目录
一、匿名管道具体介绍
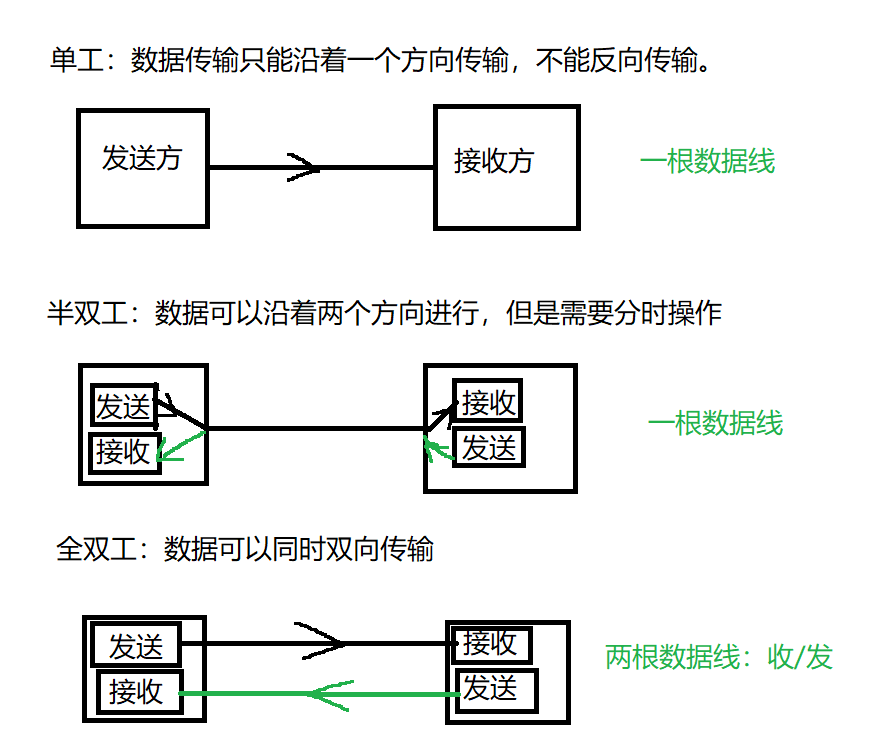
管道是一种半双工的通信方式,数据只能单向流动,而且只能在具有亲缘关系的进程间使用,进程的亲缘关系通常是指父子进程关系。
二、代码实现
1、mypipes.cpp
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"client.h"
#include"server.h"
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
int fd[2];
int fd1[2];
pipe(fd);
pipe(fd1);
pid_t child=fork();
if(child==0){
close(fd[0]);
close(fd1[1]);
client(fd[1],fd1[0]);
close(fd[1]);
close(fd1[0]);
exit(0);
}else{
close(fd[1]);
close(fd1[0]);
server(fd[0],fd1[1]);
close(fd[0]);
close(fd1[1]);
wait(NULL);
}
return 0;
}2、server.h
void server(const int rfd1,int wfd2);3、server.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include"server.h"
const int LEN=4096;
void server(const int rfd1,const int wfd2){
char buf[LEN]={'\0'};
int len=read(rfd1,buf,LEN-1);
buf[len]='\0';
int fd=open(buf,O_RDONLY);
if(fd==-1){
char buf1[]="don't open file";
write(wfd2,buf1,strlen(buf1));
}else{
while((len=read(fd,buf,LEN-1))>0){
buf[LEN]='\0';
write(wfd2,buf,strlen(buf));
}
}
close(fd);
}4、client.h
void client(const int wfd1,const int rfd2);5、client.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include"client.h"
const int LEN=4096;
void client(const int wfd1,const int rfd2){
char buf[LEN]={'\0'};
std::cout<<"please enter file name:";
std::cin>>buf;
write(wfd1,buf,strlen(buf));
int len=0;
while((len=read(rfd2,buf,LEN-1))>0){
buf[LEN]='\0';
std::cout<<buf<<std::endl;
}
}
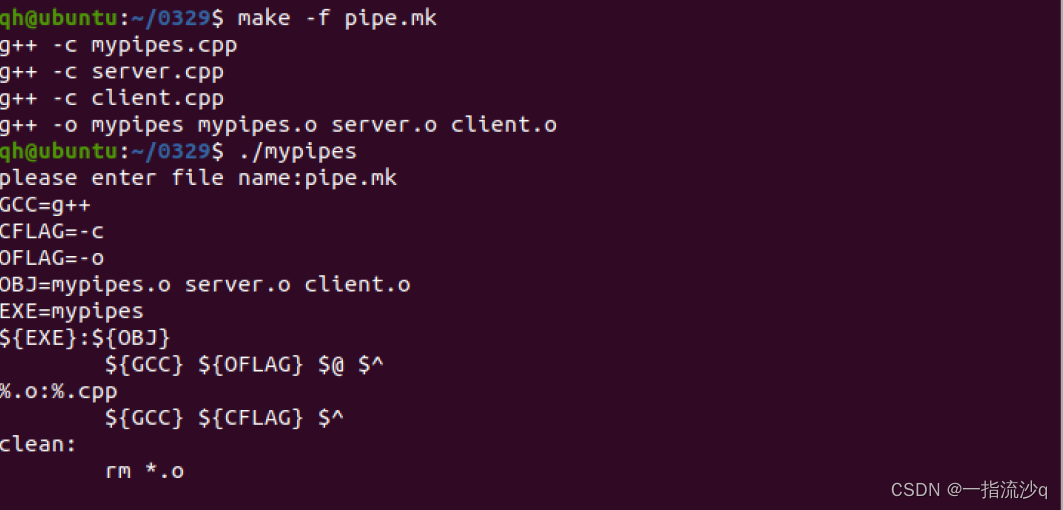
6、pipe.mk
GCC=g++
CFLAG=-c
OFLAG=-o
OBJ=mypipes.o server.o client.o
EXE=mypipes
${EXE}:${OBJ}
${GCC} ${OFLAG} $@ $^
%.o:%.cpp
${GCC} ${CFLAG} $^
clean:
rm *.o
mypipes:mypipe.o server.o client.o
g++ -o mypipes mypipes.o server.o client.o
mypipes.o:mypipes.cpp
g++ -c mypipes.cpp
server.o:server.cpp
g++ -c server.cpp
client.o:client.cpp
g++ -c client.cpp
clean:
rm *.o三、运行结果





 这篇博客详细介绍了匿名管道在父子进程间通信的实现,通过示例代码展示了如何创建匿名管道、定义客户端和服务端的功能,并给出了编译与运行的步骤。读者可以了解到如何使用C++进行简单的进程间通信操作。
这篇博客详细介绍了匿名管道在父子进程间通信的实现,通过示例代码展示了如何创建匿名管道、定义客户端和服务端的功能,并给出了编译与运行的步骤。读者可以了解到如何使用C++进行简单的进程间通信操作。

















 8752
8752

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








