redis 缓存淘汰策略
淘汰策略
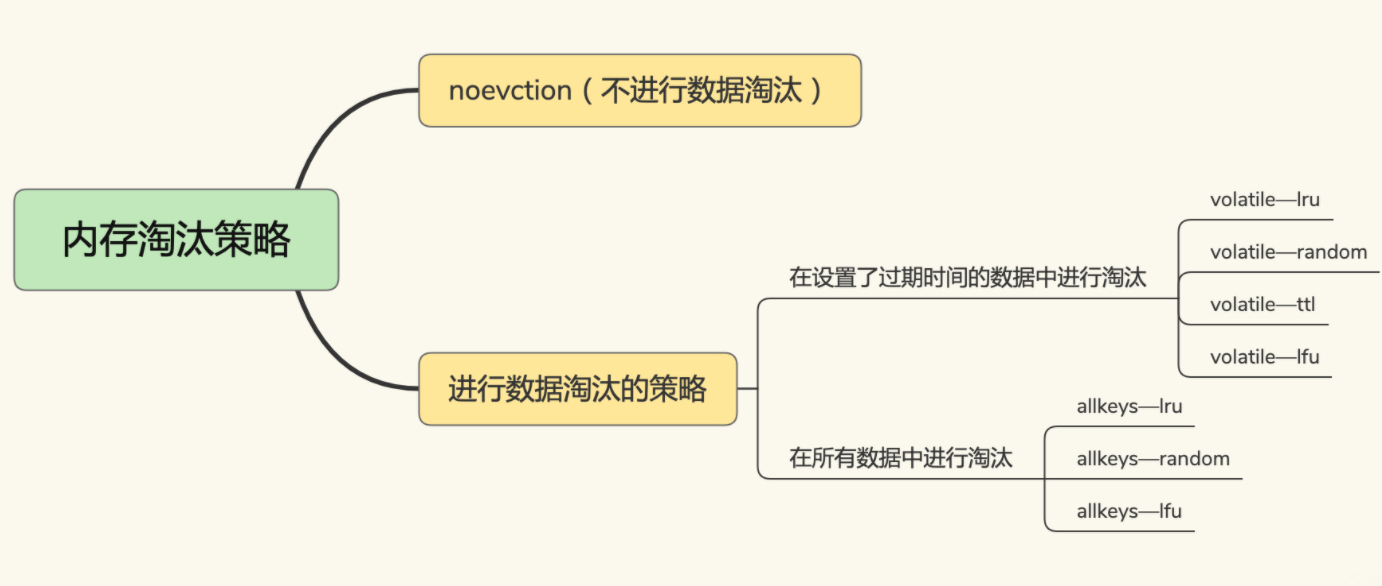
- noevction:一旦数据被写满了,再有写请求的时候直接返回错误。
- volatile-ttl:在筛选时,会针对设置了过期时间的键值对,根据过期时间的先后进行删除,越早过期的越先被删除。
- volatile-random:就像它的名称一样,在设置了过期时间的键值对中,进行随机删除。
- volatile-lru 会使用:LRU 算法筛选设置了过期时间的键值对。
- volatile-lfu 会使用:LFU 算法选择设置了过期时间的键值对。
- allkeys-randoms:从所有键值对选择并随机删除。
- allkeys-lru策略:使用lru算法在所有数据中筛选。
- allkeys-lfu:使用lfu算法在所有数据中筛选。
LRU算法
LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据。redis采用的是近似LRU算法:每次访问时,给该对象记录一下当前的时间戳(单位/秒),当需要删除数据时,随机选取5个元素,删除最久未被访问的。、
LRU配置参数
Redis配置中和LRU有关的有三个:
maxmemory: 配置Redis存储数据时指定限制的内存大小,比如100m。当缓存消耗的内存超过这个数值时,
将触发数据淘汰。该数据配置为0时,表示缓存的数据量没有限制,
即LRU功能不生效。64位的系统默认值为0,32位的系统默认内存限制为3GB。maxmemory_policy: 触发数据淘汰后的淘汰策略。maxmemory_samples: 随机采样的精度,也就是随即取出key的数目。该数值配置越大,
越接近于真实的LRU算法,但是数值越大,相应消耗也变高,对性能有一定影响,样本值默认为5。
实现逻辑
redis的lru近似算法有三个要点:
-
守护线程,每秒更新10次server.lruclock值(unix time的低24位)。
-
redis对象首次创建和后续访问时,把当前server.lruclock赋值给该对象的lru。
-
redis在处理命令时,会检查内存使用情况,如果超过限制且配置了LRU策略,则:
a). 随机选择5个元素。
b). 删除其中最久未被访问的元素。
c). 已使用内存是否还是超过限制,如果是则跳转到步骤a继续,否则本次删除结束。
再来看看源代码:
LRU算法需要一个双向链表来记录数据的最近被访问顺序,但是出于节省内存的考虑,Redis的LRU算法并非完整的实现。
/* The actual Redis Object */
#define REDIS_LRU_BITS 24 // 记录unix time的低24bits
#define REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_MAX // 最大值
#define REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION 1 // 精度
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4; // 对象的类型如zset/set/hash等等
unsigned encoding:4; // 对象编码如 ziplist/intset/skiplist 等等
unsigned lru:REDIS_LRU_BITS; // 对象的"热度"
int refcount; // 引用计数
void *ptr; // 指向对象的指针
} robj;
创建redis对象时的代码:
robj *createObject(int type, void *ptr) {
robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(*o));
o->type = type;
o->encoding = REDIS_ENCODING_RAW;
o->ptr = ptr;
o->refcount = 1;
// server.lruclock会由redis的后台线程每秒更新10次
o->lru = server.lruclock;
return o;
}
后续再次访问redis对象时。更新lru字段:
robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
// 在执行rdb或者aof任务时,不能更新该字段
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1)
val->lru = server.lruclock;
return val;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
当LRU策略触发时,如何选择对象:
else if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU ||
server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU)
{
for (k = 0; k < server.maxmemory_samples; k++) { // server.maxmemory_samples 默认是5
sds thiskey;
long thisval;
robj *o;
de = dictGetRandomKey(dict); // 随机选择一个对象
thiskey = dictGetKey(de);
/* When policy is volatile-lru we need an additional lookup
* to locate the real key, as dict is set to db->expires. */
if (server.maxmemory_policy == REDIS_MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU)
de = dictFind(db->dict, thiskey);
o = dictGetVal(de);
thisval = estimateObjectIdleTime(o); // 获取对象的lru值
/* Higher idle time is better candidate for deletion */
if (bestkey == NULL || thisval > bestval) {
bestkey = thiskey;
bestval = thisval;
}
}
}
/* Given an object returns the min number of seconds the object was never
* requested, using an approximated LRU algorithm. */
unsigned long estimateObjectIdleTime(robj *o) { // 计算对象距离上次访问流逝的时间,单位秒
if (server.lruclock >= o->lru) {
return (server.lruclock - o->lru) * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION;
} else { // o->lru > server.lruclock,说明距离上次访问已经至少超过一个REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_MAX了(194天)
return ((REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_MAX - o->lru) + server.lruclock) *
REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION;
}
}
Redis3.0之后又改善了算法的性能,会提供一个待淘汰候选key的pool,里面默认有16个key,按照空闲时间排好序。更新时从Redis键空间随机选择N个key,分别计算它们的空闲时间idle,key只会在pool不满或者空闲时间大于pool里最小的时,才会进入pool,然后从pool中选择空闲时间最大的key淘汰掉。
Redis随机选择maxmemory_samples数量的key,然后计算这些key的空闲时间idle time,当满足条件时(比pool中的某些键的空闲时间还大)就可以进pool。pool更新之后,就淘汰pool中空闲时间最大的键。
estimateObjectIdleTime用来计算Redis对象的空闲时间:
/* Given an object returns the min number of milliseconds the object was never
* requested, using an approximated LRU algorithm. */
unsigned long long estimateObjectIdleTime(robj *o) {
unsigned long long lruclock = LRU_CLOCK();
if (lruclock >= o->lru) {
return (lruclock - o->lru) * LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION;
} else {
return (lruclock + (LRU_CLOCK_MAX - o->lru)) *
LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION;
}
}
空闲时间基本就是就是对象的lru和全局的LRU_CLOCK()的差值乘以精度LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION,将秒转化为了毫秒。
LFU算法
LFU(Least Frequently Used,使用频率最少的)优先淘汰最近使用的少的数据,其核心思想是“如果一个数据在最近一段时间很少被访问到,那么将来被访问的可能性也很小”。
与LRU的区别:
| 对比项 | 近似LRU算法 | LFU算法 |
|---|---|---|
| 最先过期的数据 | 最近未被访问的 | 最近一段时间访问的最少的 |
| 适用场景 | 数据被连续访问场景 | 数据在一段时间内被连续访问 |
| 缺点 | 新增key将占据缓存 | 历史访问次数超大的key淘汰速度取决于lfu-decay-time |
LFU数据淘汰策略下,redisObject 的 lru:LRU_BITS 字段(24位)将分为2部分存储:
- Ldt:last decrement time,16位,精度分钟,存储上一次 LOG_C 更新的时间。
- LOG_C:logarithmic counter,8位,最大255,存储key被访问频率,随时间衰减。
LFU的核心配置:
- lfu-log-factor:counter 增长对数因子,调整
概率计数器 counter 的增长速度,lfu-log-factor值越大
counter 增长越慢;lfu-log-factor 默认10。 - lfu-decay-time:衰变时间周期,调整
概率计数器的减少速度,单位分钟,默认1。- N 分钟未访问,counter 将衰减 N/lfu-decay-time,直至衰减到0;
- 若配置为0:表示每次访问都将衰减 counter;
counter 的区间是0-255, 其增长与访问次数呈现对数增长的趋势,随着访问次数越来越大,counter 增长的越来越慢。Redis 官网提供的在 不同 factor 下,不同命中率 时 counter 的值示例如下:
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| factor | 100 hits | 1000 hits | 100K hits | 1M hits | 10M hits |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| 0 | 104 | 255 | 255 | 255 | 255 |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| 1 | 18 | 49 | 255 | 255 | 255 |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| 10 | 10 | 18 | 142 | 255 | 255 |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| 100 | 8 | 11 | 49 | 143 | 255 |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
不同于 LRU 算法,LFU 算法下 Ldt 的值不是在key被访问时更新,而是在 内存达到 maxmemory时,触发淘汰策略时更新。
Redis LFU 淘汰策略逻辑:
- 随机抽样选出N个数据放入【待淘汰数据池 evictionPoolEntry】;
- 再次淘汰:随机抽样选出【最多N个数据】,更新 Ldt 和 counter 的值,只要 counter 比【待淘汰数据池
evictionPoolEntry】中的【任意一条】数据的 counter 小,则将该数据填充至 【待淘汰数据池】;- evictionPoolEntry 的容容量是 EVPOOL_SIZE = 16;
- 执行淘汰: 挑选【待淘汰数据池】中 counter 最小的一条数据进行淘汰;
接下来看一下源码:
在lookupKey中:
robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key, int flags) {
dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
/* Update the access time for the ageing algorithm.
* Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger
* a copy on write madness. */
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 &&
server.aof_child_pid == -1 &&
!(flags & LOOKUP_NOTOUCH))
{
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
updateLFU(val);
} else {
val->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
}
}
return val;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
当采用LFU策略时,updateLFU更新lru:
// 访问对象时更新 LFU。
// 首先,如果达到递减时间,则递减计数器。
// 然后对数递增计数器,并更新访问时间。
void updateLFU(robj *val) {
// 首先 根据当前时间 参考 lfu-decay-time 配置 进行一次衰减;
unsigned long counter = LFUDecrAndReturn(val);
// 再参考 lfu_log_factor 配置 进行一次增长;
counter = LFULogIncr(counter);
// 更新 lru;
val->lru = (LFUGetTimeInMinutes()<<8) | counter;
}
降低LFUDecrAndReturn
首先,LFUDecrAndReturn对counter进行减少操作:
/* If the object decrement time is reached decrement the LFU counter but
* do not update LFU fields of the object, we update the access time
* and counter in an explicit way when the object is really accessed.
* And we will times halve the counter according to the times of
* elapsed time than server.lfu_decay_time.
* Return the object frequency counter.
*
* This function is used in order to scan the dataset for the best object
* to fit: as we check for the candidate, we incrementally decrement the
* counter of the scanned objects if needed. */
unsigned long LFUDecrAndReturn(robj *o) {
unsigned long ldt = o->lru >> 8;
unsigned long counter = o->lru & 255;
unsigned long num_periods = server.lfu_decay_time ? LFUTimeElapsed(ldt) / server.lfu_decay_time : 0;
if (num_periods)
counter = (num_periods > counter) ? 0 : counter - num_periods;
return counter;
}
函数首先取得高16 bits的最近降低时间ldt与低8 bits的计数器counter,然后根据配置的lfu_decay_time计算应该降低多少。
LFUTimeElapsed用来计算当前时间与ldt的差值:
/* Return the current time in minutes, just taking the least significant
* 16 bits. The returned time is suitable to be stored as LDT (last decrement
* time) for the LFU implementation. */
unsigned long LFUGetTimeInMinutes(void) {
return (server.unixtime/60) & 65535;
}
/* Given an object last access time, compute the minimum number of minutes
* that elapsed since the last access. Handle overflow (ldt greater than
* the current 16 bits minutes time) considering the time as wrapping
* exactly once. */
unsigned long LFUTimeElapsed(unsigned long ldt) {
unsigned long now = LFUGetTimeInMinutes();
if (now >= ldt) return now-ldt;
return 65535-ldt+now;
}
具体是当前时间转化成分钟数后取低16 bits,然后计算与ldt的差值now-ldt。当ldt > now时,默认为过了一个周期(16 bits,最大65535),取值65535-ldt+now。
然后用差值与配置lfu_decay_time相除,LFUTimeElapsed(ldt) / server.lfu_decay_time,已过去n个lfu_decay_time,则将counter减少n,counter - num_periods。
增长LFULogIncr
增长函数LFULogIncr如下:
/* Logarithmically increment a counter. The greater is the current counter value
* the less likely is that it gets really implemented. Saturate it at 255. */
uint8_t LFULogIncr(uint8_t counter) {
if (counter == 255) return 255;
double r = (double)rand()/RAND_MAX;
double baseval = counter - LFU_INIT_VAL;
if (baseval < 0) baseval = 0;
double p = 1.0/(baseval*server.lfu_log_factor+1);
if (r < p) counter++;
return counter;
}
新生key策略
另外一个问题是,当创建新对象的时候,对象的counter如果为0,很容易就会被淘汰掉,还需要为新生key设置一个初始counter,createObject:
robj *createObject(int type, void *ptr) {
robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(*o));
o->type = type;
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_RAW;
o->ptr = ptr;
o->refcount = 1;
/* Set the LRU to the current lruclock (minutes resolution), or
* alternatively the LFU counter. */
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
o->lru = (LFUGetTimeInMinutes()<<8) | LFU_INIT_VAL;
} else {
o->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
}
return o;
}
counter会被初始化为LFU_INIT_VAL,默认5。
pool
pool算法就与LRU算法一致了:
if (server.maxmemory_policy & (MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LRU|MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) ||
server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL)
计算idle时有所不同:
} else if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
/* When we use an LRU policy, we sort the keys by idle time
* so that we expire keys starting from greater idle time.
* However when the policy is an LFU one, we have a frequency
* estimation, and we want to evict keys with lower frequency
* first. So inside the pool we put objects using the inverted
* frequency subtracting the actual frequency to the maximum
* frequency of 255. */
idle = 255-LFUDecrAndReturn(o);
使用了255-LFUDecrAndReturn(o)当做排序的依据。
参考资料








 本文详细介绍了Redis中各种缓存淘汰策略,包括LRU和LFU算法的工作原理及其实现细节。
本文详细介绍了Redis中各种缓存淘汰策略,包括LRU和LFU算法的工作原理及其实现细节。
















 958
958

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








