老师评语:可以再利用骨架提取做一遍,两种方法比较精度,有需要的小伙伴可以直接参考!
- 整体思路
通过观察原图像,图像存在噪声点,且黑色条纹边界不清晰,使用滤波、图像增强、二值化等方法对原图像进行预处理,另外为保证测量结果的准确性,使用图像三作为原图像,测量多个距离值并求均值。

原图像

中值滤波

图像增强(锐化)
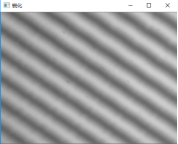
二值化

按位取反

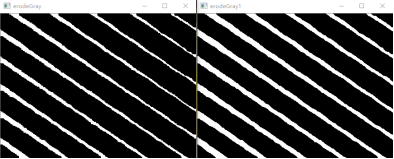
膨胀:矩形结构元素、十字形结构元素,效果相差不大

腐蚀:矩形结构元素、十字形结构元素,十字形效果较好,选择十字形
轮廓检测及绘制
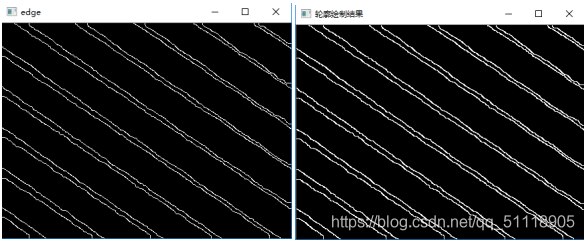
观察图像20个轮廓特征都为不规则曲线,利用霍夫直线检测无法准确检测出直线,由于图像由一个个图像点组成所以使用直线拟合的方法,将每个由像素点组成的轮廓拟合成直线。
获取轮廓像素坐标点
直线拟合
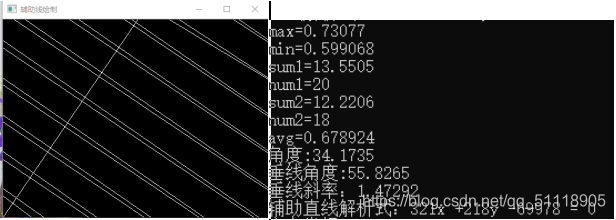
获取拟合直线斜率及解析式
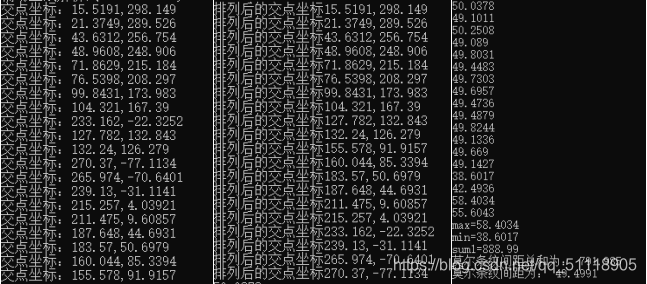
由于直线非平行直线无法直接求出图像之间的距离,求条纹间距时,两个阴影中心的距离=一个轮廓至下下轮廓的距离,使用等价代换的原则,计算直线1和直线3之间的距离。无法直接求解:方法1:两条直线,一条直线保持不变,另一条直线理解为一个个的点,求点到直线直接的距离再求均值
方法二:考虑到直线数量众多,方法一的计算量巨大,且受直线偏移影响严重。20条直线的斜率差别不大,求取20条直线的斜率,去掉最大值和最小值求均值,做出20条直线的类垂直线,求取他们之间的交点,获取交点坐标,利用公式计算交点1和交点3之间的距离,一共18个交点距离,去掉最大值和最小值求出均值,得出最终的距离49.4991个像素点。
2、程序源码
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void drawLine(Mat &img, vector<Vec4i>lines, double rows, double cols, Scalar scalar, int n)
{
Point pt1, pt2;
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size();i++)
{
float rho = lines[i][0];
float theta = lines[i][1];
double a = cos(theta);
double b = sin(theta);
double x0 = a*rho, y0 = b*rho;
double length = max(rows, cols);
pt1.x = cvRound(x0 + length*(-b));
pt1.y = cvRound(y0 + length*(a));
pt2.x = cvRound(x0 - length*(-b));
pt2.y = cvRound(y0 - length*(a));
line(img, pt1, pt2, scalar, n);
}
}
int main() {
Mat image, gray, src, dst, gray1;//定义Mat类型的变量
image = imread("莫尔条纹3.png", 0);//读取程序文件夹中的图像,并赋值给变量image,0代表灰度图,1代表彩色图
if (!image.data) {
printf("could not find image");
return -1;
}
namedWindow("image", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); //定义用户可调节大小的窗口,并命名为image
imshow("image", image); //在image窗口里展示image图像
int w = image.cols;
int h = image.rows;
cout << "图像宽:" << w << endl;
cout << "图像高:" << h << endl;
//图像去噪(中值滤波)
medianBlur(image, src, 7);
imshow("meidan denoise demo", src);
//图像锐化
Mat kernel = (Mat_<char>(3, 3) << 0, -1, 0, -1, 5, -1, 0, -1, 0);
filter2D(src, dst, src.depth(), kernel);
imshow("锐化", dst);
//二值化
threshold(dst, gray, 120, 255, THRESH_BINARY );
imshow("gray", gray);
//按位取反
bitwise_not(gray, gray1);
imshow("gray1",gray1);
//形态学操作-膨胀
Mat struct1, struct2;
struct1 = getStructuringElement(0, Size(3, 3)); //矩形结构元素
struct2 = getStructuringElement(1, Size(3, 3)); //十字结构元素
Mat dilateGray, dilateGray1;
dilate(gray1, dilateGray, struct1, Point(-1, -1), 1);
dilate(gray1, dilateGray1, struct2, Point(-1, -1), 2);
imshow("dilateGray", dilateGray);
imshow("erodeGray1", dilateGray1);
//形态学操作-腐蚀
Mat erodeGray, erodeGray1;
Mat struct3, struct4;
struct3 = getStructuringElement(0, Size(3, 3)); //矩形结构元素
struct4 = getStructuringElement(1, Size(3, 3)); //十字结构元素
erode(dilateGray, erodeGray, struct3, Point(-1, -1), 3);
erode(dilateGray, erodeGray1, struct4, Point(-1, -1), 3);
imshow("erodeGray", erodeGray);
imshow("erodeGray1", erodeGray1);
Mat edge;
Canny(erodeGray, edge, 80, 180, 3, false);
//imshow("edge",edge);
//轮廓发现与绘制
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
Vec4f line0, line1, line2, line3, line4, line5, line6, line7, line8,line9,line10,line11,line12,line13,line14,line15, line16, line17, line18,line19;
findContours(edge, contours, hierarchy, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point());
//绘制轮廓
for (int t = 0; t < hierarchy.size(); t++)
{
drawContours(edge, contours, t, Scalar(255, 255, 255), 1, 4);
//printf("%d", t);
}
int m0, n0;
for (m0 = 0; m0 < contours.size(); m0++)
{
for (n0 = 0; n0 < contours[m0].size(); n0++)
cout << contours[m0][n0] << "";
cout << "\n";
}
//显示结果
imshow("轮廓绘制结果", edge);
vector<Point2f>point_0;
vector<Point2f>point_1;
vector<Point2f>point_2;
vector<Point2f>point_3;
vector<Point2f>point_4;
vector<Point2f>point_5;
vector<Point2f>point_6;
vector<Point2f>point_7;
vector<Point2f>point_8;
vector<Point2f>point_9;
vector<Point2f>point_10;
vector<Point2f>point_11;
vector<Point2f>point_12;
vector<Point2f>point_13;
vector<Point2f>point_14;
vector<Point2f>point_15;
vector<Point2f>point_16;
vector<Point2f>point_17;
vector<Point2f>point_18;
vector<Point2f>point_19;
int m, n;
for (m = 0; m < contours.size(); m++)
{
for (n = 0; n < contours[m].size(); n++)
{
switch (m)
{
case 0:
point_0.push_back(contours[m][n]);
break;
case 1:








 本文介绍了一种C++处理和分析莫尔条纹的方法,包括图像预处理(中值滤波、图像增强、二值化、按位取反)、形态学操作(膨胀和腐蚀)、轮廓检测、直线拟合等步骤。通过对20个轮廓的直线拟合,计算莫尔条纹间距,最后通过去除最大和最小值求得平均间距49.4991像素。
本文介绍了一种C++处理和分析莫尔条纹的方法,包括图像预处理(中值滤波、图像增强、二值化、按位取反)、形态学操作(膨胀和腐蚀)、轮廓检测、直线拟合等步骤。通过对20个轮廓的直线拟合,计算莫尔条纹间距,最后通过去除最大和最小值求得平均间距49.4991像素。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








