一、顺序栈的定义
- 栈是限定仅在表尾进行插入或删除操作的线性表。因此,对顺序栈来说,表尾端有其特殊含义,成为栈顶,相应的,表头成为栈底。不含元素的栈成为空栈。
- 栈是一种先进后出,后进先出的数据结构。(访问受限)
- 对于栈的操作都是从栈顶开始操作,即插入删除都是从栈顶开始操作。

1.顺序栈设计
typedef struct Stack
{
int* base; //用来申请动态内存;
int stackSize; //当前栈总体个数;
int top; //栈顶指针,实际为下标,书上为指针;
}Stack,*PStack;
2.顺序栈的基本操作
(1)初始化

void InitStack(PStack ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if (ps == NULL)return;
ps->base = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * INIT_SIZE);//申请了默认大小个字节数;
assert(ps->base != NULL);
ps->top = 0; //有效个数为0;
ps->stackSize = INIT_SIZE;//申请的总长度;
}
(2)判满
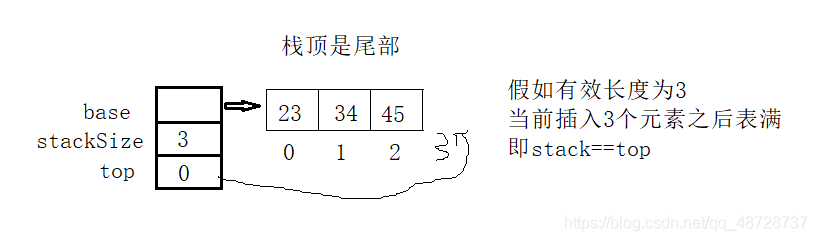
bool IsFull(PStack ps)
{
return ps->top == ps->stackSize;//stackSize==top时,栈满;
}
(3)扩容操作
扩容操作之后栈的长度如图,用realloc扩容时,不用动数据,数据会自动拷贝。如果用malloc重新申请空间时,数据需要手动拷贝,原来的空间也需要释放。

//扩容,假如扩充两倍
void Inc(PStack ps)
{
ps->stackSize *= 2;
ps->base = (int*)realloc(ps->base,sizeof(int) * ps->stackSize);//表示将扩充两倍后的空间给base;
assert(ps->base != NULL);
}
(4)入栈操作
bool Push(PStack ps, int val)
{
if (IsFull(ps)) //判满,由于我们做的是不定长栈,所以有自动扩容功能;
{
Inc(ps); //此操作后,放数据时空间肯定够用;
}
ps->base[ps->top] = val;//将top位置填充数据;
ps->top++;
return true;
}
(5)获取栈顶元素
获取栈顶元素时,我们一般用int型但是不对,int型的数据返回值类型和base相同,所以不能保证肯定冲突,所以用bool类型。
bool IsEmpty(PStack ps)//判空函数;
{
return ps->top == 0;
}
//int GetTop(PStack ps)//出错时的返回值一定和某个正常值冲突;所以不能这样设计函数。
//所以要得到栈顶元素需要定义一个输出参数rtval;在调用时传入参数地址即可;
bool GetTop(PStack ps,int* rtval)
{
if (IsEmpty(ps)) return false;
*rtval = ps->base[ps->top - 1];
return true;
}
(6)获取栈顶元素并删除
和获取栈顶元素设计是一样的,现在需要将获取栈顶元素的top直接–就可以,将值直接覆盖掉。

bool IsEmpty(PStack ps)//判空函数;
{
return ps->top == 0;
}
bool DelTop(PStack ps, int* rtval)
{
if (IsEmpty(ps)) return false; //判空;
*rtval = ps->base[--ps->top]; //两种方法都可以;
//*rtval = ps->base[ps->top - 1];
//ps->top--;
return true;
}
(7)清空数据
void Clear(PStack ps)
{
ps->top == 0;
}
(8)销毁
void Destroy(PStack ps)
{
free(ps->base);
ps->base = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->stackSize = 0;
}
3.完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#define INIT_SIZE 10
typedef struct Stack
{
int* base; //用来申请动态内存;
int stackSize; //当前栈总体个数;
int top; //栈顶指针,实际为当前可以存放数据的下标,书上为指针;
}Stack,*PStack;
//初始化
void InitStack(PStack ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if (ps == NULL)return;
ps->base = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * INIT_SIZE);
assert(ps->base != NULL);
ps->top = 0;
ps->stackSize = INIT_SIZE;
}
//判满
bool IsFull(PStack ps)
{
return ps->top == ps->stackSize;
}
//扩容,假如扩充两倍
void Inc(PStack ps)
{
ps->stackSize *= 2;
ps->base = (int*)realloc(ps->base,sizeof(int) * ps->stackSize);//表示将扩充两倍后的空间给base;
assert(ps->base != NULL);
}
//入栈操作
bool Push(PStack ps, int val)
{
if (IsFull(ps))
{
Inc(ps); //此操作后,放数据时空间肯定够用;
}
ps->base[ps->top] = val;//将top位置填充数据;
ps->top++;
return true;
}
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PStack ps)
{
return ps->top == 0;
}
//获取栈顶元素的值
//int GetTop(PStack ps)//出错时的返回值一定和某个正常值冲突;
bool GetTop(PStack ps,int* rtval)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
if (ps == NULL)return false;
if (IsEmpty(ps)) return false;
*rtval = ps->base[ps->top - 1];
return true;
}
//获取栈顶元素的值并删除
bool Pop(PStack ps, int* rtval)
{
assert(ps != NULL && !IsEmpty(ps));
if (ps == NULL || IsEmpty(ps)) return false;
*rtval = ps->base[--ps->top]; //两种方法都可以;
//*rtval = ps->base[ps->top - 1];
//ps->top--;
return true;
}
//获取有效元素个数
int Get_length(PStack ps)
{
return ps->top;
}
//清空数据
void Clear(PStack ps)
{
ps->top == 0;
}
//销毁
void Destroy(PStack ps)
{
free(ps->base);
ps->base = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->stackSize = 0;
}
int main()
{
Stack head;
InitStack(&head);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Push(&head, i);
}
int a = Get_length(&head);
printf("%d\n",a );
int rtval = 0;
while (!IsEmpty(&head))
{
GetTop(&head, &rtval);
printf("%d ", rtval);
Pop(&head, &rtval);
}
printf("\n");
a = Get_length(&head);
printf("%d\n", a);
return 0;
}
运行结果:









 本文介绍了顺序栈的定义,详细阐述了顺序栈的设计,包括初始化、判满、扩容操作、入栈、获取栈顶元素、获取栈顶元素并删除、清空数据以及销毁等基本操作。特别提到在扩容时,使用realloc可以自动拷贝数据,而使用malloc则需要手动拷贝并释放原有空间。
本文介绍了顺序栈的定义,详细阐述了顺序栈的设计,包括初始化、判满、扩容操作、入栈、获取栈顶元素、获取栈顶元素并删除、清空数据以及销毁等基本操作。特别提到在扩容时,使用realloc可以自动拷贝数据,而使用malloc则需要手动拷贝并释放原有空间。
















 701
701

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








