面试经典算法题100-单词搜索 II
公众号:阿Q技术站
LeetCode.212
问题描述
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个单词(字符串)列表 words, 返回所有二维网格上的单词 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
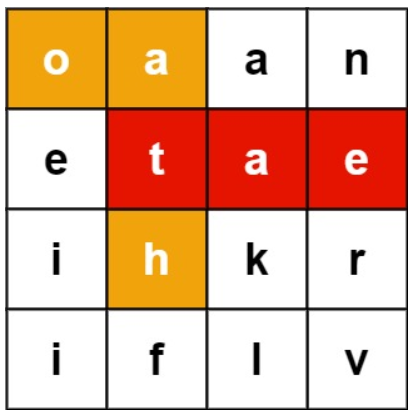
输入:board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
输出:["eat","oath"]
示例 2:
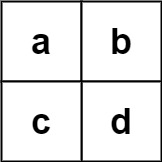
输入:board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"]
输出:[]
思路
-
Trie(前缀树)构建:使用前缀树(Trie)来存储所有单词
words。前缀树是一种适用于快速查找字符串的树形数据结构。 -
深度优先搜索(DFS):遍历二维网格
board的每一个单元格,使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来查找所有可能的单词。通过将字符从board中标记为已访问来防止重复使用。 -
回溯:在搜索的过程中,需要回溯以恢复状态。例如,访问一个字符后,需要在搜索完成后将其恢复到未访问状态。
-
优化搜索:通过前缀树,能够快速判断是否有可能找到一个以当前字符开始的单词,从而避免不必要的搜索。
参考代码
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
// TrieNode 结构定义
struct TrieNode {
TrieNode* children[26]; // 子节点
string word; // 存储完整单词
TrieNode() : word("") {
fill(begin(children), end(children), nullptr); // 初始化子节点为空
}
};
// Trie 树结构
class Trie {
public:
TrieNode* root;
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* node = root;
for (char c : word) {
if (!node->children[c - 'a']) {
node->children[c - 'a'] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node->children[c - 'a'];
}
node->word = word; // 结尾存储单词
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<string>& words) {
Trie trie;
for (string word : words) {
trie.insert(word); // 将所有单词插入到前缀树中
}
unordered_set<string> result_set; // 使用集合避免重复单词
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].size(); j++) {
dfs(board, i, j, trie.root, result_set); // 对每个字符进行 DFS 搜索
}
}
return vector<string>(result_set.begin(), result_set.end());
}
private:
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, int i, int j, TrieNode* node, unordered_set<string>& result_set) {
// 边界条件或已经访问过的条件
if (i < 0 || i >= board.size() || j < 0 || j >= board[0].size() || board[i][j] == '#' || !node->children[board[i][j] - 'a']) {
return;
}
char c = board[i][j];
node = node->children[c - 'a'];
if (!node->word.empty()) {
result_set.insert(node->word); // 找到一个完整单词
}
board[i][j] = '#'; // 标记该位置已访问
// 对四个方向进行 DFS 搜索
dfs(board, i + 1, j, node, result_set);
dfs(board, i - 1, j, node, result_set);
dfs(board, i, j + 1, node, result_set);
dfs(board, i, j - 1, node, result_set);
board[i][j] = c; // 回溯,恢复标记
}
};
int main() {
Solution solution;
vector<vector<char>> board = {
{'o','a','a','n'},
{'e','t','a','e'},
{'i','h','k','r'},
{'i','f','l','v'}
};
vector<string> words = {"oath","pea","eat","rain"};
vector<string> result = solution.findWords(board, words);
cout << "找到的单词: ";
for (string word : result) {
cout << word << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class TrieNode {
// TrieNode 定义,包含子节点和完整单词
TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26];
String word = null;
}
class Trie {
// Trie 树定义
TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// 插入单词到 Trie 树
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int index = c - 'a';
if (node.children[index] == null) {
node.children[index] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node.children[index];
}
node.word = word;
}
}
public class Solution {
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
for (String word : words) {
trie.insert(word); // 将所有单词插入到 Trie 树中
}
Set<String> resultSet = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
dfs(board, i, j, trie.root, resultSet); // 从每个位置进行 DFS 搜索
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(resultSet);
}
private void dfs(char[][] board, int i, int j, TrieNode node, Set<String> resultSet) {
if (i < 0 || i >= board.length || j < 0 || j >= board[0].length || board[i][j] == '#' || node.children[board[i][j] - 'a'] == null) {
return; // 超出边界或已访问或无匹配单词
}
char c = board[i][j];
node = node.children[c - 'a'];
if (node.word != null) {
resultSet.add(node.word); // 找到一个完整单词
node.word = null; // 防止重复添加
}
board[i][j] = '#'; // 标记已访问
dfs(board, i + 1, j, node, resultSet); // 向下搜索
dfs(board, i - 1, j, node, resultSet); // 向上搜索
dfs(board, i, j + 1, node, resultSet); // 向右搜索
dfs(board, i, j - 1, node, resultSet); // 向左搜索
board[i][j] = c; // 恢复未访问状态
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
char[][] board = {
{'o', 'a', 'a', 'n'},
{'e', 't', 'a', 'e'},
{'i', 'h', 'k', 'r'},
{'i', 'f', 'l', 'v'}
};
String[] words = {"oath", "pea", "eat", "rain"};
List<String> result = solution.findWords(board, words);
System.out.println("找到的单词: " + result);
}
}
Python
from typing import List
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.word = None # 当节点代表一个完整的单词时,存储该单词
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word: str):
node = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in node.children:
node.children[char] = TrieNode()
node = node.children[char]
node.word = word # 单词结束,存储单词在节点上
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
# 构建Trie树
trie = Trie()
for word in words:
trie.insert(word)
result = set() # 使用集合来避免重复单词
rows, cols = len(board), len(board[0])
def dfs(r, c, node):
char = board[r][c]
if char not in node.children:
return # 如果当前字符不在Trie树的子节点中,返回
node = node.children[char]
if node.word:
result.add(node.word) # 找到完整单词
board[r][c] = '#' # 标记当前字符为已访问
# 搜索相邻的四个方向
for dr, dc in [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]:
nr, nc = r + dr, c + dc
if 0 <= nr < rows and 0 <= nc < cols and board[nr][nc] != '#':
dfs(nr, nc, node)
board[r][c] = char # 恢复字符,进行回溯
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
if board[r][c] in trie.root.children: # 如果Trie树中有该起始字符
dfs(r, c, trie.root)
return list(result)
# 测试代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
solution = Solution()
board = [
['o', 'a', 'a', 'n'],
['e', 't', 'a', 'e'],
['i', 'h', 'k', 'r'],
['i', 'f', 'l', 'v']
]
words = ["oath", "pea", "eat", "rain"]
print("找到的单词:", solution.findWords(board, words))


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








