-
一、错误处理perror,strerror和error
1.perror,strerror和error的定义
errno:这是一个整数型的宏,其值依赖于上一个函数调用是否发生错误。在发生错误时,errno被设置为一个特定的错误代码。strerror:这个函数将errno值转换为一个错误描述字符串。perror:这个函数首先输出errno对应的错误描述字符串,然后输出指定的字符串,最后是一个换行符。
2.简单示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
// 使errno值为0
errno = 0;
// 以读模式打开一个不存在的文件
fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("errno = %d\n", errno);
// 输出错误描述字符串
perror("Error");
// 输出errno对应的错误描述字符串
fprintf(stderr, "Error opening file: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
return 0;
}
~ 运行结果:

二、open(),close()
1.open()函数的原型
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
pathname:要打开的文件的路径名,可以是相对路径或绝对路径。flags:打开文件的标志,用于指定文件的打开方式和操作选项。常见的标志包括:

mode:一个权限参数,用于指定新创建文件的访问权限,只有在使用O_CREAT标志创建文件时才有效。

- 返回值:成功时返回一个非负整数的文件描述符,用于后续对文件的读写操作;失败时返回-1,并可以使用error全局变量获取具体的错误码。
2.close()函数原型
int close(int fd);
fd是函数返回的文件描述符。如果成功关闭文件,函数返回0;如果失败,返回-1。
3.简单示例
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
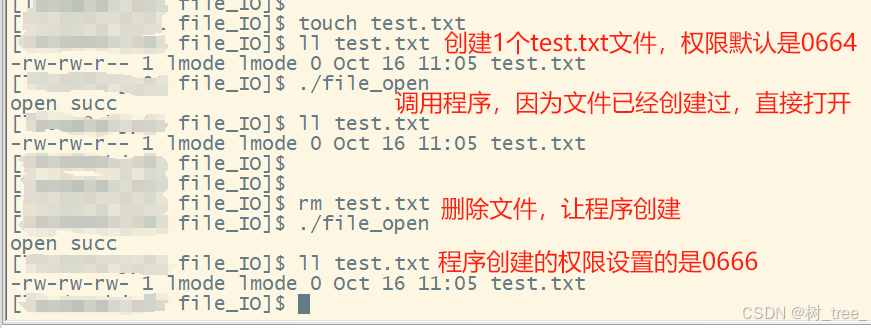
int main(void)
{
umask(0);
int fd;
fd = open("test.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0666);
if(fd == -1)
perror("open error");
printf("open succ\n");
close(fd);
return 0;
}运行结果:
三、read(),write()
1.read()函数的原型
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
fd:文件描述符,代表需要读取的文件或设备。buf:指向用户分配的缓冲区的指针,read()函数将把读取到的数据写入该缓冲区。count:需要读取的字节数,表示最多读取count字节数据。- read()函数的返回值,成功返回取的字节数,如果读取到文件末尾,返回0;返回-1,并设置
errno来指示具体错误原因。
2.write()函数的原型
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);fd:文件描述符。buf:指向要写入数据的缓冲区的指针。count:要写入的字节数。- 函数返回写入的字节数,如果出错则返回-1。
3.简单示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define EXIT_ERR(m)\
do{\
perror(m);\
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);\
}while(0)
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int infd;
int outfd;
char buf[1024];
int n;
if(argc != 3){
fprintf(stderr,"usage:%s src des\n",argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if((infd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) == -1)
EXIT_ERR("open error");
if((outfd = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY| O_CREAT| O_TRUNC, 0644)) == -1)
EXIT_ERR("OPEN ERROR");
while((n = read(infd, buf, 32)) > 0){
write(outfd, buf, n);
}
close(infd);
close(outfd);
return 0;
}运行结果:
把file_read.c复制到file_read.c.cp


四、lseek()
1.lseek()的函数原型
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
- fd:文件描述符,表示要操作的文件。
- offset:偏移量,表示从whence指定的位置开始移动的字节数。
- whence:指定offset的起始位置,可以是以下三个值之一:

- 返回值是新的文件偏移量,即从文件开头到当前位置的字节数。如果函数失败,返回(off_t)-1,并设置errno以指示错误。
2.简单示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do \
{ \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while(0)
int main(void)
{
int fd;
int ret;
fd = open("hole.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0644);
if(fd == -1)
ERR_EXIT("open error");
write(fd,"hello",5);
ret = lseek(fd,32,SEEK_CUR);
if(ret == -1)
ERR_EXIT("lseek error");
write(fd,"world",5);
close(fd);
return 0;
}运行结果:
vim hole.txt
![]()
五、stat()
1.stat()的函数原型
#include <sys/stat.h>
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file :该文件所属设备的设备号,设备号包括主设备和和次设备号,dev_t是16位整数,高8位表示主设备号,低8位表示次设备号*/
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* protection :包含文件访问权限信息及文件类型*/
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file):如果该文件是特殊文件即设备文件,则表示设备号 */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated :分配的块数量*/
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change:如修改文件的权限 */
};
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








