目录
- 程序的耦合和解耦
- 使用spring的ioc解决程序耦合
一、什么是程序的耦合和解耦
耦合:描述程序间的依赖关系,类、方法间的依赖关系。划分模块的依据就是高内聚低耦合
解耦:降低程序间的依赖关系,只能降低,不能完全消失
在实际开发中,我们往往减少编译期的依赖,尽量在运行期依赖。
实例说明程序间的耦合:
-
项目架构:

-
代码:
/**
* 表现层实现类
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IAccountService as=new AccountServiceImpl();//表现层调用业务层,类之间相互依赖,具有耦合性
as.saveAccount();
}
}
/**
* 业务层接口
*/
public interface IAccountService {
public void saveAccount();
}
/**
* 业务层实现类
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
IAccountDao accountDao =new AccountDaoImpl();//业务层调用持久层,类之间相互依赖,具有耦合性
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
// System.out.println("业务层保存账户方法");
}
}
/**
* 持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
void saveAccount();
}
/**
* 持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("持久层保存账户方法");
}
}
- 运行结果

- 其中表现层调用业务层的类创建对象,业务层调用持久层的类创建对象,类之间具有依赖关系,若将其中一个类删掉,则程序会运行报错,所以我们项目代码模块划分时要求低耦合


二、解耦的思路
方法一:工厂模式解耦
在实际开发中,我们往往将三层的对象都使用配置文件配置起来,当启动服务器应用时,用一个类中的方法来读取配置文件,创建对象并存起来,在接下来使用时,之间拿过来用就好。这个读取配置文件,创建对象并存起来,获取对象的方法就是工厂。
第一个:需要一个配置文件来配置我们的service和dao
配置的内容:唯一标识=全限定类名(key=value)
第二个:通过读取配置文件中配置的内容,反射创建对象
我们的配置文件可以是XML也可以是properties
实例:
- 项目架构

- 代码
配置文件:bean.properties

/**
* 业务层接口
*/
public interface IAccountService {
public void saveAccount();
}
/**
* 业务层实现类
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
// IAccountDao accountDao =new AccountDaoImpl();//业务层调用持久层,类之间相互依赖,具有耦合性
IAccountDao accountDao= (IAccountDao) BeanFactory.getBeans("accountDao");
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("业务层保存账户方法");
accountDao.saveAccount();
// System.out.println("业务层保存账户方法");
}
}
/**
* 持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
void saveAccount();
}
/**
* 持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("持久层保存账户方法");
}
}
/**
* 工厂解耦
*/
public class BeanFactory {
/**
* 1、定义一个pproperties对象
* 2、获取properties文件的流对象
* 3、为Properties对象赋值
* 4、其他类中根据bean的名称获取bean对象的方法
*/
//1、定义一个properties对象
private static Properties props;
//2、使用静态代码块获取properties文件的流对象,并为properties对象赋值
static {
try {
//实例化roperties对象
props = new Properties();
//获取流对象
InputStream in = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties");
//赋值
props.load(in);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError("失败");
}
}
//3、其他类传入bean的名称调用该方法获取bean对象
public static Object getBeans(String beanName) {
Object bean = null;
try {
//通过beanName得到类路径
String beanPath = props.getProperty(beanName);
System.out.println(beanPath);
//根据得到的路径去找对应类创建对象
bean = Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bean;
}
}
/**
* 表现层实现类
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IAccountService as=new AccountServiceImpl();//表现层调用业务层,类之间相互依赖,具有耦合性
IAccountService as= (AccountServiceImpl) BeanFactory.getBeans("accountService");
as.saveAccount();
}
}
#单例对象与多例对象
我们将BeanFactory,java中的System.out.println(beanPath);删掉
将Client.java中的代码修改如下:
/**
* 表现层实现类
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IAccountService as=new AccountServiceImpl();//表现层调用业务层,类之间相互依赖,具有耦合性
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
IAccountService as = (AccountServiceImpl) BeanFactory.getBeans("accountService");
System.out.println(as);
// as.saveAccount();
}
}
}
此时我们会发现创建了五个不同的as对象,说明此时为多例对象;
 若要使它成为一个单例对象,我们如何做呢?这时只需要创建好一个对象后,我们就将它存入容器中,之后从容器中取就好了。修改BeanFactory.java如下:
若要使它成为一个单例对象,我们如何做呢?这时只需要创建好一个对象后,我们就将它存入容器中,之后从容器中取就好了。修改BeanFactory.java如下:
/**
* 工厂解耦:单例型,用一个容器存放创建好的对象
*/
public class BeanFactory02 {
//1、定义一个Properties对象
private static Properties props;
//2、定义一个容器,用于存放创建好的对象
private static Map<String, Object> beans;
//一个静态方法用于获取.properties流对象,同时将创建好的实例加入容器
static {
try {
//实例化Properties对象
props = new Properties();
//获取流对象
InputStream in = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties");
props.load(in);
//实例化容器
beans=new HashMap<String,Object>();
/**
* 将配置文件中对应的键名及其键值创建的对象放入beans中
*/
//定义枚举类型获取props中的键名
Enumeration keys= props.keys();
//根据键名寻找键值并创建对象
while(keys.hasMoreElements()){
String key=keys.nextElement().toString();
String beanPath= props.getProperty(key);
Object object=Class.forName(beanPath).newInstance();
beans.put(key,object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Object getBeans(String beanName){
//直接根据id从容器中取对象
return beans.get(beanName);
}
}
打印出来就是我们的单例对象

方法二:使用spring的IOC解决程序耦合
什么是IoC?
IoC(Inverce of Control)即控制反转,是spring的两大核心之一。
控制反转的含义:
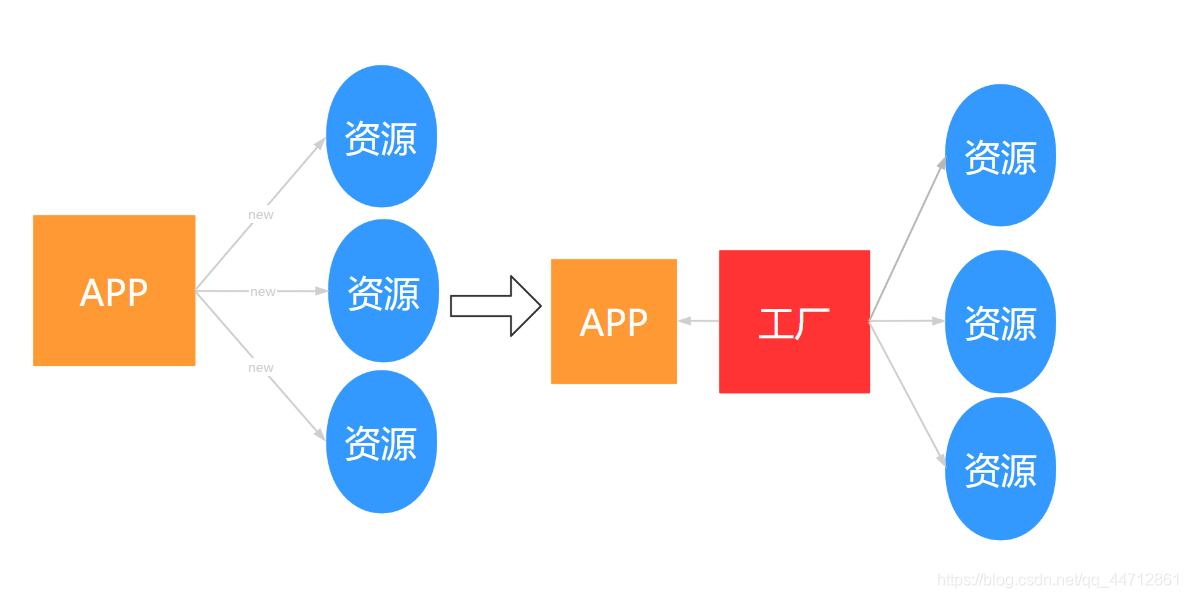
以前我们创建对象都是主动去new的,类之间具有依赖关系,但引入控制反转后,我们将自己创建对象的主动权交给工厂,由工厂为我们创建对象,在返回对象给我们,减少了依赖关系,这种主动放弃自己控制权的行为叫做控制反转。
控制反转的功能:削减程序间依赖关系,降低耦合。
 实例:
实例:
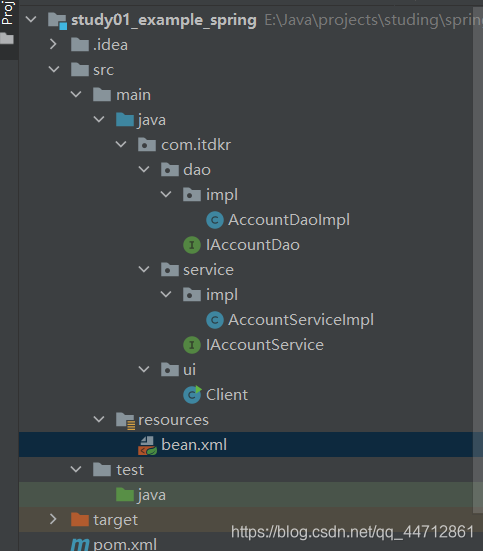
项目架构:
#在pom.xml中引入spring依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itdkr</groupId>
<artifactId>study01_example_spring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
#写bean.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 其实与我们之前的bean.properties文件大同小异-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itdkr.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itdkr.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
/**
* 账户业务层的接口
*/
public interface IAccountService {
/**
* 模拟保存账户
*/
void saveAccount();
}
/**
* 账户的实现类
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
public void saveAccount(){
}
}
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 模拟保存账户
*/
void saveAccount();
}
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存账户");
}
}
/**
* 获取spring容器,在容器中通过查找id创建对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取spring容器
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//在容器中根据id创建对象
IAccountService as= (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService");
System.out.println(as);
IAccountDao dao= (IAccountDao) ac.getBean("accountDao");
System.out.println(dao);
}
}
#运行结果:
 #当然我们也可以使用工厂来创建对象,将Client.java修改如下:
#当然我们也可以使用工厂来创建对象,将Client.java修改如下:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// //获取spring容器
// ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//
// //在容器中根据id创建对象
// IAccountService as= (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService");
// System.out.println(as);
//
// IAccountDao dao= (IAccountDao) ac.getBean("accountDao");
// System.out.println(dao);
// =======================BeanFactory=======================
//1、读取配置文件
Resource resource=new ClassPathResource("bean.xml");//注意导入的是spring的Resource
//2、构造工厂
BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
//3、创建对象
IAccountService as= (IAccountService) factory.getBean("accountService");
System.out.println(as);
}
}
#运行结果
#ApplicationContext与BeanFactory的区别
ApplicationContext:
它在读取配置文件时,采取的是立即加载的方式,即读取完配置文件后就立即创建了对象。适用于单例对象。
BeanFactory:
它在创建核心容器时,采取的是延迟加载的方式,即什么时候根据id获取对象,则什么时候创建对象,适合于多例对象。
#简而言之,如下图所示:










 本文探讨了程序的耦合与解耦概念,解释了如何通过工厂模式进行解耦,并详细介绍了Spring的IoC(控制反转)机制。通过实例展示了Spring如何通过配置文件管理对象,降低依赖关系,实现程序的低耦合。同时,对比了ApplicationContext与BeanFactory在对象创建时机上的区别。
本文探讨了程序的耦合与解耦概念,解释了如何通过工厂模式进行解耦,并详细介绍了Spring的IoC(控制反转)机制。通过实例展示了Spring如何通过配置文件管理对象,降低依赖关系,实现程序的低耦合。同时,对比了ApplicationContext与BeanFactory在对象创建时机上的区别。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








