链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,其物理结构不能只管的表示数据元素的逻辑顺序,数据元
素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列的结点(链表中的每一个元素称为结点)组成,
结点可以在运行时动态生成。
单向链表



/**
* 单向链表
* @param <T>
*/
public class LinkList<T> implements Iterable<T> {
//记录头结点
private Node head;
//记录链表的长度
private int N;
public LinkList() {
//初始化头结点
head = new Node(null, null);
N = 0;
}
//清空链表
public void clear() {
head.next = null;
head.item = null;
N = 0;
}
//获取链表的长度
public int length() {
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
//获取指定位置i出的元素
public T get(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法!");
}
Node n = head.next;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
n = n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
//向链表中添加元素t
public void insert(T t) {
//找到最后一个节点
Node n = head;
while (n.next != null) {
n = n.next;
}
Node newNode = new Node(t, null);
n.next = newNode;
//链表长度+1
N++;
}
//向指定位置i处,添加元素t
public void insert(int i, T t) {
if (i < 0 || i > N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法!");
}
//寻找位置i之前的结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index <= i - 1; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//位置i的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//构建新的结点,让新结点指向位置i的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, curr);
//让之前的结点指向新结点
pre.next = newNode;
//长度+1
N++;
}
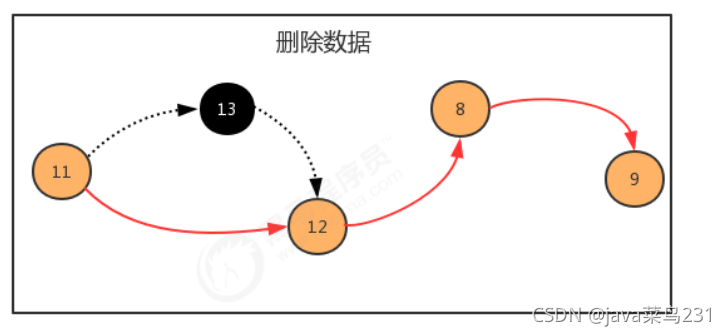
//删除指定位置i处的元素,并返回被删除的元素
public T remove(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//寻找i之前的元素
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index <= i - 1; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//当前i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//前一个结点指向下一个结点,删除当前结点
pre.next = curr.next;
//长度-1
N--;
return curr.item;
}
//查找元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t) {
Node n = head;
for (int i = 0; n.next != null; i++) {
n = n.next;
if (n.item.equals(t)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//结点类
private class Node {
//存储数据
T item;
//下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new LIterator();
}
private class LIterator implements Iterator<T> {
private Node n;
public LIterator() {
this.n = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next != null;
}
@Override
public T next() {
n = n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
public void reverse() {
if (N == 0) {
//当前是空链表,不需要反转
return;
}
reverse(head.next);
}
/**
* @param curr 当前遍历的结点
* @return 反转后当前结点上一个结点
*/
public Node reverse(Node curr) {
//已经到了最后一个元素
if (curr.next == null) {
//反转后,头结点应该指向原链表中的最后一个元素
head.next = curr;
return curr;
}
//当前结点的上一个结点
Node pre = reverse(curr.next);
pre.next = curr;
//当前结点的下一个结点设为null
curr.next = null;
//返回当前结点
return curr;
}
}
双向链表
双向链表也叫双向表,是链表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点都由一个数据域和两个指针域组成,数据域用
来存储数据,其中一个指针域用来指向其后继结点,另一个指针域用来指向前驱结点。链表的头结点的数据域不存
储数据,指向前驱结点的指针域值为null,指向后继结点的指针域指向第一个真正存储数据的结点。

/**
* 双向链表
*
* @param <T>
*/
public class TowWayLinkList<T> implements Iterable<T> {
//首结点
private Node head;
//最后一个结点
private Node last;
//链表的长度
private int N;
public TowWayLinkList() {
last = null;
head = new Node(null, null, null);
N = 0;
}
//清空链表
public void clear() {
last = null;
head.next = last;
head.pre = null;
head.item = null;
N = 0;
}
//获取链表长度
public int length() {
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
//插入元素t
public void insert(T t) {
if (last == null) {
last = new Node(t, head, null);
head.next = last;
} else {
Node oldLast = last;
Node node = new Node(t, oldLast, null);
oldLast.next = node;
last = node;
}
//长度+1
N++;
}
//向指定位置i处插入元素t
public void insert(int i, T t) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//找到位置i的前一个结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//当前结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//构建新结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, pre, curr);
curr.pre = newNode;
pre.next = newNode;
//长度+1
N++;
}
//获取指定位置i处的元素
public T get(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//寻找当前结点
Node curr = head.next;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
return curr.item;
}
//找到元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t) {
Node n = head;
for (int i = 0; n.next != null; i++) {
n = n.next;
if (n.next.equals(t)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//删除位置i处的元素,并返回该元素
public T remove(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= N) {
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//寻找i位置的前一个元素
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//i位置的元素
Node curr = pre.next;
//i位置的下一个元素
Node curr_next = curr.next;
pre.next = curr_next;
curr_next.pre = pre;
//长度-1;
N--;
return curr.item;
}
//获取第一个元素
public T getFirst() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return head.next.item;
}
//获取最后一个元素
public T getLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return last.item;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new TIterator();
}
private class TIterator implements Iterator {
private Node n = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next != null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n = n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
//结点类
private class Node {
public Node(T item, Node pre, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
//存储数据
public T item;
//指向上一个结点
public Node pre;
//指向下一个结点
public Node next;
}
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








