Mybatis笔记
核心工作原理图
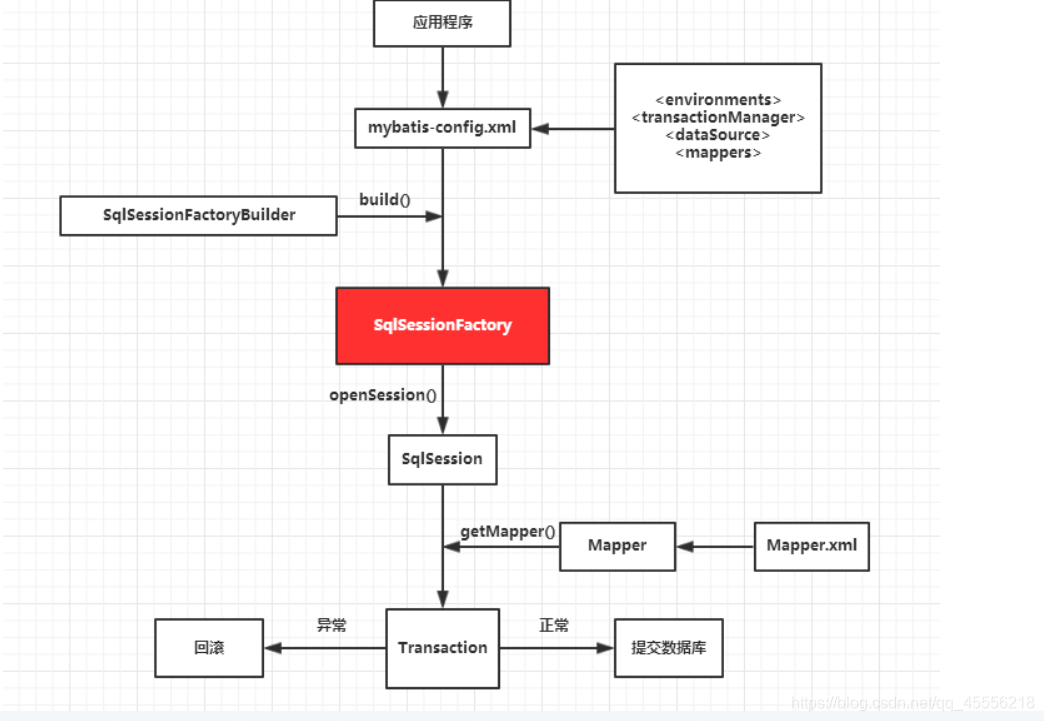
1.核心配置文件(mybatisconfig.xml)
mybatis的相关依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="database.properties"/> <!--读取配置文件-->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.hp.domain"/> <!--类型别名(typeAliases)-->
</typeAliases>
<!--环境配置(environments)-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> <!--指定mapper文件位置-->
</mappers>
</configuration>
1.2 :数据库配置文件(database.properties)
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisuseSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456
2.mapper.xml配置文件(*mapper.xml)
编写sql语句 进行CLUD操作.
- 2.1. resultType:期望从这条语句中返回结果的类全限定名或别名。 注意,如果返回的是集合,那应该设置为集合包含的类型,而不是集合本身的类型。 resultType 和 resultMap 之间只能同时使用一个。
- 2.2 resultMap: 对外部 resultMap 的命名引用。结果映射是 MyBatis 最强大的特性,如果你对其理解透彻,许多复杂的映射问题都能迎刃而解。 resultType 和 resultMap 之间只能同时使用一个。
- **2.3 parameterType:**将会传入这条语句的参数的类全限定名或别名。这个属性是可选的,因为 MyBatis 可以通过类型处理器(TypeHandler)推断出具体传入语句的参数,默认值为未设置(接受参数类型)
- 2.4 万能的map : 。。。。。(实际开发用处大,处理多个复杂数据)
3 测试mybatis的环境
public class TestMapper {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private UserMapper mapper;
private SqlSession session;
@Before
public void init() {
String resources = "mybatis-config.xml";
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resources);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
}
@After
public void destory() throws IOException {
session.commit(); //提交事务
session.close();
}
@Test
public void findAll() {
List<User> userList = mapper.findAll();
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
4日志
1.STDOUT_LOGGING标准日志输出
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
- log4j
2.1 导入log4j的依赖
log4j
log4j
1.2.17
2.2 日志对象当前class
static Logger logger=Logger.getLogger(UserMapper.class);
3.3 日志有3种级别
logger.info(“我是info”);
logger.debug(“我是debug”);
logger.error(“我是error”);
5. limit实现分页
6. @Param()注解的注意事项
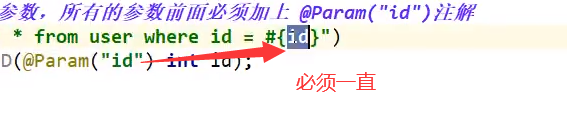
- 关于@Param()
- 基于类型的参数和String要加上
- 引用类型不需要加上
- 如果只有一个基本类型的话就可以忽略但是建议还是加上
- 我们在sql中引用的就是我们这里@Param()中设定的属性名
7. Lombook
每一种语言都会面临改变,进化或淘汰,能高效,快速达到目的,提高生产力的就是好方法,或许会有另一面隐患,但因为可能的隐患就不用就太不智了
江山代有才人出,各领风骚数百年。java现世不短时间,就算高度发展后被替代也只是完成了他的历史使命而已,新的语言又会开启新时代
@Data :注解在类上;提供类所有属性的 getting 和 setting 方法,此外还提供了equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString 方法
@Setter:注解在属性上;为属性提供 setting 方法
@Getter:注解在属性上;为属性提供 getting 方法
@Log4j :注解在类上;为类提供一个 属性名为log 的 log4j 日志对象
@NoArgsConstructor:注解在类上;为类提供一个无参的构造方法
@AllArgsConstructor:注解在类上;为类提供一个全参的构造方法
8. 多对一
CREATE TABLE teacher (
id INT(10) NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
INSERT INTO teacher(id, name) VALUES (1, ‘秦老师’);
CREATE TABLE student (
id INT(10) NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
tid INT(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
KEY fktid (tid),
CONSTRAINT fktid FOREIGN KEY (tid) REFERENCES teacher (id)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
select * from student
INSERT INTO student (id, name, tid) VALUES (‘1’, ‘小明’, ‘1’);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, tid) VALUES (‘2’, ‘小红’, ‘1’);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, tid) VALUES (‘3’, ‘小张’, ‘1’);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, tid) VALUES (‘4’, ‘小李’, ‘1’);
INSERT INTO student (id, name, tid) VALUES (‘5’, ‘小王’, ‘1’);
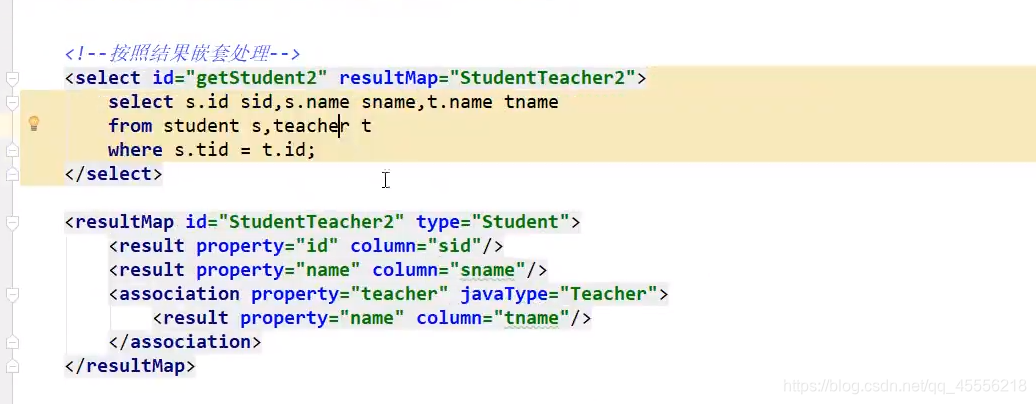
9. 一对多
10动态sql
<!--开启下划线驼峰自动转换-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
mapper.xml例子
`<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.hp.mapper.BlogMapper">
<select id="findbythis" parameterType="map" resultType="Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<if test="title !=null">
title=#{title}
</if>
<if test="author !=null">
and author=#{author}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<update id="update" parameterType="map">
update mybatis.blog
<set>
<if test="title !=null">
title=#{title}
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
<select id="findbythis22" resultType="com.hp.domain.Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<choose>
<when test="title !=null">
title=#{title}
</when>
<otherwise>
and views=#{views}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>`
-
choose语句
有时候,我们不想用到所有的查询条件,只想选择其中的一个,查询条件有一个满足即可,使用 choose 标签可以解决此类问题,类似于 Java 的 switch 语句
我觉得其实类似于switch语句
otherwise 就是必须会执行的语句 -
forEach
<select id="findbyforeach" parameterType="map" resultType="com.hp.domain.Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="(" separator="or" close=")">
id=#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
11. mybatis缓存
- 一级缓存
- 二级缓存
select * from mybatis.blog
id=#{id}
</select>
## 11. mybatis缓存
1. 一级缓存 sqlsession缓存
2. 二级缓存 (Ehcache+Memcache+Redis)
3. 需要配置 实际工作用的更多的是Redis
























 2214
2214

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








