目录
一、Set系列集合
1.1 认识Set集合的特点
Set集合是属于Collection体系下的另一个分支,他的特点如下图所示

Set系列集合特点:无序:添加数据的顺序和获取的数据顺序不一致;不重复;无索引;
- HashSet:无序、不重复、无索引。
- LinkedHashSet:有序、不重复、无索引。
- TreeSet:排序、不重复、无索引。
1.2 HashSet集合底层原理
HashSet集合底层是基于哈希表实现的,哈希表根据JDK版本的不同,也是有点区别的
-
JDK8以前:哈希表 = 数组+链表
-
JDK8以后:哈希表 = 数组+链表+红黑树

我们发现往HashSet集合中存储元素时,底层调用了元素的两个方法:一个是hashCode方法获取元素的hashCode值(哈希值);另一个是调用了元素的equals方法,用来比较新添加的元素和集合中已有的元素是否相同。
-
只有新添加元素的hashCode值和集合中以后元素的hashCode值相同、新添加的元素调用equals方法和集合中已有元素比较结果为true, 才认为元素重复。
-
如果hashCode值相同,equals比较不同,则以链表的形式连接在数组的同一个索引为位置(如上图所示)
在JDK8开始后,为了提高性能,当链表的长度超过8时,就会把链表转换为红黑树,如下图所示:

1.3 HashSet去重原理
要想保证在HashSet集合中没有重复元素,我们需要重写元素类的hashCode和equals方法。比如以下面的Student类为例,假设把Student类的对象作为HashSet集合的元素,想要让学生的姓名和年龄相同,就认为元素重复。
public class Student{
private String name; //姓名
private int age; //年龄
private double height; //身高
//无参数构造方法
public Student(){}
//全参数构造方法
public Student(String name, int age, double height){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.height=height;
}
//...get、set、toString()方法自己补上..
//按快捷键生成hashCode和equals方法
//alt+insert 选择 hashCode and equals
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (age != student.age) return false;
if (Double.compare(student.height, height) != 0) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result;
long temp;
result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(height);
result = 31 * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32));
return result;
}
}接着,写一个测试类,往HashSet集合中存储Student对象。
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Set<Student> students = new HashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("至尊宝",20, 169.6);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s3 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s4 = new Student("牛魔王",48, 169.6);
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
for(Student s : students){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}打印结果如下,我们发现存了两个蜘蛛精,当时实际打印出来只有一个,而且是无序的。
Student{name='牛魔王', age=48, height=169.6}
Student{name='至尊宝', age=20, height=169.6}
Student{name='蜘蛛精', age=23, height=169.6}1.4 LinkedHashSet底层原理
LinkedHashSet它底层采用的是也是哈希表结构,只不过额外新增了一个双向链表来维护元素的存取顺序。如下下图所示:

每次添加元素,就和上一个元素用双向链表连接一下。第一个添加的元素是双向链表的头节点,最后一个添加的元素是双向链表的尾节点。
把上个案例中的集合改成LinkedList集合,我们观察效果怎样
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Set<Student> students = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("至尊宝",20, 169.6);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s3 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s4 = new Student("牛魔王",48, 169.6);
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
for(Student s : students){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}Student{name='至尊宝', age=20, height=169.6}
Student{name='蜘蛛精', age=23, height=169.6}
Student{name='牛魔王', age=48, height=169.6}1.5 TreeSet集合
最后,我们学习一下TreeSet集合。TreeSet集合的特点是可以对元素进行排序,但是必须指定元素的排序规则。
如果往集合中存储String类型的元素,或者Integer类型的元素,它们本身就具备排序规则,所以直接就可以排序。
Set<Integer> set1= new TreeSet<>();
set1.add(8);
set1.add(6);
set1.add(4);
set1.add(3);
set1.add(7);
set1.add(1);
set1.add(5);
set1.add(2);
System.out.println(set1); //[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
Set<Integer> set2= new TreeSet<>();
set2.add("a");
set2.add("c");
set2.add("e");
set2.add("b");
set2.add("d");
set2.add("f");
set2.add("g");
System.out.println(set1); //[a,b,c,d,e,f,g]如果往TreeSet集合中存储自定义类型的元素,比如说Student类型,则需要我们自己指定排序规则,否则会出现异常。
//创建TreeSet集合,元素为Student类型
Set<Student> students = new TreeSet<>();
//创建4个Student对象
Student s1 = new Student("至尊宝",20, 169.6);
Student s2 = new Student("紫霞",23, 169.8);
Student s3 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s4 = new Student("牛魔王",48, 169.6);
//添加Studnet对象到集合
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
System.out.println(students); 
我们想要告诉TreeSet集合按照指定的规则排序,有两种办法:
第一种:让元素的类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo方法
第二种:在创建TreeSet集合时,通过构造方法传递Compartor比较器对象
-
排序方式1:我们先来演示第一种排序方式
//第一步:先让Student类,实现Comparable接口
//注意:Student类的对象是作为TreeSet集合的元素的
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
//无参数构造方法
public Student(){}
//全参数构造方法
public Student(String name, int age, double height){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.height=height;
}
//...get、set、toString()方法自己补上..
//第二步:重写compareTo方法
//按照年龄进行比较,只需要在方法中让this.age和o.age相减就可以。
/*
原理:
在往TreeSet集合中添加元素时,add方法底层会调用compareTo方法,根据该方法的
结果是正数、负数、还是零,决定元素放在后面、前面还是不存。
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//this:表示将要添加进去的Student对象
//o: 表示集合中已有的Student对象
return this.age-o.age;
}
}此时,再运行测试类,结果如下
Student{name='至尊宝', age=20, height=169.6}
Student{name='紫霞', age=20, height=169.8}
Student{name='蜘蛛精', age=23, height=169.6}
Student{name='牛魔王', age=48, height=169.6}排序方式2:接下来演示第二种排序方式
//创建4个Student对象
Student s1 = new Student("至尊宝",20, 169.6);
Student s2 = new Student("紫霞",23, 169.8);
Student s3 = new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.6);
Student s4 = new Student("牛魔王",48, 169.6);
//添加Studnet对象到集合
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
System.out.println(students); 1.6 并发修改异常
我们先把这个异常用代码演示出来,再解释一下为什么会有这个异常产生
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("王麻子");
list.add("小李子");
list.add("李爱花");
list.add("张全蛋");
list.add("晓李");
list.add("李玉刚");
System.out.println(list); // [王麻子, 小李子, 李爱花, 张全蛋, 晓李, 李玉刚]
//需求:找出集合中带"李"字的姓名,并从集合中删除
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String name = it.next();
if(name.contains("李")){
list.remove(name);
}
}
System.out.println(list);运行上面的代码,会出现下面的异常。这就是并发修改异常

为什么会出现这个异常呢?那是因为迭代器遍历机制,规定迭代器遍历集合的同时,不允许集合自己去增删元素,否则就会出现这个异常。
怎么解决这个问题呢?不使用集合的删除方法,而是使用迭代器的删除方法,代码如下:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("王麻子");
list.add("小李子");
list.add("李爱花");
list.add("张全蛋");
list.add("晓李");
list.add("李玉刚");
System.out.println(list); // [王麻子, 小李子, 李爱花, 张全蛋, 晓李, 李玉刚]
//需求:找出集合中带"李"字的姓名,并从集合中删除
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String name = it.next();
if(name.contains("李")){
//list.remove(name);
it.remove(); //当前迭代器指向谁,就删除谁
}
}
System.out.println(list);二、Collection的其他操作
2.1 可变参数
首先,我们来学习一下可变参数。关于可变参数我们首先要知道它是什么,然后要知道它的本质。搞清楚这两个问题,可变参数就算你学明白了。
可变参数是一种特殊的形式参数,定义在方法、构造器的形参列表处,它可以让方法接收多个同类型的实际参数。
可变参数在方法内部,本质上是一个数组
接下来,我们编写代码来演示一下
public class ParamTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
//不传递参数,下面的nums长度则为0, 打印元素是[]
test();
//传递3个参数,下面的nums长度为3,打印元素是[10, 20, 30]
test(10,20,30);
//传递一个数组,下面数组长度为4,打印元素是[10,20,30,40]
int[] arr = new int[]{10,20,30,40}
test(arr);
}
public static void test(int...nums){
//可变参数在方法内部,本质上是一个数组
System.out.println(nums.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
System.out.println("----------------");
}
}最后还有一些错误写法,需要让大家写代码时注意一下,不要这么写哦!!!
一个形参列表中,只能有一个可变参数;否则会报错
一个形参列表中如果多个参数,可变参数需要写在最后;否则会报错
2.2 Collections工具类
有了可变参数的基础,我们再学习Collections这个工具类就好理解了,因为这个工具类的方法中会用到可变参数。
注意Collections并不是集合,它比Collection多了一个s,一般后缀为s的类很多都是工具类。这里的Collections是用来操作Collection的工具类。它提供了一些好用的静态方法,如下

我们把这些方法用代码来演示一下:
public class CollectionsTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
//1.public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T...e)
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, "张三","王五","李四", "张麻子");
System.out.println(names);
//2.public static void shuffle(List<?> list):对集合打乱顺序
Collections.shuffle(names);
System.out.println(names);
//3.public static <T> void short(List<T list): 对List集合排序
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(3);
list.add(5);
list.add(2);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}上面我们往集合中存储的元素要么是Stirng类型,要么是Integer类型,他们本来就有一种自然顺序所以可以直接排序。但是如果我们往List集合中存储Student对象,这个时候想要对List集合进行排序自定义比较规则的。指定排序规则有两种方式,如下:
排序方式1:让元素实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo方法
比如现在想要往集合中存储Studdent对象,首先需要准备一个Student类,实现Comparable接口。
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
//排序时:底层会自动调用此方法,this和o表示需要比较的两个对象
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o){
//需求:按照年龄升序排序
//如果返回正数:说明左边对象的年龄>右边对象的年龄
//如果返回负数:说明左边对象的年龄<右边对象的年龄,
//如果返回0:说明左边对象的年龄和右边对象的年龄相同
return this.age - o.age;
}
//...getter、setter、constructor..
} 然后再使用Collections.sort(list集合)对List集合排序,如下:
//3.public static <T> void short(List<T list): 对List集合排序
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(new Student("蜘蛛精",23,169.7));
students.add(new Student("紫霞",22,169.8));
students.add(new Student("紫霞",22,169.8));
students.add(new Student("至尊宝",26,169.5));
/*
原理:sort方法底层会遍历students集合中的每一个元素,采用排序算法,将任意两个元素两两比较;
每次比较时,会用一个Student对象调用compareTo方法和另一个Student对象进行比较;
根据compareTo方法返回的结果是正数、负数,零来决定谁大,谁小,谁相等,重新排序元素的位置
注意:这些都是sort方法底层自动完成的,想要完全理解,必须要懂排序算法才行;
*/
Collections.sort(students);
System.out.println(students);排序方式2:使用调用sort方法是,传递比较器
/*
原理:sort方法底层会遍历students集合中的每一个元素,采用排序算法,将任意两个元素两两比较;
每次比较,会将比较的两个元素传递给Comparator比较器对象的compare方法的两个参数o1和o2,
根据compare方法的返回结果是正数,负数,或者0来决定谁大,谁小,谁相等,重新排序元素的位置
注意:这些都是sort方法底层自动完成的,不需要我们完全理解,想要理解它必须要懂排序算法才行.
*/
Collections.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>(){
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2){
return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
}
});
System.out.println(students);三、Map集合
3.1 Map概述体系
所谓双列集合,就是说集合中的元素是一对一对的。Map集合中的每一个元素是以key=value的形式存在的,一个key=value就称之为一个键值对,而且在Java中有一个类叫Entry类,Entry的对象用来表示键值对对象。
所有的Map集合有如下的特点:键不能重复,值可以重复,每一个键只能找到自己对应的值。
下面我们先写一个Map集合,保存几个键值对,体验一下Map集合的特点
public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 一行经典代码。 按照键 无序,不重复,无索引。
Map<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // 有序,不重复,无索引。
map.put("手表", 100);
map.put("手表", 220); // 后面重复的数据会覆盖前面的数据(键)
map.put("手机", 2);
map.put("Java", 2);
map.put(null, null);
System.out.println(map);
Map<Integer, String> map1 = new TreeMap<>(); // 可排序,不重复,无索引
map1.put(23, "Java");
map1.put(23, "MySQL");
map1.put(19, "李四");
map1.put(20, "王五");
System.out.println(map1);
}
}Map集合也有很多种,在Java中使用不同的类来表示的,每一种Map集合其键的特点是有些差异的,值是键的一个附属值,所以我们只关注键的特点就可以了。

3.2 Map集合的常用方法

public class MapTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.添加元素: 无序,不重复,无索引。
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("手表", 100);
map.put("手表", 220);
map.put("手机", 2);
map.put("Java", 2);
map.put(null, null);
System.out.println(map);
// map = {null=null, 手表=220, Java=2, 手机=2}
// 2.public int size():获取集合的大小
System.out.println(map.size());
// 3、public void clear():清空集合
//map.clear();
//System.out.println(map);
// 4.public boolean isEmpty(): 判断集合是否为空,为空返回true ,反之!
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
// 5.public V get(Object key):根据键获取对应值
int v1 = map.get("手表");
System.out.println(v1);
System.out.println(map.get("手机")); // 2
System.out.println(map.get("张三")); // null
// 6. public V remove(Object key):根据键删除整个元素(删除键会返回键的值)
System.out.println(map.remove("手表"));
System.out.println(map);
// 7.public boolean containsKey(Object key): 判断是否包含某个键 ,包含返回true ,反之
System.out.println(map.containsKey("手表")); // false
System.out.println(map.containsKey("手机")); // true
System.out.println(map.containsKey("java")); // false
System.out.println(map.containsKey("Java")); // true
// 8.public boolean containsValue(Object value): 判断是否包含某个值。
System.out.println(map.containsValue(2)); // true
System.out.println(map.containsValue("2")); // false
// 9.public Set<K> keySet(): 获取Map集合的全部键。
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
System.out.println(keys);
// 10.public Collection<V> values(); 获取Map集合的全部值。
Collection<Integer> values = map.values();
System.out.println(values);
// 11.把其他Map集合的数据倒入到自己集合中来。(拓展)
Map<String, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("java1", 10);
map1.put("java2", 20);
Map<String, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put("java3", 10);
map2.put("java2", 222);
map1.putAll(map2); // putAll:把map2集合中的元素全部倒入一份到map1集合中去。
System.out.println(map1);
System.out.println(map2);
}
}3.3 Map集合遍历方式1

/**
* 目标:掌握Map集合的遍历方式1:键找值
*/
public class MapTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 准备一个Map集合。
Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("蜘蛛精", 162.5);
map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);
map.put("紫霞", 165.8);
map.put("至尊宝", 169.5);
map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);
System.out.println(map);
// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊宝=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}
// 1、获取Map集合的全部键
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
// System.out.println(keys);
// [蜘蛛精, 牛魔王, 至尊宝, 紫霞]
// key
// 2、遍历全部的键,根据键获取其对应的值
for (String key : keys) {
// 根据键获取对应的值
double value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=====>" + value);
}
}
}3.4 Map集合遍历方式2
这里Map集合的第二种方式,是直接获取每一个Entry对象,把Entry存储扫Set集合中去,再通过Entry对象获取键和值。

/**
* 目标:掌握Map集合的第二种遍历方式:键值对。
*/
public class MapTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);
map.put("紫霞", 165.8);
map.put("至尊宝", 169.5);
map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);
System.out.println(map);
// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊宝=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}
// entries = [(蜘蛛精=169.8), (牛魔王=183.6), (至尊宝=169.5), (紫霞=165.8)]
// entry = (蜘蛛精=169.8)
// entry = (牛魔王=183.6)
// ...
// 1、调用Map集合提供entrySet方法,把Map集合转换成键值对类型的Set集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Double> entry : entries) {
String key = entry.getKey();
double value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
}
}
}3.5 Map集合遍历方式3

/**
* 目标:掌握Map集合的第二种遍历方式:键值对。
*/
public class MapTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);
map.put("紫霞", 165.8);
map.put("至尊宝", 169.5);
map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);
System.out.println(map);
// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊宝=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}
//遍历map集合,传递匿名内部类
map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, Double>() {
@Override
public void accept(String k, Double v) {
System.out.println(k + "---->" + v);
}
});
//遍历map集合,传递Lambda表达式
map.forEach(( k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "---->" + v);
});
}
}3.6HashMap
HashMap集合的特点是由键决定的: 它的键是无序、不能重复,而且没有索引的。
HashSet的原理我们之前已经学过了,所以HashMap是一样的,底层是哈希表结构。
HashMap底层数据结构: 哈希表结构
JDK8之前的哈希表 = 数组+链表
JDK8之后的哈希表 = 数组+链表+红黑树
哈希表是一种增删改查数据,性能相对都较好的数据结构
往HashMap集合中键值对数据时,底层步骤如下
第1步:当你第一次往HashMap集合中存储键值对时,底层会创建一个长度为16的数组
第2步:把键然后将键和值封装成一个对象,叫做Entry对象
第3步:再根据Entry对象的键计算hashCode值(和值无关)
第4步:利用hashCode值和数组的长度做一个类似求余数的算法,会得到一个索引位置
第5步:判断这个索引的位置是否为null,如果为null,就直接将这个Entry对象存储到这个索引位置
如果不为null,则还需要进行第6步的判断
第6步:继续调用equals方法判断两个对象键是否相同
如果equals返回false,则以链表的形式往下挂
如果equals方法true,则认为键重复,此时新的键值对会替换就的键值对。
HashMap底层需要注意这几点:
1.底层数组默认长度为16,如果数组中有超过12个位置已经存储了元素,则会对数组进行扩容2倍
数组扩容的加载因子是0.75,意思是:16*0.75=12
2.数组的同一个索引位置有多个元素、并且在8个元素以内(包括8),则以链表的形式存储
JDK7版本:链表采用头插法(新元素往链表的头部添加)
JDK8版本:链表采用尾插法(新元素我那个链表的尾部添加)
3.数组的同一个索引位置有多个元素、并且超过了8个,则以红黑树形式存储
从HashMap底层存储键值对的过程中我们发现:决定键是否重复依赖与两个方法,一个是hashCode方法、一个是equals方法。有两个键计算得到的hashCode值相同,并且两个键使用equals比较为true,就认为键重复。
所以,往Map集合中存储自定义对象作为键,为了保证键的唯一性,我们应该重写hashCode方法和equals方法。
3.7 LinkedHashMap
学习完HashMap集合的特点,以及底层原理。接下来我们学习一下LinkedHashMap集合。
-
LinkedHashMap集合的特点也是由键决定的:有序的、不重复、无索引。
/**
* 目标:掌握LinkedHashMap的底层原理。
*/
public class Test2LinkedHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 按照键 无序,不重复,无索引。
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // 按照键 有序,不重复,无索引。
map.put("手表", 100);
map.put("手表", 220);
map.put("手机", 2);
map.put("Java", 2);
map.put(null, null);
System.out.println(map);
}
}-
LinkedHashMap的底层原理,和LinkedHashSet底层原理是一样的。底层多个一个双向链表来维护键的存储顺序。
取元素时,先取头节点元素,然后再依次取下一个几点,一直到尾结点。所以是有序的。
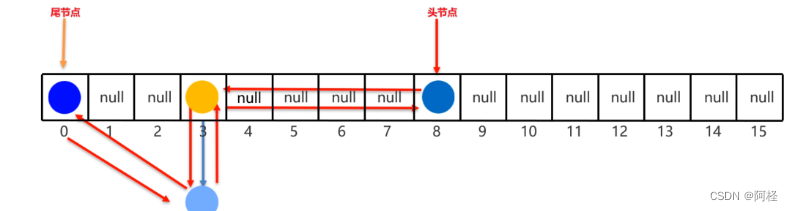
3.8 TreeMap
TreeMap集合的特点也是由键决定的,默认按照键的升序排列,键不重复,也是无索引的。
-
TreeMap集合的底层原理和TreeSet也是一样的,底层都是红黑树实现的。所以可以对键进行排序。
比如往TreeMap集合中存储Student对象作为键,排序方法有两种。直接看代码吧
排序方式1:写一个Student类,让Student类实现Comparable接口
//第一步:先让Student类,实现Comparable接口
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
//无参数构造方法
public Student(){}
//全参数构造方法
public Student(String name, int age, double height){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.height=height;
}
//...get、set、toString()方法自己补上..
//按照年龄进行比较,只需要在方法中让this.age和o.age相减就可以。
/*
原理:
在往TreeSet集合中添加元素时,add方法底层会调用compareTo方法,根据该方法的
结果是正数、负数、还是零,决定元素放在后面、前面还是不存。
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//this:表示将要添加进去的Student对象
//o: 表示集合中已有的Student对象
return this.age-o.age;
}
}排序方式2:在创建TreeMap集合时,直接传递Comparator比较器对象。
/**
* 目标:掌握TreeMap集合的使用。
*/
public class Test3TreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Student, String> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight());
}
});
// Map<Student, String> map = new TreeMap<>(( o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight()));
map.put(new Student("蜘蛛精", 25, 168.5), "盘丝洞");
map.put(new Student("蜘蛛精", 25, 168.5), "水帘洞");
map.put(new Student("至尊宝", 23, 163.5), "水帘洞");
map.put(new Student("牛魔王", 28, 183.5), "牛头山");
System.out.println(map);
}
}这种方式都可以对TreeMap集合中的键排序。注意:只有TreeMap的键才能排序,HashMap键不能排序。





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








