实训第3天的主要任务是将昨天的代码进行封装。构造Java的实体类,对这个实体类的对象进行操作,实现对数据库中数据的增、删、查、改。
今天老师还介绍了MVC三层模式的一些知识。
1、三层架构 (3-tier application) 是将整个业务应用划分为:表现层(UI)、业务逻辑层(BLL)、数据访问层(DAL)。区分层次的目的即为了“高内聚,低耦合”的思想。
(1)表现层(UI):展现给用户的界面,即用户在使用一个系统的时候的所见所得。
(2)业务逻辑层(BLL):对数据层的操作,对数据业务逻辑处理。
(3)数据访问层(DAL):直接操作数据库,针对数据的增、删、查、改等操作。
2、MVC是 Model-View-Controller,严格说这三个加起来才是三层架构中的UI层,也就是说,MVC把三层架构中的UI层再度进行了分化,分成了控制器、视图、实体。控制器完成页面逻辑,通过实体来与界面层完成通话,而Controller层直接与三层中的BLL进行对话。
3、MVC 可以是三层中的一个表现层框架,属于表现层。三层和mvc可以共存。 三层是基于业务逻辑来分的,是一个架构设计,而MVC是基于页面来分的,是一种设计模式。
————————————————————————————————————————————
下面是源码部分。
源码项目百度云链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1sUUyDjZBuL0_qQt1GztrGA
提取码:rkrm
1、最终的包结构:
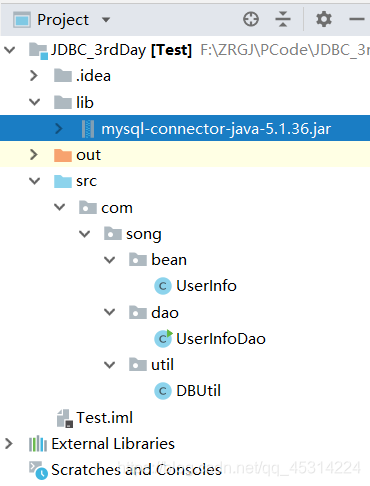
2、新建一个项目,在项目目录中添加Directory:lib,导入架包。
架包下载:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1l_Hu8MQlhrWTfLA5Vqg-Yg
提取码:llwf
3、在项目下新建package,如上图所示
bean 存放实体类
package com.song.bean;
public class UserInfo {
public UserInfo(int id,String username, String password){
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
@Override
public String toString(){
return "UserInfo{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
4、dao 持久层,实现数据库增删改查。即MVC的model层。
package com.song.dao;
import com.song.bean.UserInfo;
import com.song.util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class UserInfoDao {
public List<UserInfo> query(){
ResultSet resultSet = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
Connection connection = null;
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// 1.加载驱动 + 2.创建连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//3.写sql
String sql = "select * from userinfo";
//4.得到statement对象
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.执行sql,得到结果集
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//6.处理结果集
while(resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
String username = resultSet.getString(2);
String password = resultSet.getString(3);
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo(id,username,password);
userInfo.setId(id);
userInfos.add(userInfo);
}
System.out.println(userInfos);
//7.关闭资源
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(resultSet,statement,connection);
}
return userInfos;
}
public void add(UserInfo userInfo){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1.加载驱动 + 2.创建连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//查询SQL
String sql = "select * from userinfo";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
int id = 0;
while (resultSet.next()){
id = resultSet.getInt(1);
}
//3.写SQL
sql = "insert into userinfo(id,username,password) values(?,?,?)";
//4.得到statement对像
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id+1);
statement.setString(2,userInfo.getUsername());
statement.setString(3,userInfo.getPassword());
//5.执行sql,得到结果集
statement.executeUpdate();
//6.处理结果集
//7.关闭资源
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(resultSet,statement,connection);
}
}
public void delete(int id){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 1.加载驱动 + 2.创建连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//3.写sql
String sql = "delete from userinfo where id = ?";
//4.得到statement对象
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id);
//5.执行sql,得到结果集
statement.executeUpdate();
//6.处理结果集
//7.关闭资源
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null,statement,connection);
}
}
public void update(UserInfo userInfo){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 1.加载驱动 + 2.创建连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//3.写sql
String sql = "update userinfo set username=?,password=? where id=?";
//4.得到statement对象
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,userInfo.getUsername());
statement.setString(2,userInfo.getPassword());
statement.setInt(3,userInfo.getId());
//5.执行sql,得到结果集
statement.executeUpdate();
//6.处理结果集
//7.关闭资源
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(null,statement,connection);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
UserInfoDao test = new UserInfoDao();
//test.query();
//test.add(new UserInfo(6,"2333","2333"));
//test.delete(10);
//test.update(new UserInfo(2,"song","song"));
}
}
5、until 这里写的是工具,具体指加载驱动、建立连接以及关闭资源的内容。
package com.song.util;
import java.sql.*;
public class DBUtil {
public static Connection getConnection(){
try{
// 1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.创建连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/idea?useSSL=true&"
+ "characterEncoding=utf-8&user=root&password=root");
return connection;
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static void close(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement,Connection connection){
if(resultSet != null){
try{
resultSet.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(statement != null){
try{
statement.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try{
connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
6、使用上次创建的idea数据库,验证一下功能。
数据库表userinfo:
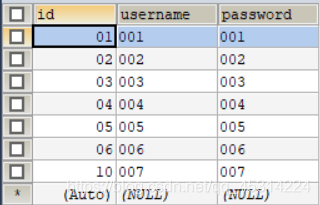
(1)运行UserInfoDao的test.query函数,运行结果:
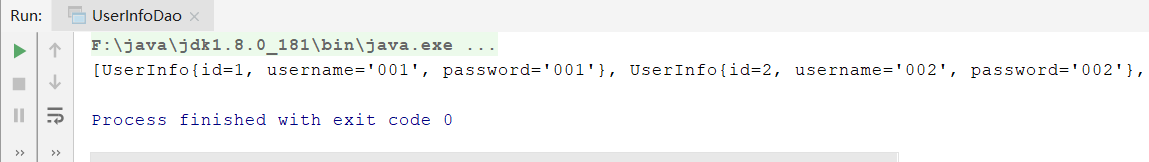
(2)运行UserInfoDao的test.add函数,运行结果:
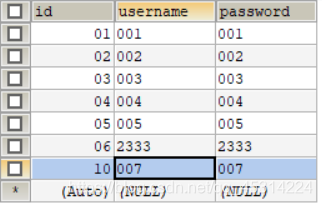
(3)运行UserInfoDao的test.delete函数,运行结果:
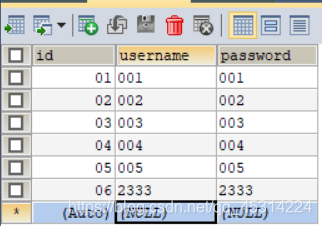
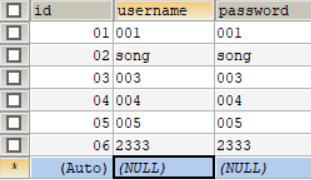
(4)运行UserInfoDao的test.update函数,运行结果:








 本文介绍Java实训中MVC模式与三层架构的应用,包括表现层、业务逻辑层和数据访问层的分工,以及如何通过实体类操作数据库,实现数据的增删查改。
本文介绍Java实训中MVC模式与三层架构的应用,包括表现层、业务逻辑层和数据访问层的分工,以及如何通过实体类操作数据库,实现数据的增删查改。
















 481
481

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








