前言
本文主要对HashMap和HashSet进行实现,以及方法进行总结,最后引入哈希冲突的避免和解决方法。
一、HashMap
1.原理
Map是接口,其中存储的是结构为<K,V>的键值对,并且key是唯一的不能重复的。
实现Map接口的类有HashMap和TreeMap,HashMap主要是根据哈希函数确定哈希地址来存放变量,而TreeMap由于继承了SortedMap接口,在其存储时是有序的。

2.实现
Map.Entry<K,V>
使用Map.Entry<K,V>可以方便对Map中的key、value进行获取,主要的方法有:getKey()、getValue()、setValue(value)
代码如下(示例):
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entrySet: set) {
System.out.println("key="+entrySet.getKey()+",values="+entrySet.getValue());
}
Map的主要方法
get():根据key获取value;
put(key,value):对应的key设置value值;
remove(key):删除key的映射关系;
set<Map.Entry<K,V>> enrtySet():所有key-value的映射关系;
containsKey(key)、containsValue(value)等。
代码如下(示例):
//统计10w个数据中每个数据出现的次数
public static void fun3(int[] array) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(map.get(array[i]) == null) {
map.put(array[i],1);
}else {
map.put(array[i],map.get(array[i])+1);
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
哈希桶的实现
(1)使用数组array和链表进行存储;
(2)存储的时候通过哈希函数(key % array.length)得到在数组中的index之后遍历链表,将其key相等的结点的val替换,没有相等的key就进行头插法插入链表;
(3)扩容的时候,由于哈希函数的变化,需要将原数组中的每一个key进行重新插入到新数组中。
(4)对于自定义类型,由于存储的时候需要比较,所以要重写hashCode()和equals()方法。
代码如下(示例):
class People{
public String name;
public People() {}
public People(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
People people = (People) o;
return Objects.equals(name, people.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name);
}
}
哈希桶实现:
public class HashBuck {
static class Node {
public int key;
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int key,int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node[] array;
public int usedSize;
public static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75F;
public HashBuck() {
this.array = new Node[10];
this.usedSize = 0;
}
public void put(int key,int val) {
Node node = new Node(key,val);
int index = key % array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while (cur!=null) {
if(cur.key == key) {
cur.val = val;
return;
}
}
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
//检查负载因子
if(loadFactor() >= DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) {
grow();
}
}
private void grow() {
Node[] tmp = new Node[array.length*2];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Node cur = array[i];
while (cur != null) {
Node curNext = cur.next;
int index = cur.key % tmp.length;
//头插法
cur.next = tmp[index];
tmp[index] = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
}
this.array = tmp;
}
public float loadFactor() {
return usedSize*1.0F / array.length;
}
public int get(int key) {
int index = key % array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.key == key) {
return cur.val;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
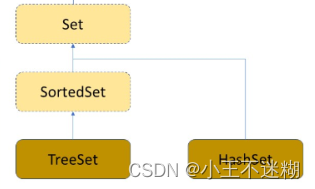
二、HashSet
1.原理
set接口下由TreeSet和HashSet进行实现,和Map不同的是set里面只存储了key。
2.案例
(1)删除重复元素
代码如下(示例):
//10w个数据,将10w个数据当中重复的元素删除掉
public static void fun1(int[] array) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
set.add(array[i]);
}
System.out.println(set);
}
(2)寻找第一个重复的数
代码如下(示例):
//寻找10w个数据中第一个重复的数
public static int fun2(int[] array) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(set.contains(array[i])) {
return array[i];
}else {
set.add(array[i]);
}
}
return -1;
}
总结
(1)两个对象的hashCode相等,但是equals不一定相等;但两个对象的equals相等,但是hashCode一定相等。
(2)HashMap<K,V> map = new HashMap<>();底层数组是0,第一次put后数组大小变成16
(3)HashMap<K,V> map = new HashMap<>(25);数组大小是32,他的大小会根据其给定容量相近的2次幂大小取上整数。
(4)扩容是由于超过了负载因子,在扩容的时候需要重新哈希。
























 1550
1550

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








