一、建模的由来以及建模思路
首先介绍一下建模。
建模其实就是将指定的xml字符串当作对象来操作
如果说当对一个指定的xml格式字符串完成了建模操作,那么就只需要调用指定的方法就可以完成预定的字符串获取。
那么建模的解决方式是什么样的呢?或者说建模的主要用处要怎么去理解呢?

在下面的xml解析的代码中
// zouyan
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<config>
<action path="/regAction" type="test.RegAction">
<forward name="failed" path="/reg.jsp" redirect="false" />
<forward name="success" path="/login.jsp" redirect="true" />
</action>
<action path="/loginAction" type="test.LoginAction">
<forward name="failed" path="/login.jsp" redirect="false" />
<forward name="success" path="/main.jsp" redirect="true" />
</action>
</config>
程序员张三需要通过 /LoginAction 获取 type=test.LoginAction串。
然后操作步骤是:
1、加载资源文件xxx.class.getResourceAsSteam('config.xml');
2、通过xpath解析获取到所有的action元素标签列表。
(xpath解析前面的博客讲过,传送门看下面)
3、遍历,如果action标签的path属性等于/loginAction,那么就是我们的action标签。
4、找到的action,就以获取到对应的action标签的type属性值。
xpath解析链接: https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_45547474/article/details/106291391.
那么根据以上步骤,如果是程序员李四需要通过 /regAction 获取 type=test.RegAction串。只是在第三步中把/loginAction替换为/regAction。
3、遍历,如果action标签的path属性等于/loginAction,那么就是我们的action标签。
替换为
3、遍历,如果action标签的path属性等于/regAction,那么就是我们的action标签。
如果是程序员王五需要通过 /regAction 获取 type=test.RegAction串。只是在第三步中把/loginAction替换为/regAction。
而相对的就是要拿一个大盒子把这些相同的东西给它装起来,也可以想象成一个工厂。想要使用的时候就把大盒子拿出来用。这也就是xml建模的一个用处。
二、xml建模的核心思想
xml建模的核心思想就是利用java面对对象的特性,用操作对象的方式来操作xml。
三、xml建模的代码完成
1、xml建模的初步代码
下面是一个xml解析的代码:
// zouyan
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<config>
<action path="/regAction" type="test.RegAction">
<forward name="failed" path="/reg.jsp" redirect="false" />
<forward name="success" path="/login.jsp" redirect="true" />
</action>
<action path="/loginAction" type="test.LoginAction">
<forward name="failed" path="/login.jsp" redirect="false" />
<forward name="success" path="/main.jsp" redirect="true" />
</action>
</config>
一个标签就是一个对象,那么在这个代码中,就存在三个对象Config、action、forward。
一个类由两部分(属性和方法)组成,那我们就通过这两部分对这三个对象进行分析:
Config对象——>Config类
属性:没有属性
行为:新增Action对象的行为,通过action path属性查找Action对象的行为。
Action类
属性:path属性、type属性
行为:新增Forward对象的行为,通过Forward对象name属性查找对应的Forward对象的行为
Forward类
属性:name属性、path属性、redirect属性
行为:没有
分析好之后,开始准备代码。
注意顺序由里到外,由forward写到config。
建包顺序也就是ForwardModel——>ActionModel——>ConfigModel
ForwardModel里面的代码是:
// zouyan
package com.zouyan.model;
public class ForwardModel {
// <forward name="failed" path="/login.jsp" redirect="false" />
private String name;
private String path;
private boolean redirect;//判断对错false 和 true,所以使用boolean
/**
* 提供set get 方法
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public boolean isRedirect() {
return redirect;
}
public void setRedirect(boolean redirect) {
this.redirect = redirect;
}
}
注:属性为String类型,子元素标签则是map的值,子元素标签的唯一标识则为map的值。
ActionModel里面的代码是:
// zouyan
package com.zouyan.model;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ActionModel {
// <action path="/regAction" type="test.RegAction">
private String path;
private String type;
private Map<String, ForwardModel> foMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 提供path跟type的set get 方法
*/
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
//两个行为
/**
* 将指定的forwardModel压入当前actionModel对象中
* <forward />放入<action></action>
* @param forwardModel
*/
public void push(ForwardModel forwardModel) {
foMap.put(forwardModel.getName(), forwardModel);
}
public ForwardModel pop(String name) {
return foMap.get(name);
}
}
ConfigModel里面的代码是:
// zouyan
package com.zouyan.model;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ConfigModel {
private Map<String, ActionModel> acMap = new HashMap<String, ActionModel>();
/**
* 将指定的actionModel压入当前ConfigModel对象中
* <action />放入<config></cinfig>
* @param forwardModel
*/
public void push(ActionModel actionModel) {
acMap.put(actionModel.getPath(), actionModel);
}
public ActionModel pop(String path) {
return acMap.get(path);
}
}
注:提供set get 方法的操作如下,空白区域右键
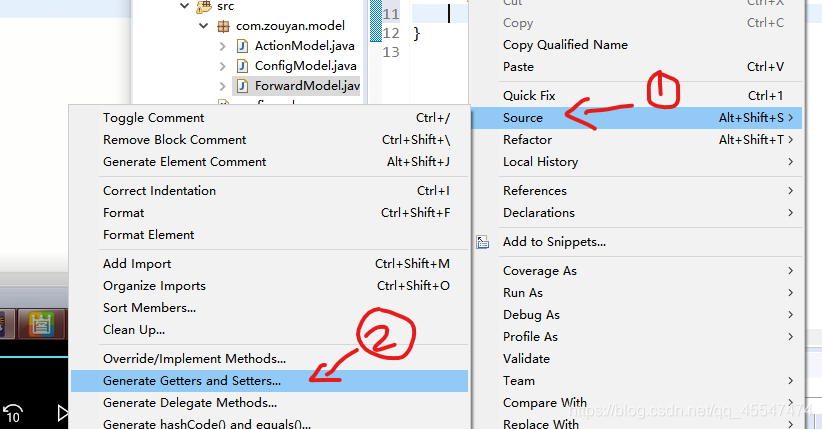
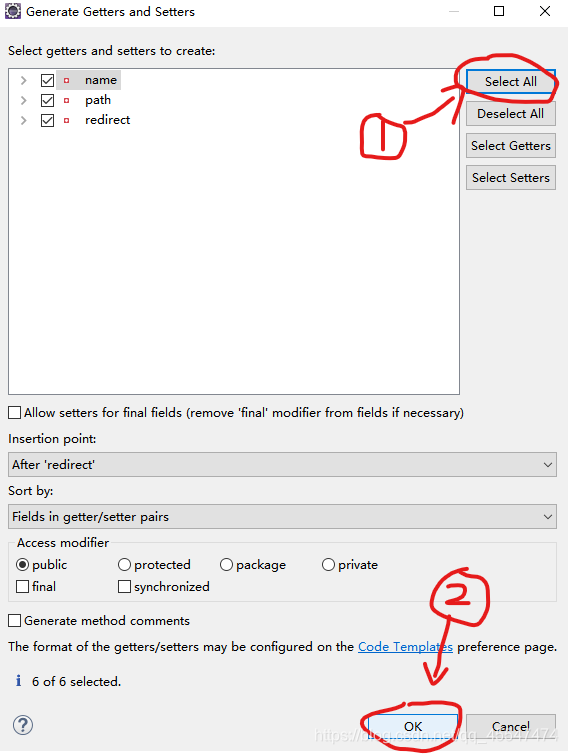
三个都完成之后,就开始撞到ConfigModel里面去,建出ConfigModelFactory工厂类。
2、Factory工厂
首先来了解一下23种设计模式之工厂模式。
工厂模式解决的问题:将代码封装,提高代码的复用性。
类比汉堡的获取方式(肯德基直接购买,原材料自己制作)
// zouyan
package com.zouyan.model;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
/**
* 23种设计模式之工厂模式。
*
*工厂模式解决的问题:将代码封装,提高代码的复用性。
*类比汉堡的获取方式(肯德基直接购买,原材料自己制作)
*
*一般工厂类一定会有一个方法,就是生产指定对象的方法 build newInstance
*
* 拥抱变化
* 注意:在工厂类中会有两个以上的构建方法,一个是默认框架路径的模型对象构建方法,
* 还有一个是动态读取任意位置下的框架配置文件
* @author zouyan
*
* Orange_南橙
*/
public class ConfigModelFactory {
/**
* 通过资源文件构建对呀的模型对象
*
* @param path
* 具体的资源文件路径
* @return
*/
public static ConfigModel build(String path) throws Exception {
// path=/config.xml
InputStream in = ConfigModelFactory.class.getResourceAsStream(path);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();//这个位置如果报错,就是没导dom4j jar包的原因
// doc=/config.xml里面的内容
Document doc = reader.read(in);//这个位置如果报错,就是没导dom4j jar包的原因
return null;
// 接下来就做一件事情——>把内容填充到configModel对象中(doc.asXML——>configModel)
ConfigModel configModel = new ConfigModel();
ActionModel actionModel = null;
ForwardModel forward = null;
List<Element> actionEles = doc.selectNodes("/config/action");
for(Element actionEle : actionEles) {
actionModel = new ActionModel();
actionModel.setPath(actionEle.attributeValue("path"));
actionModel.setType(actionEle.attributeValue("type"));
// 给actionModel中放入Forward对象????
// 拿到forward标签内容
List<Element> forwardEles = actionEle.selectNodes("forward");
for(Element forwardEle : forwardEles) {
ForwardModel = new ForwardModel();
forwardModel.setName(forwardEle.attributeValue("name"));
forwardModel.setPath(forwardEle.attributeValue("path"));
// redirect属性是boolean类型的
// 需求:只有config.xml中redirect属性值填写了false,它才代表转发
// forwardEle.attributeValue("redirect")获取到config中的redirect属性值
forwardModel.setRedirect(!"false".equals(forwardEle).attributeValue("redirect"));
actionModel.push(forwardModel);
}
configModel.push(actionModel);
}
return configModel;
}
public static ConfigModel build() throws Exception{
return build("/config.xml");//这个文件也就是最初的xml解析代码 文件名为config.xml
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConfigModel model = ConfigModelFactory.build();
ActionModel actionModel = model.pop("/loginAction");
System.out.println(actionModel.getType());
}
}
这段代码首先得到的结果是: 也就是满足最初的李四的需求。
也就是满足最初的李四的需求。
继续代码找张三的需求:
// zouyan
package com.zouyan.model;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
/**
* 23种设计模式之工厂模式。
*
*工厂模式解决的问题:将代码封装,提高代码的复用性。
*类比汉堡的获取方式(肯德基直接购买,原材料自己制作)
*
*一般工厂类一定会有一个方法,就是生产指定对象的方法 build newInstance
*
* 拥抱变化
* 注意:在工厂类中会有两个以上的构建方法,一个是默认框架路径的模型对象构建方法,
* 还有一个是动态读取任意位置下的框架配置文件
* @author zouyan
*
* Orange_南橙
*/
public class ConfigModelFactory {
/**
* 通过资源文件构建对呀的模型对象
*
* @param path
* 具体的资源文件路径
* @return
*/
public static ConfigModel build(String path) throws Exception {
// path=/config.xml
InputStream in = ConfigModelFactory.class.getResourceAsStream(path);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();//这个位置如果报错,就是没导dom4j jar包的原因
// doc=/config.xml里面的内容
Document doc = reader.read(in);//这个位置如果报错,就是没导dom4j jar包的原因
return null;
// 接下来就做一件事情——>把内容填充到configModel对象中(doc.asXML——>configModel)
ConfigModel configModel = new ConfigModel();
ActionModel actionModel = null;
ForwardModel forward = null;
List<Element> actionEles = doc.selectNodes("/config/action");
for(Element actionEle : actionEles) {
actionModel = new ActionModel();
actionModel.setPath(actionEle.attributeValue("path"));
actionModel.setType(actionEle.attributeValue("type"));
// 给actionModel中放入Forward对象????
// 拿到forward标签内容
List<Element> forwardEles = actionEle.selectNodes("forward");
for(Element forwardEle : forwardEles) {
forwardModel = new ForwardModel();
forwardModel.setName(forwardEle.attributeValue("name"));
forwardModel.setPath(forwardEle.attributeValue("path"));
// redirect属性是boolean类型的
// 需求:只有config.xml中redirect属性值填写了false,它才代表转发
// forwardEle.attributeValue("redirect")获取到config中的redirect属性值
forwardModel.setRedirect(!"false".equals(forwardEle).attributeValue("redirect"));
actionModel.push(forwardModel);
}
configModel.push(actionModel);
}
return configModel;
}
public static ConfigModel build() throws Exception{
return build("/config.xml");//这个文件也就是最初的xml解析代码 文件名为config.xml
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConfigModel model = ConfigModelFactory.build();
// ActionModel actionModel = model.pop("/regAction");
// System.out.println(actionModel.getType());
// 需求:获取/loginAction下的success结果代码对应的页面/main.jsp
ActionModel actionModel = model.pop("/loginAction");
System.out.println(actionModel.getType());
ForwardModel forwardModel = actionModel.pop("/success");
System.out.println(forwardModel.getPath());
}
}
最终结果就是找出张三的结果:
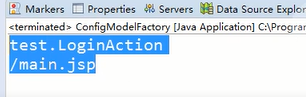
四、总结
如果没有这个xml建模,那么需要得到张三、李四和王五的需求,就可能需要敲三遍相同的代码,使用xml建模工厂大大的减少了代码的重复性。
这就是侧面看出xml建模的一个强大性。
我是南橙,一个逐渐秃头的橙子Orange。



























 261
261










