : math);
cout << "最大值 = " << re << endl;
4.1.3 swith语句
作用:执行多条分支语句
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score = 0;
cin >> score;
cout << "你输入的值为 = " << score << endl;
switch (score)
{
case 10:
cout << "垃圾" << endl;
break;
case 50:
cout << "还是垃圾" << endl;
break;
case 80:
cout << "还可以" <<endl;
break;
default:
cout << "不错" << endl;
break;
}
//switch缺点:判断时候只能是整形或者字符型,不可以是同一个区间
//switch有点:结构清晰,执行效率高
}
4.2.1 while 循环
作用:满足条件,执行循环语句
语法:while(循环条件){循环语句}
解释:只要循环条件为真,就执行循环语句
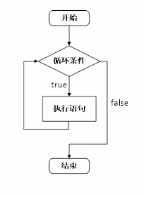
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num = 5;
int n = 0;
while (num > 0)//条件执行语句为真就执行
{
num--;
n++;
}
cout << n << endl;
}
循环结构案例
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int num = rand()% 100 + 1;
cout << num << endl;
int nn = 0;
while(1)
{
cout << "请输入你猜的值" << endl;
cin >> nn;
if(nn > num){
cout << "big" << endl;
}else if(nn < num){
cout << "small" << endl;
}else if(nn == num){
cout << "相等" << endl;
cout << "游戏结束" << endl;
break;
}else{
cout << "请输入数字" << endl;
}
}
}//其中一个致命的缺点就是输入字符时,会导致无限循环
4.2.2 do…while循环语句
作用:满足循环条件,执行循环语句
语法:do{循环语句} while(循环条件)
注意:与while的区别在于do…while会先执行一次循环语句,再判断循环条件

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num = 0;
do{
num++;
cout << num << endl;
}while(num < 9);
}//与while的区别就是会先执行一遍语句,
do while循环的案例
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num = 100;
int a , b , c;
do{
a = num%10;
b = num / 10 % 10;
c = num / 100;
if (a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c == num)
{
cout << num << endl;
}
num++;
}while(num < 1000);
}
4.2.3 for循环语句
作用:满足循环条件,执行循环语句
语法:for(起始表达式;条件表达式;末属表达式){循环语句;}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int i = 0;i <10;i++)
{
if(i >= 10)
{
break;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
}
4.2.4 嵌套循环
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int j = 1;j <= 9;j++)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= j;i++)
{
int sum = i * j ;
cout << i << "*" << j <<"=" << sum << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
4.3 跳转语句
4.3.1 break跳转
作用:用于跳出悬着结果或者循环结构
break使用的时机:
(1)出现在switch条件语句中,作用是终止case并跳出switch
(2)出现在循环语句中,作用是跳出当前的循环语句
(3)出现在嵌套循环中,跳出最近的内层循环语句
4.3.2 continue语句
作用:在循环语句中,跳过本次循环余下尚未执行的语句,继续执行下一次循环
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 100;i++)
{
if(i % 2 == 0)
{
continue;
}
cout << i << " ";
n++;
if(n % 5 == 0)
{
cout << endl;
}
}
}
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1et411b73Z?p=41&spm_id_from=pageDriver







 这篇博客详细介绍了C++中的程序流程控制结构,包括顺序结构、选择结构(if语句、三目运算符、switch语句)和循环结构(while、do...while、for循环),以及跳转语句(break和continue)的应用场景和作用。
这篇博客详细介绍了C++中的程序流程控制结构,包括顺序结构、选择结构(if语句、三目运算符、switch语句)和循环结构(while、do...while、for循环),以及跳转语句(break和continue)的应用场景和作用。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








