一、exec族函数
exec族函数作用:fork创建新进程后,经常会在新进程中调用exec函数去执行另外一个程序。当进程调用exec函数时,该进程被完全替换成新程序。exec函数并不创建新进程,前后进程的id并不改变。
功能:在调用进程内部执行一个可执行文件。可执行文件既可以是二进制文件,也可以是Linux下可执行的脚本文件。
返回值:exec函数族的函数执行成后不会返回,调用失败时,会设置error返回-1,然后从原程序的调用点接着往下执行。
1.execl:参数最后必须以NULL结尾
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//函数原型:int execl(const char *path,const char *arg,...)
int main(void)
{
printf("before execl\n");
if(execl("./bin/echoarg","echoarg","abc","def",NULL) == -1)
//if(execl("/bin/ls","ls","-l",NULL) == -1)
{
printf("execl failed!\n");
perror("why");
}
printf("after execl\n");
return 0;
}
结果是: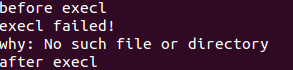
perror函数的作用是将错误的原因显示出来
2.execlp:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//函数原型:int execlp(const char *file,const char *arg,...)
int main(void)
{
printf("this pro get system date:\n");
if(execlp("ps","ps",NULL,NULL) == -1){
printf("execl failed!\n");
perror("why");
}
printf("after execl\n");
return 0;
}
execlp能够通过环境变量PATH查找到可执行文件ps
3.execvp:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//函数原型:int execvp(const char *file,char *const argv[])
int main(void)
{
printf("this pro get system date:\n");
char *argv[] = {"ps",NULL,NULL};
if(execvp("ps",argv) == -1){
printf("execl failed!\n");
perror("why");
}
printf("after execl\n");
return 0;
}
exec配合fork使用:实现功能,当父进程检测到输入为1的时候,创建进程把配置文件的字段值修改掉。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
int data = 10;
while(1){
printf("please input a data\n");
scanf("%d",&data);
if(data == 1){
pid = fork();
if(pid > 0){
wait(NULL); //防止僵尸进程产生
}
if(pid == 0){
int fdSrc;
char *readBuf = NULL;
fdSrc = open("config.txt",O_RDWR);
int size = lseek(fdSrc,0,SEEK_END);
lseek(fdSrc,0,SEEK_SET);
readBuf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*size + 8);
int n_read = read(fdSrc,readBuf,size);
char *p = strstr(readBuf,"LENG=");
if(p == NULL){
printf("not found\n");
exit(-1);
}
p = p+strlen("LENG=");
*p = '5';
lseek(fdSrc,0,SEEK_SET);
int n_write = write(fdSrc,readBuf,strlen(readBuf));
close(fdSrc);
exit(0);
}
}
else
{
printf("wait,:do nothing\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
int data = 10;
while(1){
printf("please input a data\n");
scanf("%d",&data);
if(data == 1){
pid = fork();
if(pid > 0){
wait(NULL);
}
if(pid == 0){
execl("./changData","changData","config.txt",NULL);
}
}
else
{
printf("wait,:do nothing\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
changdata为修改数字的程序,调用execl函数,直接执行changdata程序
二、system函数
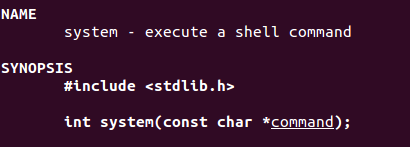
system()函数的返回值:成功,则返回进程的状态值;当sh不能执行时,返回127;失败返回-1。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
int data = 10;
while(1){
printf("please input a data\n");
scanf("%d",&data);
if(data == 1){
pid = fork();
if(pid > 0){
wait(NULL);
}
if(pid == 0){
system("./changData config.txt");
}
}
else
{
printf("wait,:do nothing\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
if(system("ps") == -1){
printf("system failed!\n");
perror("why");
}
printf("after system\n");
return 0;
}
system执行完之后还会返回原代码中继续执行。
三、popen函数:
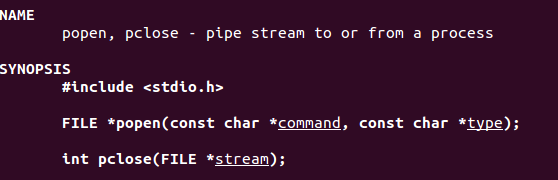
比system在应用中的好处:可以获取运行的输出结果。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
char ret[1024] = {0};
FILE *fp;
fp = popen("ps","r");
int nread = fread(ret,1,1024,fp);
printf("read ret %d byte,ret = %s\n",nread,ret);
return 0;
}





 本文详细介绍了Linux系统中用于进程执行的exec族函数,包括execl、execlp和execvp的用法及特点。接着讨论了system函数,解释了其返回值和执行流程。最后探讨了popen函数,强调了它相比system函数能获取程序运行输出的优势。
本文详细介绍了Linux系统中用于进程执行的exec族函数,包括execl、execlp和execvp的用法及特点。接着讨论了system函数,解释了其返回值和执行流程。最后探讨了popen函数,强调了它相比system函数能获取程序运行输出的优势。
















 1860
1860

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








