Vuex变量运用
了解Vuex
官方解释:Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。可以想象为一个“前端数据库”(数据仓库),让其在各个页面上实现数据的共享包括状态,并且可操作
Vuex分成五个部分:
1.State:单一状态树
2.Getters:状态获取
3.Mutations:触发同步事件
4.Actions:提交mutation,可以包含异步操作
5.Module:将vuex进行分模块
vuex安装
进入控制器到项目安装
npm install vuex -S
创建store模块,分别维护state/actions/mutations/getters

在store/index.js文件中新建vuex的store实例,并注册上面引入的各大模块
index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import state from './state'
import getters from './getters'
import actions from './actions'
import mutations from './mutations'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations
})
export default store
在main.js中导入并使用store实例

vuex综合案例
需求:两个组件A和B,vuex维护的公共数据是餐馆名:resturantName,默认值:飞歌餐馆,
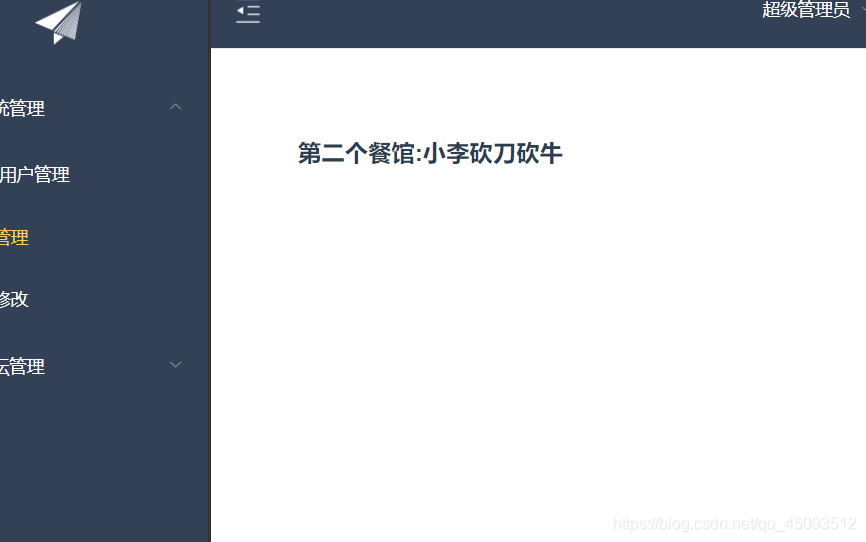
那么现在A和B页面显示的就是飞歌餐馆。如果A修改餐馆名称为A餐馆,则B页面显示的将会是A餐馆,反之B修改同理。
这就是vuex维护公共状态或数据的魅力,在一个地方修改了数据,在这个项目的其他页面都会变成这个数据。
vuePage1.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3 style="margin: 70px;">第一个餐馆:{{title}}</h3>
<button @click="changeTitle">餐馆易主</button>
<button @click="changeTitleAsync">两月后易主</button>
<button @click="doAjax">测试Vuex中使用Ajax</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return {
};
},
methods:{
changeTitle(){
this.$store.commit('setResturantName',{
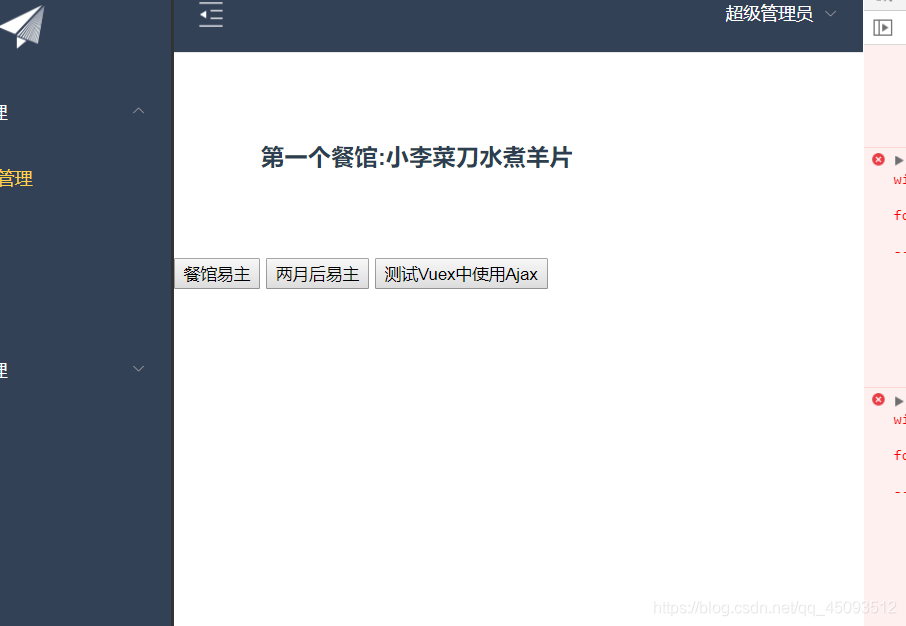
resturantName:'小李菜刀水煮羊片'
});
},
changeTitleAsync(){
this.$store.dispatch('setResturantNameAsync',{
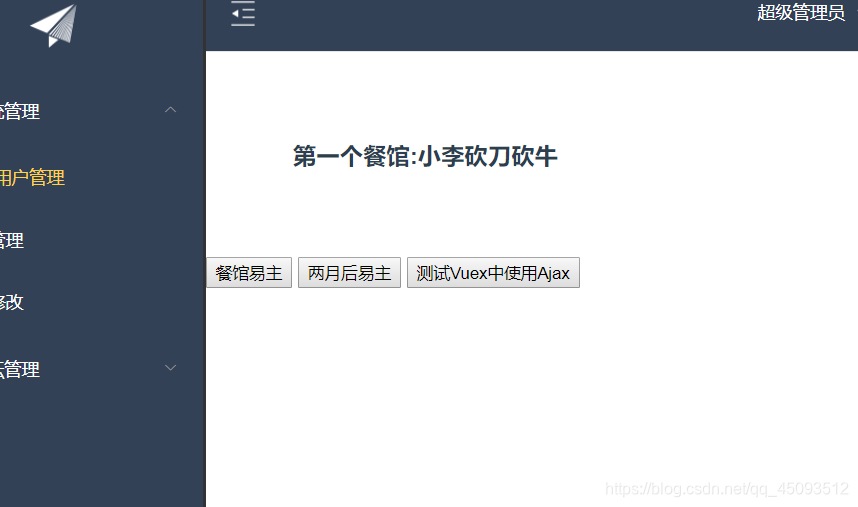
resturantName:'小李砍刀砍牛'
});
},
doAjax(){
this.$store.dispatch('doAjax',{
_this:this
});
}
},
computed:{
title(){
// return this.$store.state.resturantName;
return this.$store.getters.getResturantName;
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
vuePage2.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3 style="margin: 70px;">第er个餐馆:{{title}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return {
title:''
};
},
created(){
this.title = this.$store.state.resturantName;
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
在router下index.js配置路径
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
import login from '@/view/login'
import Reg from '@/view/Reg'
import AppMain from '@/components/AppMain'
import Articles from '@/view/sys/Articles'
import VuexPage1 from '@/view/sys/VuexPage1'
import VuexPage2 from '@/view/sys/VuexPage2'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [{
path: '/',
name: 'login',
component: login
},
{
path: '/login',
name: 'login',
component: login
},
{
path: '/Reg',
name: 'Reg',
component: Reg
},
{
path: '/AppMain',
name: 'AppMain',
component: AppMain,
children:[
{
path: '/sys/Articles',
name: 'Articles',
component: Articles
},
{
path: '/sys/VuexPage1',
name: 'VuexPage1',
component: VuexPage1,
},
,
{
path: '/sys/VuexPage2',
name: 'VuexPage2',
component: VuexPage2,
}
]
}
]
})
Action类似于 mutation,不同在于:
1.Action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态
2.Action可以包含任意异步操作
3.Action的回调函数接收一个 context 上下文参数,注意,这个参数可不一般,它与 store 实例有着相同的方法和属性
但是他们并不是同一个实例,context 包含:
- state、2. rootState、3. getters、4. mutations、5. actions 五个属性
所以在这里可以使用 context.commit 来提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。
export default{
setResturantNameAsync: (context, payload) => {
console.log("zzz")
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('setResturantName', payload); //Action提交的是mutation
console.log("aaa")
},3000);
console.log("bbb")
},
doAjax: (context, payload) => {
//vuex是不能使用Vue实例的
let _this = payload._this;
let url = _this.axios.urls.SYSTEM_USER_DOLOGIN;
// let url = 'http://localhost:8080/SSH/vue/userAction_login.action';
console.log(url)
_this.axios.post(url, {}).then((response) => {
console.log('doAjax.........');
console.log(response);
}).catch((response) => {
//carch则是异常
console.log(response);
});
}
}
state
每一个Vuex应用的核心就是store(仓库),store基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)。
export default{
resturantName:'飞歌餐馆'
}
mutations
处理数据的唯一途径,state的改变或赋值只能在这里
export default {
setResturantName: (state, payload) => {
state.resturantName = payload.resturantName;
}
}
getters
获取数据并渲染,
export default {
getResturantName: (state) => {
return state.resturantName;
}
}
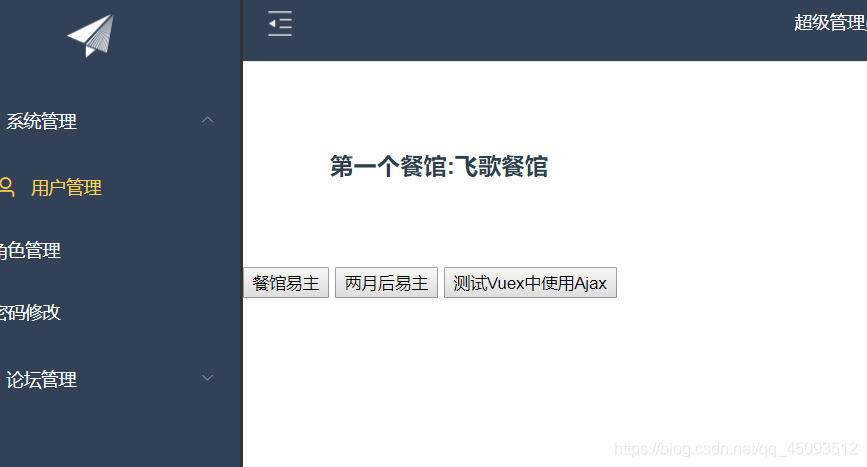
点击第二个按钮后再点击第一个按钮会发现是…水煮羊片
等第二个按钮时间一到又会转换成相应的 …砍刀砍牛
第二页面也会相应的保持一致








 本文介绍了Vuex,一个专为Vue.js应用程序设计的状态管理模式。通过五个核心部分——State、Getters、Mutations、Actions和Module,实现数据的共享和状态管理。详细讲解了Vuex的安装、创建store模块、在main.js中使用,以及如何通过Action处理异步操作。通过一个综合案例展示了如何在组件A和B之间共享和更新餐馆名称,以体现Vuex维护公共状态的特性。
本文介绍了Vuex,一个专为Vue.js应用程序设计的状态管理模式。通过五个核心部分——State、Getters、Mutations、Actions和Module,实现数据的共享和状态管理。详细讲解了Vuex的安装、创建store模块、在main.js中使用,以及如何通过Action处理异步操作。通过一个综合案例展示了如何在组件A和B之间共享和更新餐馆名称,以体现Vuex维护公共状态的特性。
















 1161
1161

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








