1.哈希表的基本介绍
哈希表(Hash table)也叫做散列表,是根据关键码值(key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构,也就是说,它通过把关键码映射到表中的一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度,这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表
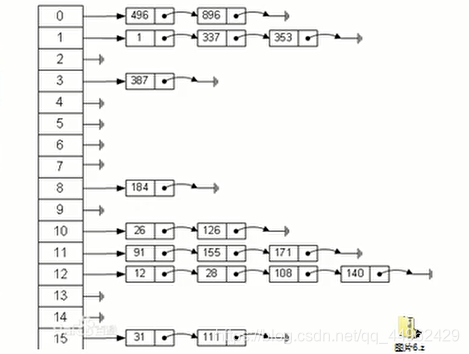
哈希表实战题
录入员工的信息,当输入员工的id时,查找出该员工
要求:不要使用数据库,越快越好
使用哈希表实现图分析
代码实现:
package com.self.dataStructure.hashTable;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HashTableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTab hashTab = new HashTab(7);
String key = "";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean a = true;
while (a){
System.out.println("add:添加");
System.out.println("show:遍历");
System.out.println("find:查找");
System.out.println("exit:退出");
System.out.println("delete:删除");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key){
case "add":
System.out.println("输入id");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入名字");
String name = scanner.next();
Emp emp = new Emp(id, name);
hashTab.addEmp(emp);
break;
case "show":
hashTab.showAllList();
break;
case "find":
int no = scanner.nextInt();
hashTab.findEmpById(no);
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
a = false;
System.out.println("program id stop");
break;
case "delete":
int number = scanner.nextInt();
hashTab.deleteById(number);
break;
}
}
}
}
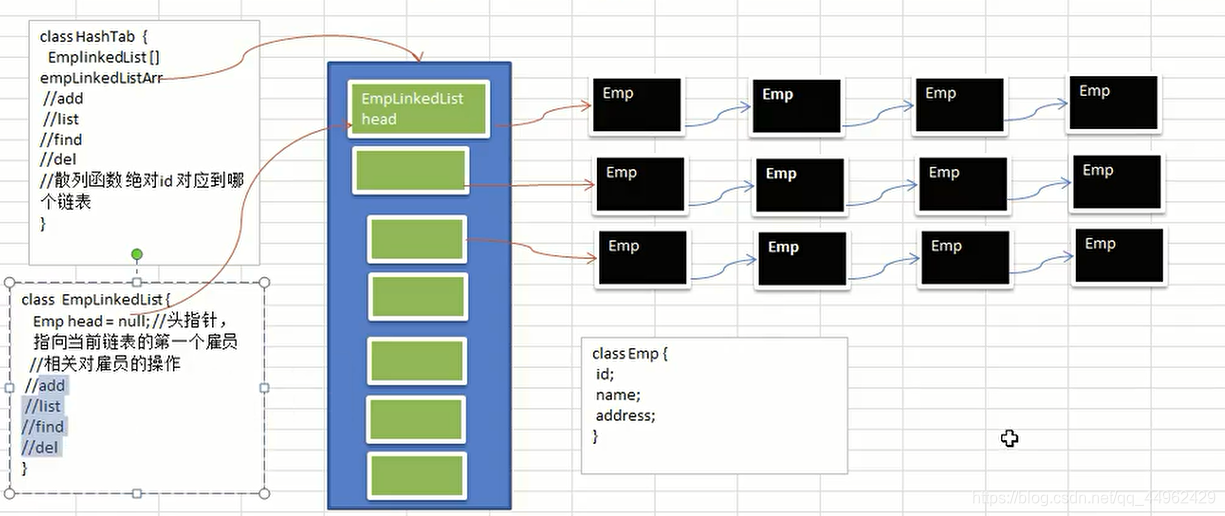
class HashTab{
private EmpLinkedList[] empLinkedListArray;
private int size;
public HashTab(int size) {
this.empLinkedListArray = new EmpLinkedList[size];
this.size = size;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedListArray[i] = new EmpLinkedList();
}
}
public void addEmp(Emp emp){
int empLinkedListNO = hashFun(emp.id);
empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNO].addEmp(emp);
}
public void showAllList(){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
empLinkedListArray[i].sowList(i);
}
}
public void findEmpById(int no){
int empLinkedListNO = hashFun(no);
Emp emp = empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNO].findEmpById(no);
System.out.println(emp);
}
public void deleteById(int no){
int empLinkedListNO = hashFun(no);
empLinkedListArray[empLinkedListNO].deleteById(no);
}
//散列函数
public int hashFun(int id){
return id % size;
}
}
class Emp{
public int id;
public String name;
public Emp next; //默认值为null
public Emp(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
class EmpLinkedList{
private Emp head; //头指针,执行第一个Emp,因此我们这个链表的head,是直接指向第一个Emp
/*添加到雇员链表
假定添加的雇员id是子增长的,即id的分配总是从小到大,所以将添加的雇员加入到本链表最后即可
* */
public void addEmp(Emp emp){
if(head == null){
head = emp;
return;
}
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true){
if(curEmp.next == null){
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
curEmp.next = emp;
}
public void sowList(int no){
if(head == null){
System.out.println(no+1+"\tcurrent linkedList is null");
return;
}
Emp curEmp = head;
System.out.println(no+1+"\tcurrent linkedList message is");
while (true){
System.out.println(curEmp);
if(curEmp.next == null){
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
}
public Emp findEmpById(int id){
if(head == null){
System.out.println("current linkedList is null");
return null;
}
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true){
if(curEmp.id == id){
break;
}
if(curEmp.next == null){
curEmp = null;
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
return curEmp;
}
public void deleteById(int id){
boolean flag = false;
if(head == null){
System.out.println("current linkedList is null");
return ;
}
if(head.id == id){
head = head.next;
return;
}
Emp curEmp = head;
while (true){
if(curEmp.next == null){
break;
}
if(curEmp.next.id == id){
flag = true;
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
if(flag){
curEmp.next = curEmp.next.next;
}
}
}
























 7899
7899

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








