3.1 自由电子模型 Free electron model
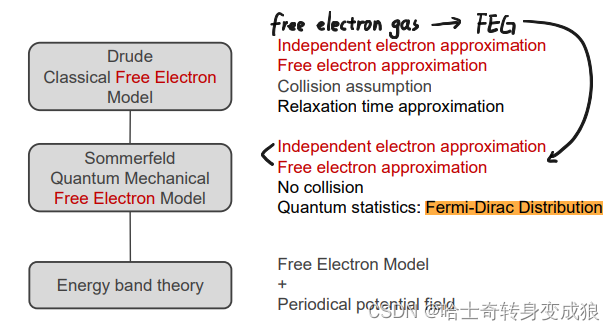
研究晶体中的电子:
- 自由电子理论:不考虑离子实
- 能带理论:考虑离子实(周期性势场)的作用
3.1.1 德鲁德模型 Drude Model - Classical Free Electron Model
(1)德鲁德模型
德鲁德模型:价电子游离于特定原子周围,弥散于整个晶体中,形成“自由电子气”。
The Drude model of electrical conduction was proposed in 1900 by Paul Drude to explain the transport properties of electrons in materials (especially metals). The model, which is an application of kinetic theory, assumes that the microscopic behavior of electrons in a solid may be treated classically and looks much like a pinball machine, with a sea of constantly jittering electrons bouncing and re-bouncing off heavier, relatively immobile positive ions.
Assumption of the electron gas:
- 独立电子近似 Independent electron approximation: No electrostatic interaction and collision among free electrons(自由电子之间没有相互作用和碰撞)
- 自由电子近似 Free electron approximation: No electrostatic interaction between free electrons and ions(电子和离子实之间只有碰撞,没有静电相互作用)
- 碰撞假设 Collision assumption: Velocity of electrons after collision with ions only concerns with temperature, but not the velocity before collision(电子和离子实的碰撞是瞬时的,碰撞后的速度仅与温度有关)
- 弛豫时间近似 Relaxation time approximation: Relaxation time τ is independent with the position and velocity of electrons(弛豫时间即同一粒子两次碰撞的时间间隔,它仅依赖于晶体结构)
在德鲁德模型中,存在电场时,电子每两次碰撞之间都会获得电场加速,从而形成漂移速度 v d v_d vd,且漂移速度远小于电子热运动的速度 v d ≪ v R M S = 3 k B T m v_d \ll v_{RMS} = \sqrt{\frac{3k_BT}{m}} vd≪vRMS=m3kBT
利用德鲁德模型能够成功解释:
- 欧姆定律
- Wiedemann-Franz ratio comes out close to right for most materials
- Many other transport properties predicted correctly
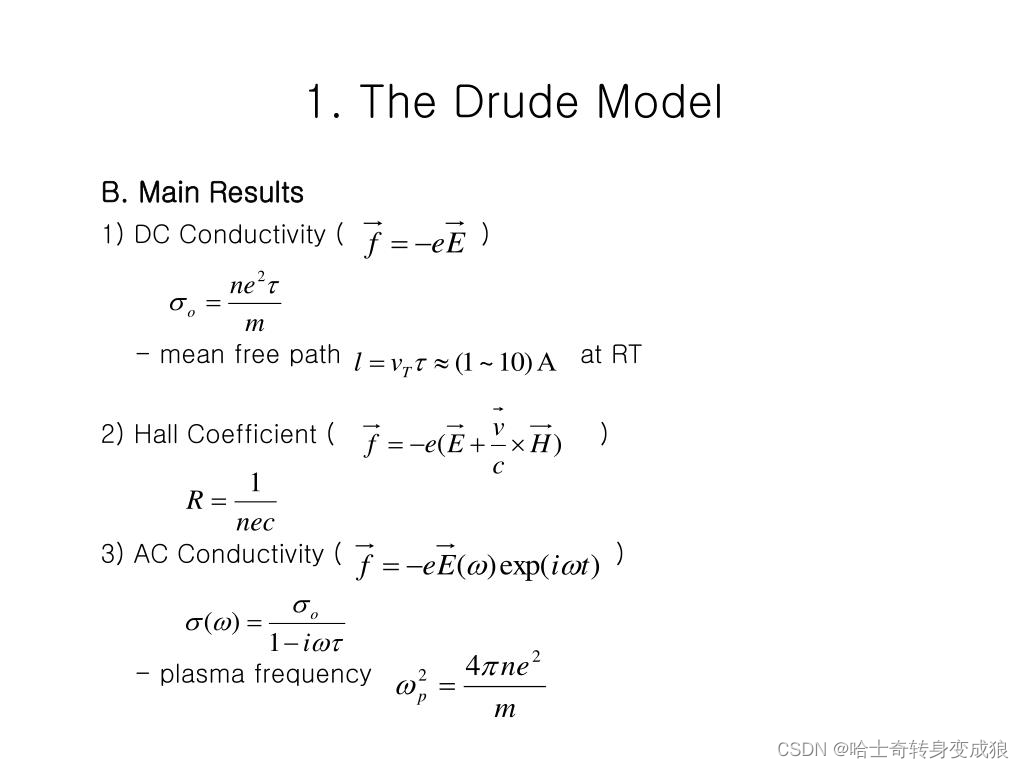

(2) failure of Drude Model
德鲁德模型存在的问题:
- 电子比热 Specific Heat of electrons
- 电导率与温度的关系 Temperature dependence of σ
- Wiedemann-Franz ratio
- The Seebeck/Peltier coefficient come out wrong by a factor of 100.
Despite the shortcomings of Drude theory, it nonetheless was the only theory of metallic conductivity for a quarter of a century (until the Sommerfeld theory improved it), and it remains quite useful today.
3.1.2 索末菲模型 Sommerfeld Model - Quantum Mechanical Free Electron Model
索末菲保留了德鲁德的自由电子气假设(前两个),但是索末菲去除了“碰撞”的概念,引入量子统计的理论(费米-狄拉克分布 Fermi-Dirac Distribution)。


(1)势阱 potential well
1D Infinite Potential Well
( − ℏ 2 2 m d 2 d x 2 + U ( x ) ) ψ ( x ) = E ψ ( x ) \left( -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m} \frac{d^2}{dx^2} + U(x) \right ) \psi (x) = E \psi(x) (−2mℏ2dx2d2+U(x))ψ(x)=Eψ(x)
k = n π L , n = 1 , 2 , 3 , … k = n \frac{\pi}{L}, \ \ n=1,2,3,\dots k=nLπ, n=1,2,3,…

3D Infinite Potential Well
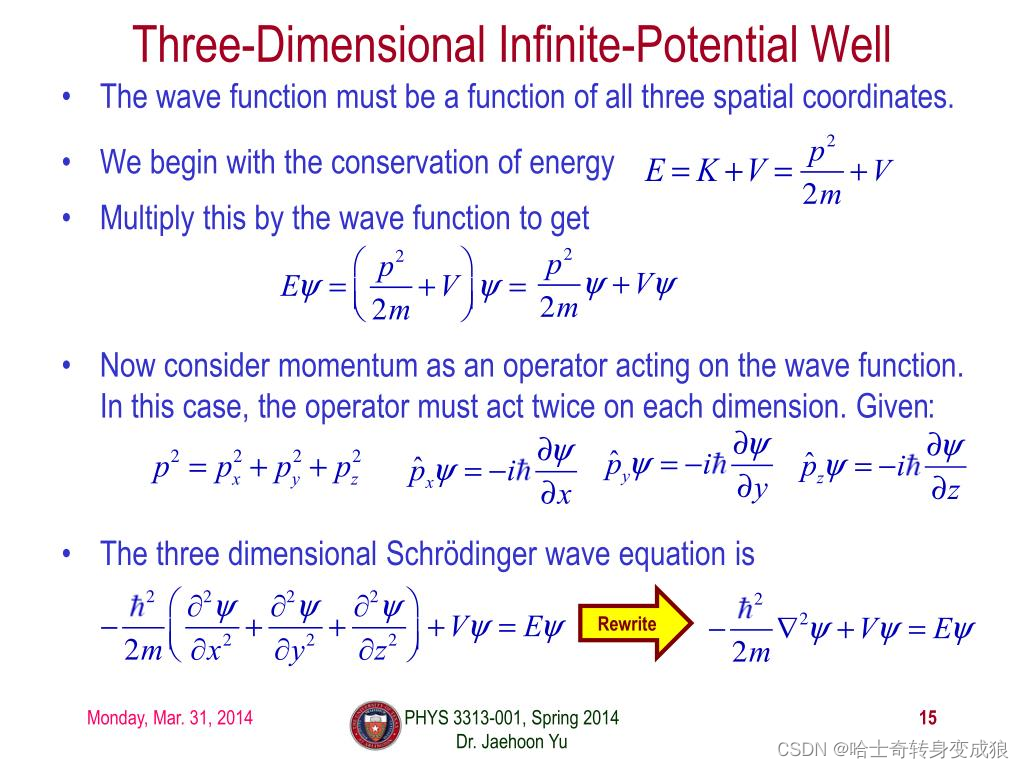
− ℏ 2 2 m ( ∂ 2 ∂ x 2 + ∂ 2 ∂ y 2 + ∂ 2 ∂ z 2 ) ψ ( x , y , z ) = E ψ ( x , y , z ) -\frac{\hbar ^2}{2m}\left( \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2}{\partial y^2} + \frac{\partial^2}{\partial z^2} \right) \psi(x,y,z) = E \psi (x,y,z) −2mℏ2(∂x2∂2+∂y2∂2+∂z2∂2)ψ(x,y,z)=Eψ(x,y,z)
ψ ( x , y , z ) = ψ ( x ) ψ ( y ) ψ ( z ) \psi(x,y,z) = \psi(x) \psi(y) \psi(z) ψ(x,y,z)=ψ(x)ψ(y)ψ(z)
∵ E = ℏ 2 k 2 2 m , k ⃗ = k x i ⃗ + k y j ⃗ + k z l ⃗ \because E = \frac{\hbar ^2 k^2}{2m}, \ \ \vec k = k_x \vec i + k_y \vec j + k_z \vec l ∵E=2mℏ2k2, k=kxi+k





 文章探讨了自由电子模型,从古典的德鲁德模型,包括其独立电子近似和碰撞假设,到量子力学的索末菲模型,涉及费米-狄拉克分布和费米能级的概念。文章还讨论了电子气的能量分布和温度依赖性,以及费米能级的量子统计解释。
文章探讨了自由电子模型,从古典的德鲁德模型,包括其独立电子近似和碰撞假设,到量子力学的索末菲模型,涉及费米-狄拉克分布和费米能级的概念。文章还讨论了电子气的能量分布和温度依赖性,以及费米能级的量子统计解释。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 8692
8692

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








