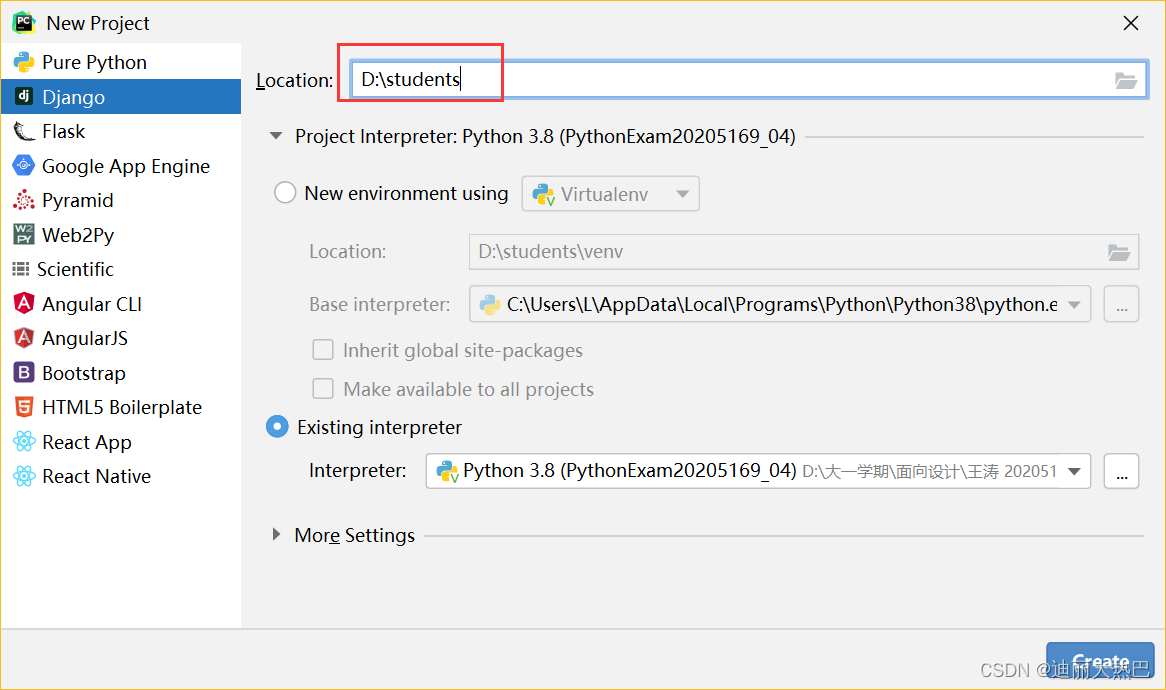
一,准备Django项目-students
- 设置Django项目的位置与名称
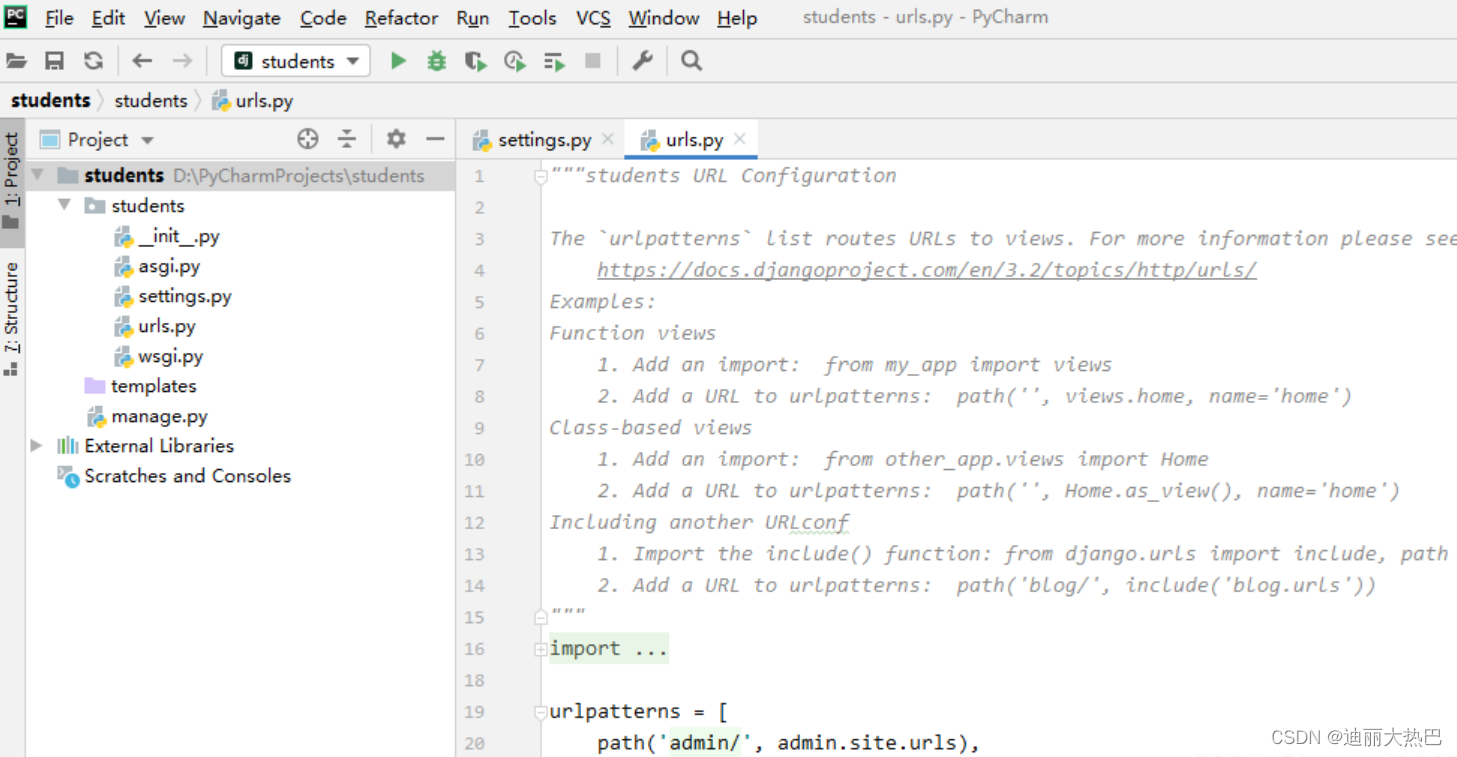
二,准备静态资源
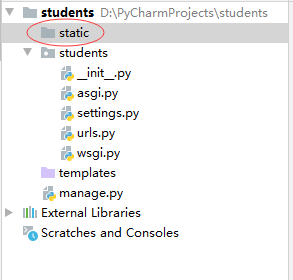
1,创建静态目录
- 在students里创建static目录
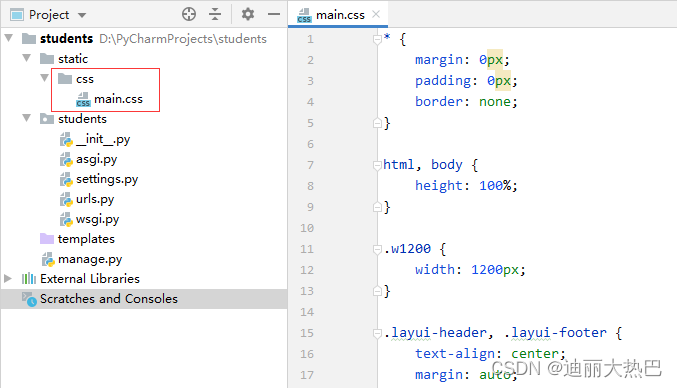
2,创建样式文件
- 在static里创建css目录,然后在css里创建main.css样式文件
* {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
border: none;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
}
.w1200 {
width: 1200px;
}
.layui-header, .layui-footer {
text-align: center;
margin: auto;
}
.layui-header {
padding: 40px 0px;
line-height: 1.5em;
position: fixed;
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom, olive, deepskyblue, cornflowerblue, mediumorchid);
}
.layui-footer {
padding: 30px 0px;
position: relative;
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom, mediumorchid, cornflowerblue, deepskyblue, olive);
}
.layui-footer a {
margin: 0px 20px;
}
.layui-footer a:hover {
color: red;
}
.layui-footer p {
margin: 15px 0px;
}
.bold {
font-weight: bold;
}
.middle {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
margin: 5px 0px;
min-height: 500px;
}
.left-menu {
flex: 1;
background: azure;
padding: 20px;
}
.right-content {
flex: 5;
margin-left: 5px;
background: azure;
padding: 20px;
}
.test-info h4 {
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bolder;
}
.test-info p {
font-size: 15px;
line-height: 2em;
text-indent: 2em;
}
form {
margin: auto;
}
form table {
width: 400px;
margin: auto;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 50px 20px !important;
}
form table th {
width: 100px;
text-align: right;
}
form table td {
width: 250px;
padding: 0px 10px;
}
tr {
line-height: 4em;
}
table tr:last-child {
text-align: center;
}
table caption {
font-weight: bolder;
padding: 10px 0px;
font-size: 1.5em;
}
.stuinfo {
width: 90% !important;
margin: auto;
text-align: center;
}
.stuinfo table {
margin: auto !important;
width: 90% !important;
}
.stuinfo table td {
width: 25%;
}
.stuinfo table tr {
border-bottom: 1px solid black;
}
.stuinfo thead {
background: black;
}
.stuinfo thead th {
color: white;
border-right: 1px solid white;
}
.stuinfo table tr:nth-child(even) {
background: #2D93CA;
}
.stuinfo table tr:hover td {
background: #00FFFF;
}
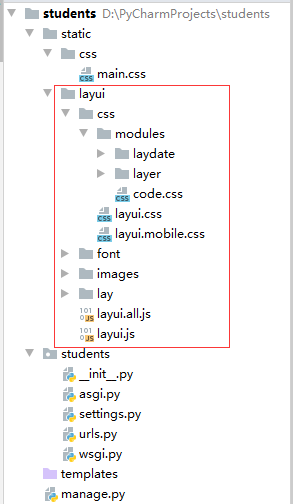
3,添加layui框架
- 在static里添加layui框架
- 下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1gXt5Qd5U5GJUUSk2dzYNtA 提取码:cgn6
此链接由我的专业老师提供的
4,创建脚本文件
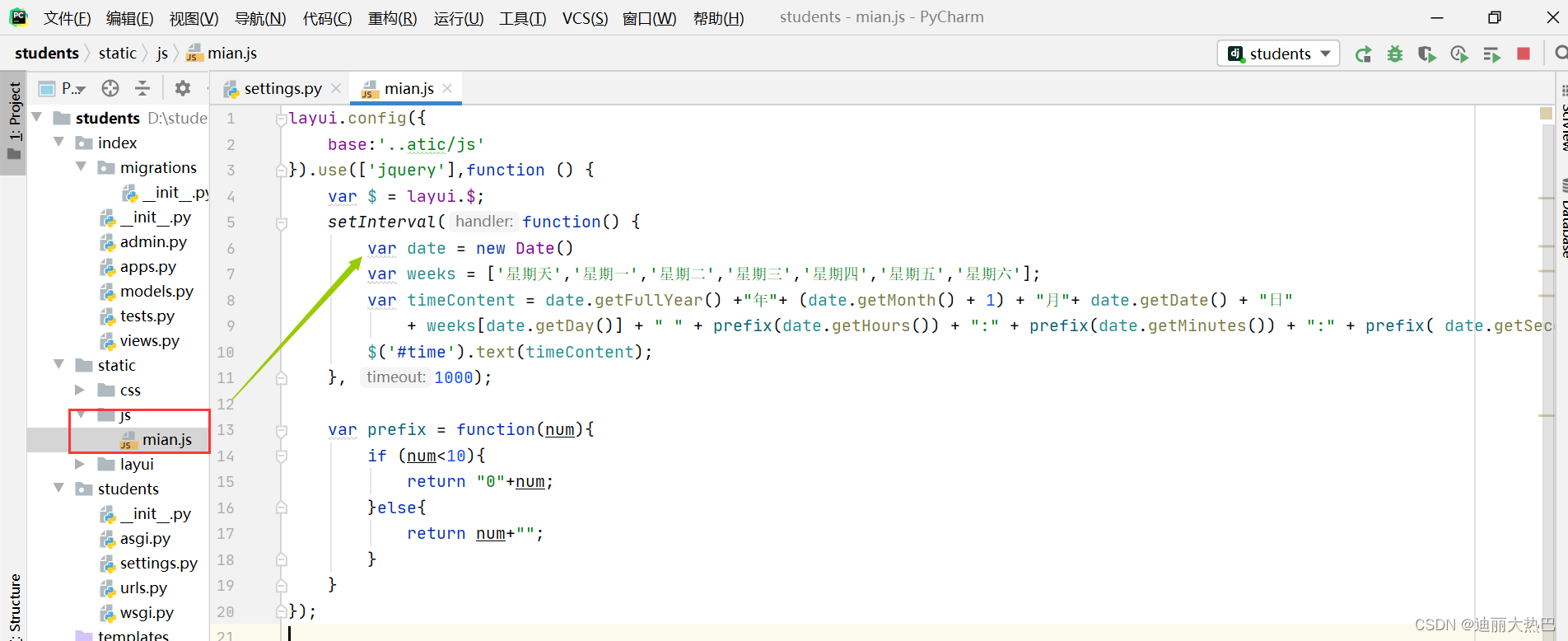
- 在static里创建js目录,然后在js里创建main.js文件
三,完成基本配置
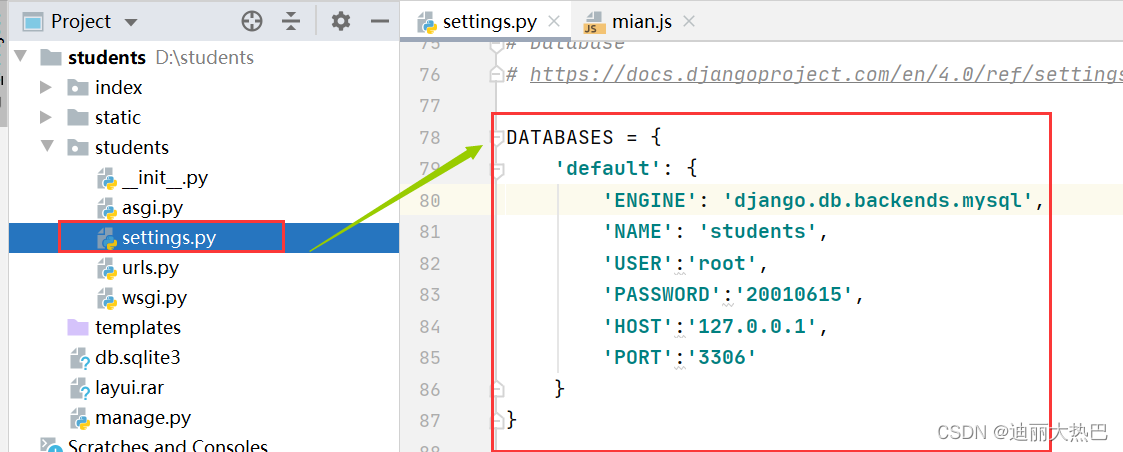
1、配置数据库信息
- 在配置文件settings.py里配置数据库信息(注意密码要换成自己数据库的密码)
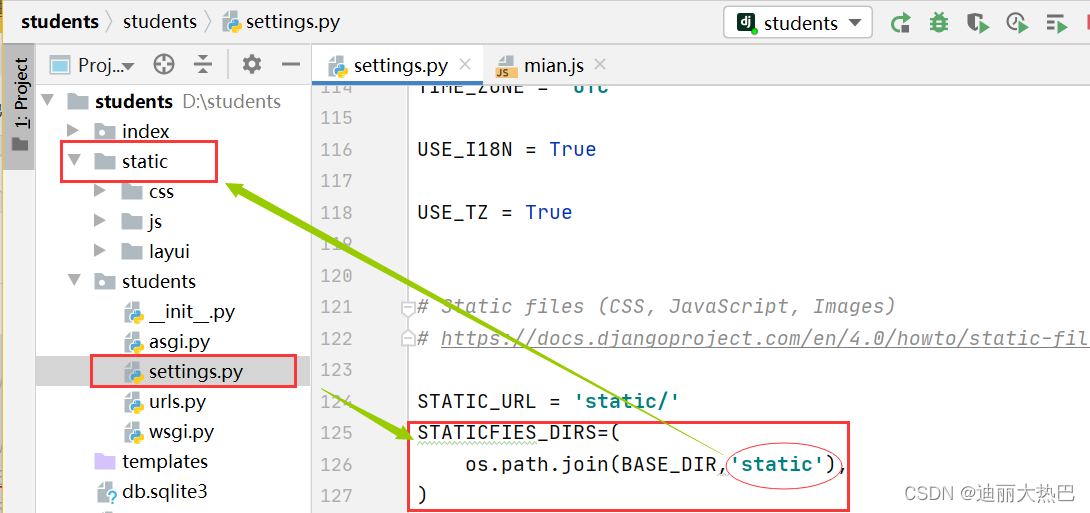
2、配置静态文件目录
- 在配置文件settings.py里配置静态文件目录
3、进行数据迁移
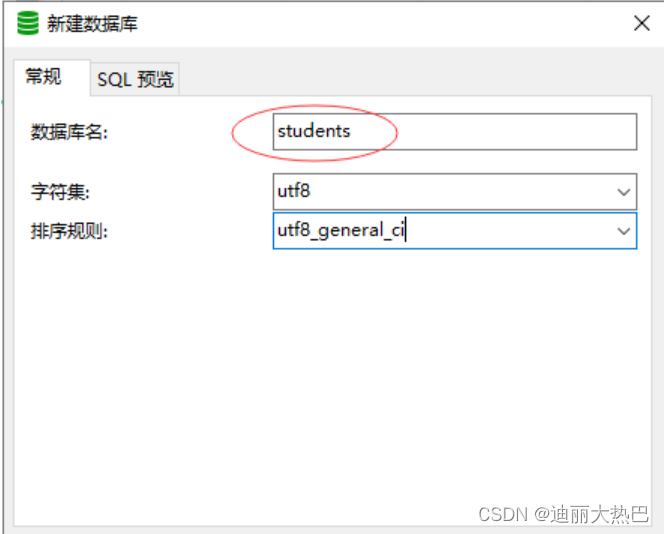
(1)创建数据库 - students
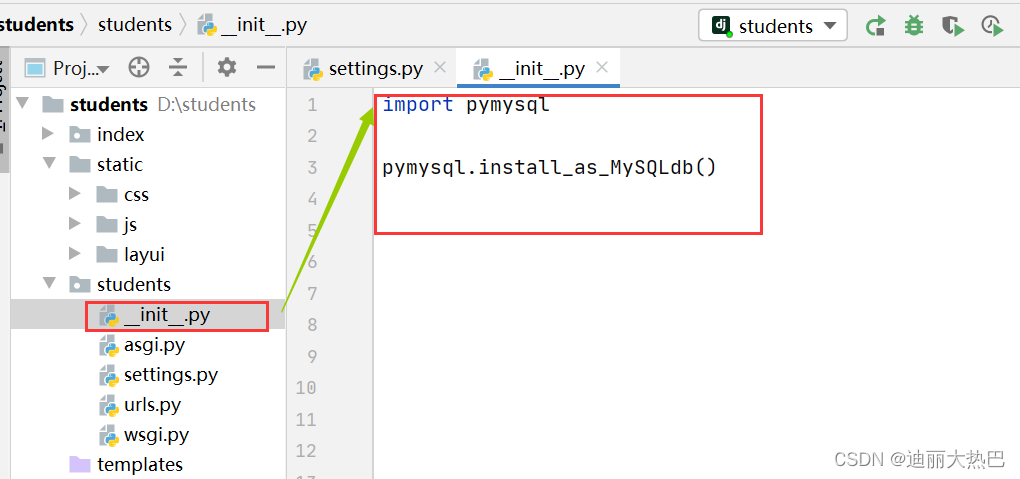
(2)设置数据库连接模块
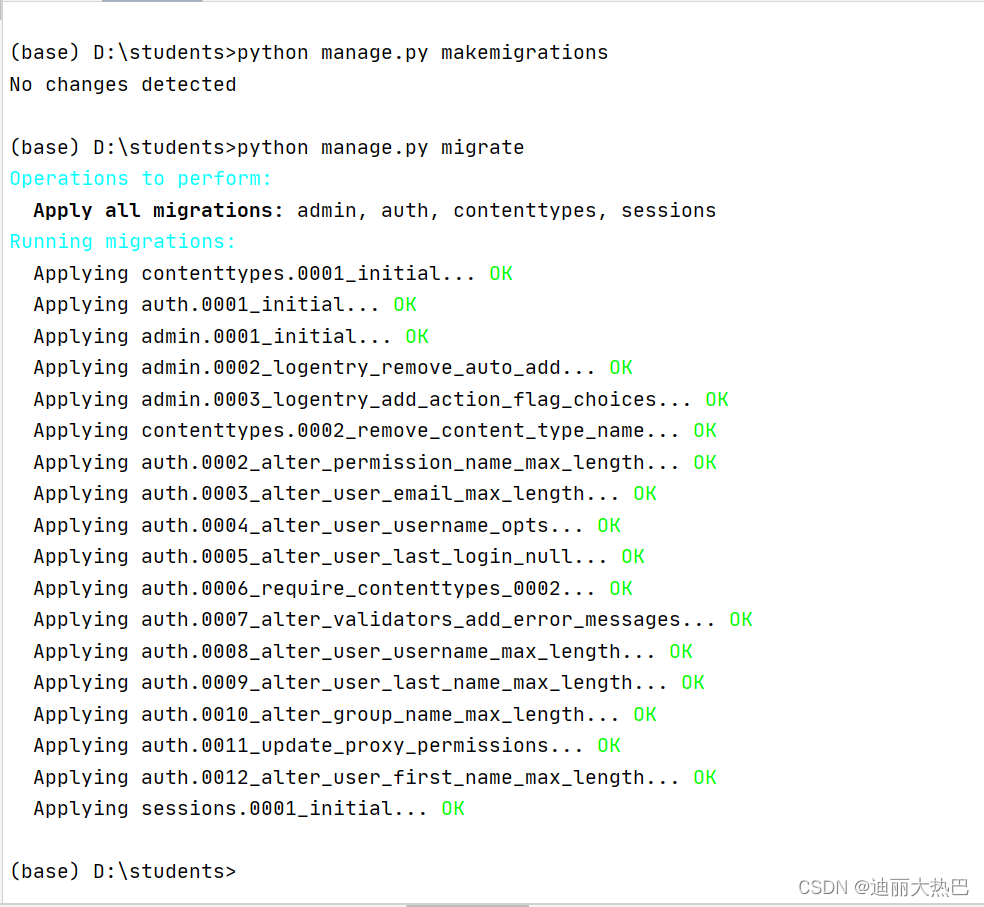
(3)执行数据迁移命令
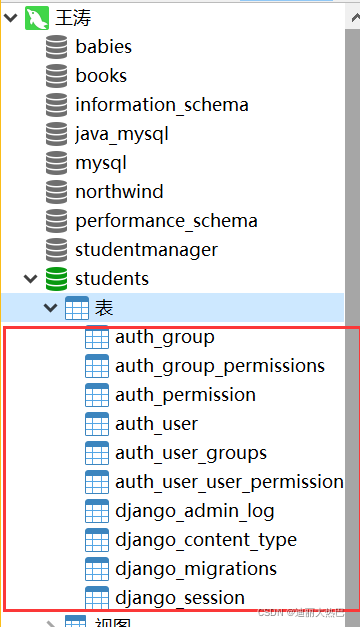
- 查看生成的数据表
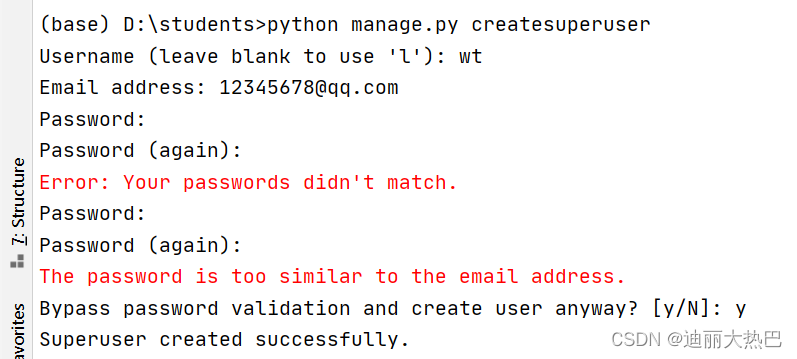
(4)添加超级管理员
- python manage.py createsuperuser
- 启动服务器查看
- http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/
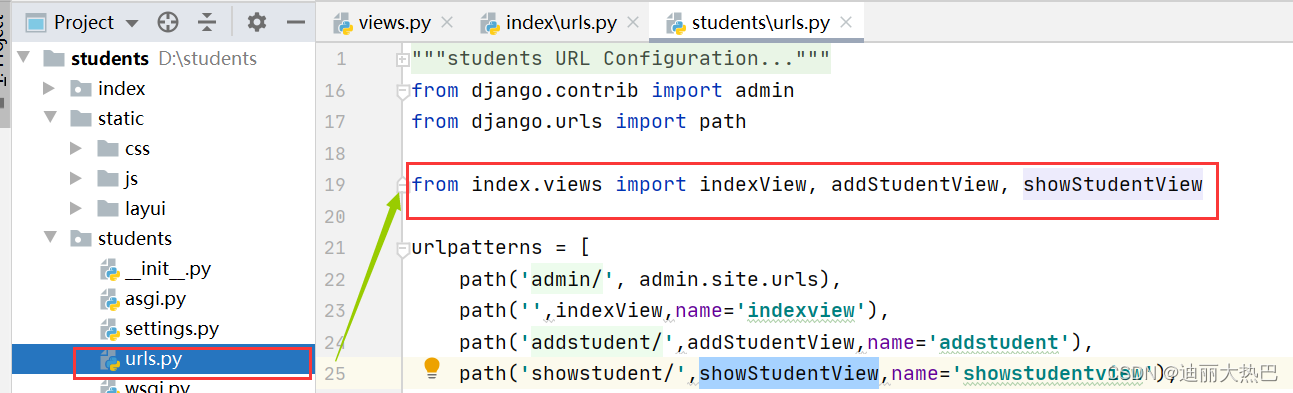
4,路由配置
(1)路由要求
- 主页面:路由地址为空,对应视图函数indexView,名称indexview
-添加学生: 路由地址addstudent/,对应视图addStudentView,名称addstudent
- 显示学生:路由地址showstudent/,对应视图showStudentView,名称showstudent
(2)完成路由配置
- 配置主路由-student里的urls.py
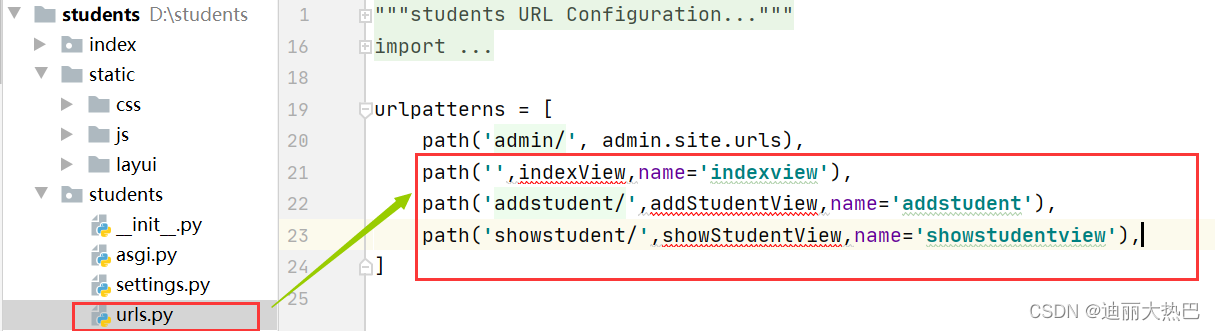
图片显示红色波浪线的原因是还没有创建对应的视图函数·四,创建应用-index
1,创建index应用
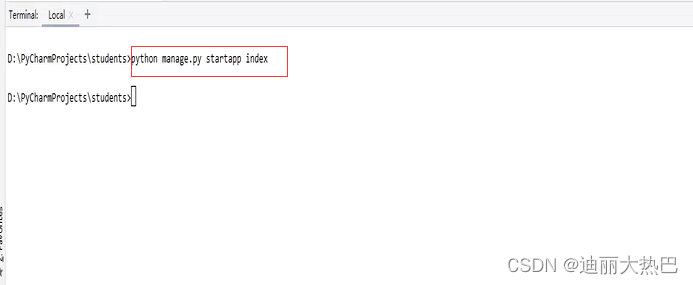
- 在控制台执行:
python manage.py startapp index
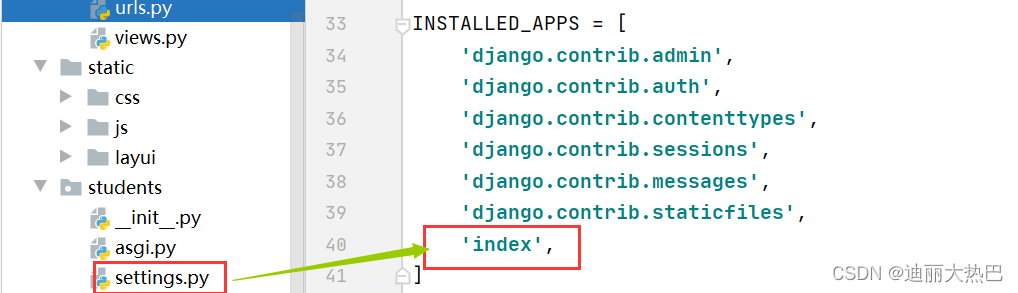
2, 注册应用
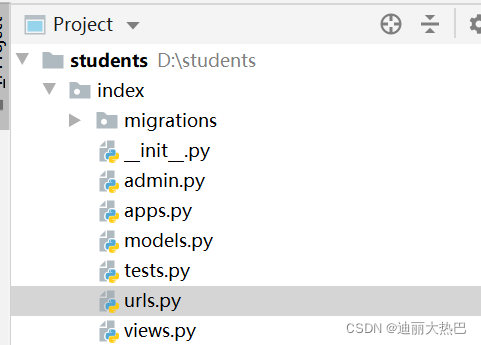
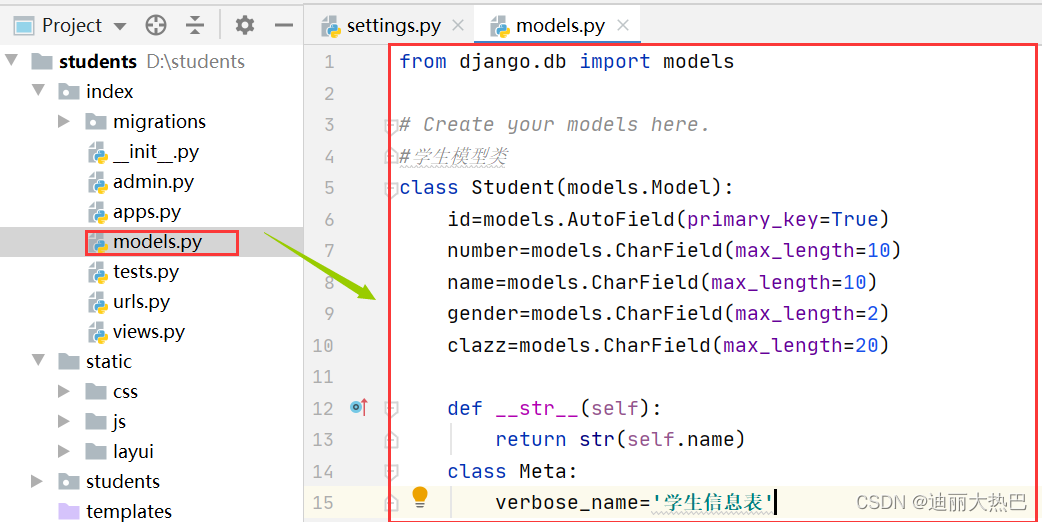
3,创建学生模型
- 在index里的models.py创建Student模型类
4,创建视图函数(空的视图函数)
- 在index里的view.py里创建三个视图函数
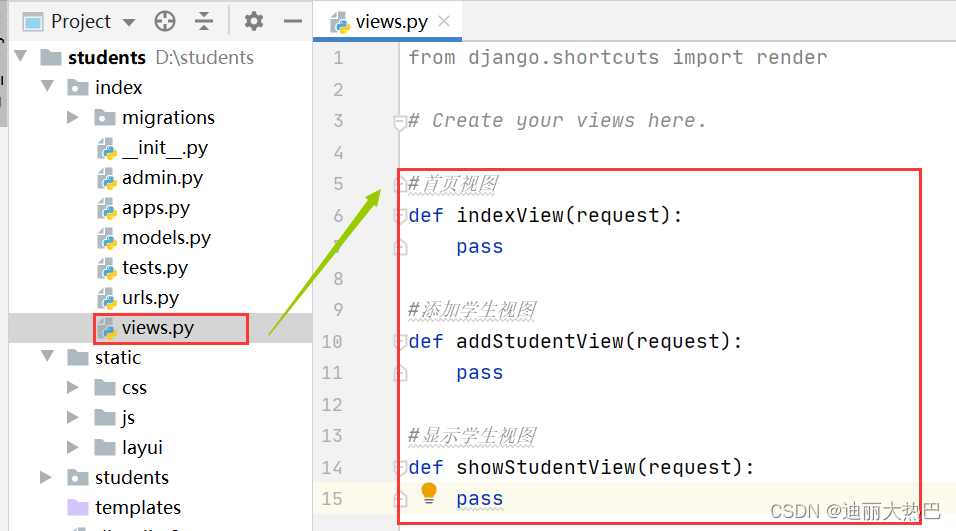
- 在主路由文件中导入上述三个视图函数
5,数据迁移,生成学生表
五,创建视图函数
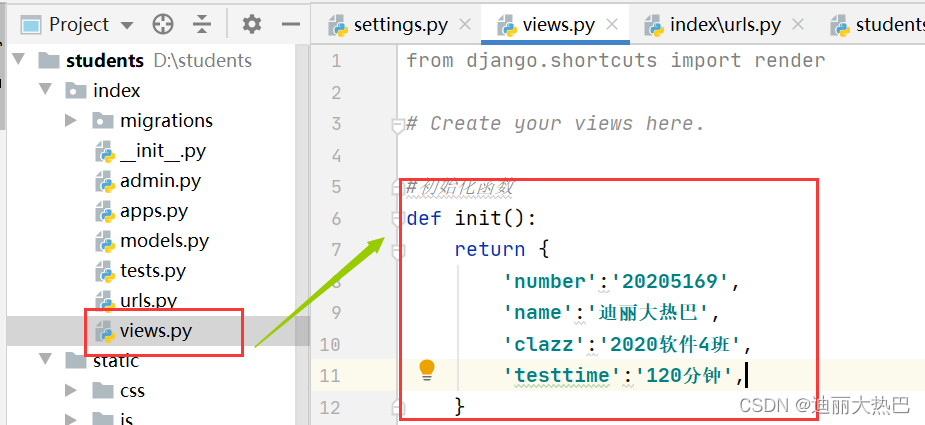
1,定义初始化函数
- 在index的view.py里创建init()函数
2,修改首页视图函数
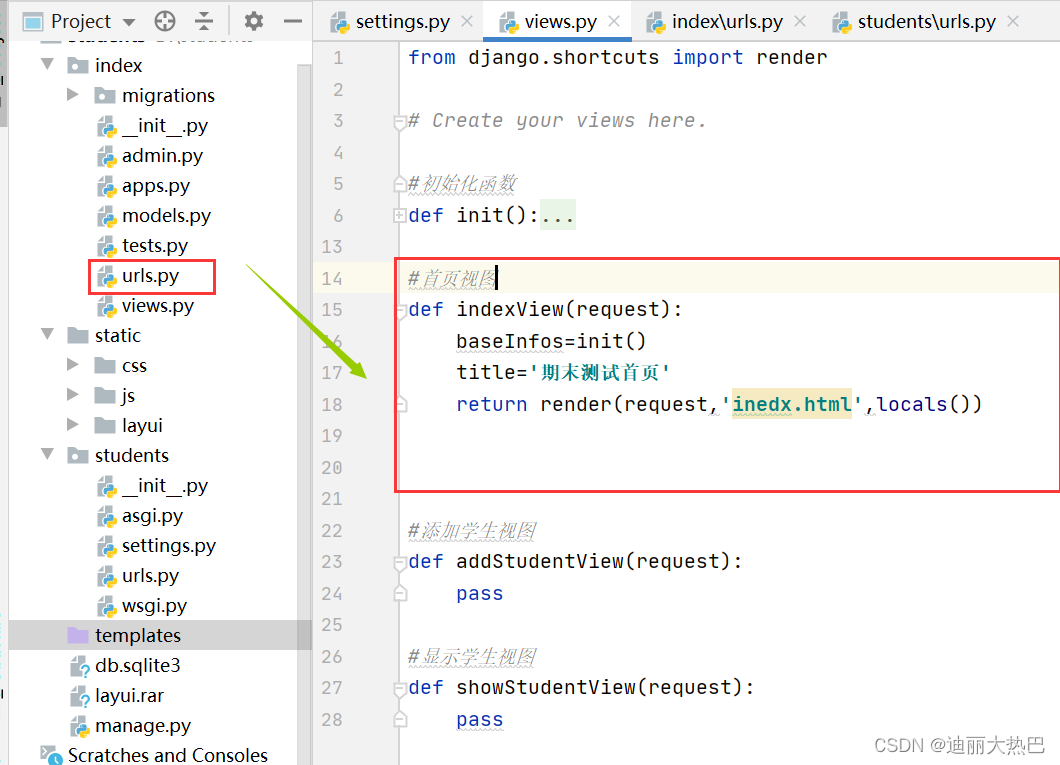
3, 修改添加学生视图函数
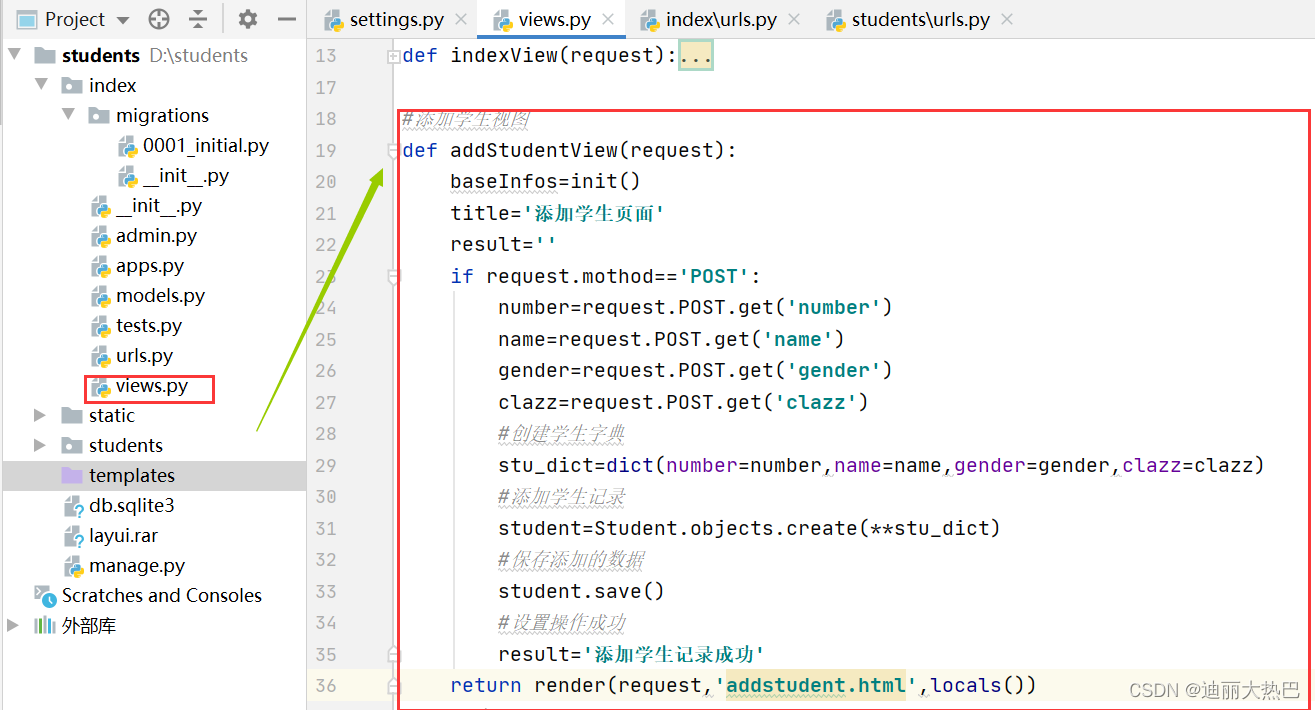
4,修改显示学生视图函数

from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect, reverse
from .models import StudentModel, StudentInformationModel, CourseModel
from django.forms.models import model_to_dict
import json
def index(request):
context = {
'status': '未登录状态'
}
return render(request, 'studentManage/index.html', context)
def login(request):
if request.method == "POST":
username = request.POST.get('username')
password = request.POST.get('password')
if not all([username, password]):
return HttpResponse('错误!用户名或密码为空!')
else:
student = StudentModel.objects.filter(username=username, password=password)
if len(student):
request.session['user'] = {
'id':student[0].stu_id,
'username': username,
'password': password
}
context = {
'status': username,
'msg': '已登录',
'lenght': 1
}
return render(request, 'studentManage/index.html',context)
else:
context = {
'msg': '用户名密码错误'
}
return render(request, 'studentManage/login.html'<





































 本文详细介绍了使用Django框架搭建一个学生信息管理系统的步骤,包括创建项目、配置静态资源、数据库配置、数据迁移、创建视图函数、实现模板页面等。通过这个教程,你可以学习到如何在Django中实现增删查改学生信息的功能。
本文详细介绍了使用Django框架搭建一个学生信息管理系统的步骤,包括创建项目、配置静态资源、数据库配置、数据迁移、创建视图函数、实现模板页面等。通过这个教程,你可以学习到如何在Django中实现增删查改学生信息的功能。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1134
1134

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








