看过一轮黑马了,重新看看侯捷老师的,记录一下不会的/忘了的
两大类:
- 基于对象Object Based
- 面向对象Object Oriented
基于对象
不含指针的class -- 设计一个复数类
Class without pointer member(s) -- complex
Header中的防伪式声明:
若曾经没有定义过该内容,则在此处定义:(以复数complex为例)
//complex.h
#ifndef _COMPLEX_
#define _COMPLEX_
//...
#endifclass template(模版)简介
inline函数 -- 解决一些频繁调用的函数大量消耗栈空间(栈内存)的问题
关键字必须与函数定义放在一起才能使函数成为内联函数【inline complex& _doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r){...}】,仅仅将inline放在函数声明前面不起任何作用
inline是一种“用于实现”的关键字,而不是一种“用于声明”的关键字。
access level(访问级别):public,private,protected
constructor(ctor,构造函数)-- 可以有很多个重载overloading
在初始化的时候给构造函数的值进行初始化:(更快)
complex (double r = 0, double i = 0)
: re (r), im (i) //initialization list(初值化 初始列)
{ }const member function(常量成员函数)
class complex{
public:
double real () const {return re};
double imag () const {return im};
//对于只读操作的函数,在函数中 + const
private:
double re, im;
}参数传递: pass by value VS pass by reference(to const)
尽量传引用(ostream& ),若不想改变量值,则+const(const complex&);
friend(友元)-- 相同class的各个objects互为friends
class body 外的各种定义
operator overloading (操作符重载)--成员函数
1.参数有两个数时用this指针?(1.和2.的参数怎么设置)
任何成员函数都有一个隐藏的this指针,谁调用这个函数this就指向谁
2.return by reference 语法分析
该例中有 conplex& 的引用返回,发送者无需知道接受者是以reference形式接受
用return by reference对连续赋值有好处
//e.g 对复数进行加法的操作符重载
{
complex c1(2,1);//定义了一个复数c1,实部为2 虚部为1
complex c2(5);//定义了一个复数c2,实部为5 虚部为0
c2 += c1;//重载+=操作符
}
//do assignment plus
inline complex _doapl(complex* ths, const complex& r)
//完成两个复数相加操作,返回结果
{
ths->re += r.re;
the->im += r.im;
return *ths;//虽然返回的是一个指针,但是传递者无需知道接受者是以reference形式接收
}
//1. = 2.
inline complex& complex::oprator += (const complex& r)
//重载+=,参数中有一个隐藏参数
{
return _doapl(this, r);
}
//2. = 1.
inline complex& complex::operator += (this, const complex& r)
{
return _doap1 (this, r);
}temp object(临时对象) typename();
没有名称,生命很短暂
绝对不能return by reference,因为返回的必定是个local object(局部变量)
ostream& os -- 每一次cout都有改变,所以在作为参数时不能加const
含指针的class -- 设计一个字符串类
Class with pointer member(s) -- string
class String
{
public:
String(const char* cstr = 0);//默认构造
//Big Three,三个特殊函数
String(const String& str);//1.拷贝构造
String& operator=(const String& str);//操作符重载,2.拷贝赋值
~String();//析构函数:若类带有指针,一定要写3.析构函数
char* get_c_str() const {
return m_data;
}
private:
char* m_data;//用指针就可以让字符串长度具有灵活性
};ctor 和 dtor (构造函数和析构函数)
//默认拷贝构造,赋初值
inline String::String(const char* cstr = 0)
{
if (cstr)
{
m_data = new char[strlen(cstr)+1];//动态分配内存
strcopy(m_data, cstr);
}
else
{
m_data = new char[1];//动态分配内存
*m_data = '\0';
}
}
inline String::~String()
{
delete[] m_data;//清理内存,防止内存泄漏
}
//test函数
{
String s1();
String s2("hello");
String* p = new String("hello");//动态分配内存
delete p;//清理内存,防止内存泄漏
}class with pointer members必须有copy ctor (拷贝构造)和 copy op=(拷贝赋值)
//拷贝构造--深拷贝
inline String::String(const String& str)
{
m_data = new char[ strlen(str.m_data) + 1 ];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
//直接取另一个object的private(兄弟之间互为friend)
}
//copy assignment operator -- 拷贝赋值函数
inline String& String::operator=(const String& str)
{
//检测自我赋值self assignment
if (this == &str)
return *this;//不仅效率更高,而且不会产生不确定行为(保证正确性)
delete[] m_data;
m_data = new char[ strlen(str.m_data) + 1 ];
strcpy(m_data, str.m_data);
return *this;
}
//test
{
String s1("hello");
String s2(s1); //拷贝构造,等同于String s2 = s1;
s2 = s1; //拷贝赋值构造
}
output函数
cout一定要设置为全局函数
#include <iostream.h>
//操作符重载 输出字符串
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const String& str)
{
os << str.get_c_str();
return os;
}
//test
{
String s1("hello");
cout << s1;
}栈stack,堆heap
全局对象global object--其生命在整个程序结束之后才结束
静态对象static object--在作用域scope结束之后仍然存在,直到整个程序结束(在整个程序结束后才调用析构函数)
创建对象新方式“new”--动态分配内存--先创建空间,再调用ctor构造函数
Complex* pc = new Complex(1,2);
//编译器将转化为如下
Complex *pc;
void* men = operator new( sizeof(Complex) );//分配内存
//其内部会调用malloc(n)
pc = static_cast<Complex*>(mem);//转型
pc->Complex::Complex(1,2);//构造函数,全名为Complex::Complex(pc,1,2);//pc为Complex的起始位置delete--先调用dtor析构函数,后释放内存
String* ps = new String("hello");
...
delete ps;
//编译器将转化为如下:
String::~String(ps);//析构函数
operator delete(ps);//释放内存,其内部调用free(ps)动态分配所得到的内存块memory block,in VC
array new 一定要搭配array delete
delete[] p; //delete后面需要有数组标志告诉计算机要delete的是一个数组字符串本身是4byte
基于对象的一些细节补充:
static
可以修饰数据,也可以修饰函数
static data members -- 静态数据会单独分配一个内存,且只有一份
static member function -- 静态函数没有this指针,只能存取静态数据
static需要在class外写一个定义:
//e.g 一个银行账户类
class Account{
static double m_rate;
static void set_rate(const double& x){
m_rate = x;
}
};
double Account::m_rate = 8.0;//外部要对类内的静态变量做一个定义
//类型 变量全名 初值(选)
//静态函数调用的两种方式
int main(){
Account::set_rate(5.0);//1.通过class name调用
Account a;
a.set_rate(7.0);//2.通过object调用
//因为是静态函数,所以不会把对象a的地址放入
}静态函数的调用方式:1.通过对象调用;2.通过类名调用
单例模式中的静态变量
把ctor放在private中
//Singleton
class A{
public:
//用一个静态函数 去得到a
static A& getInstance{
return a;
}
setup(){...}
private:
A();
A(const A& rhs);
static A a;//a只有一份它自己
...
};
//调用函数:
A::getInstance().setup();
//用getInstance取得a,再调用setup函数
//Singleton优化:在没有使用时不先创建a
//Meyers Singleton
class A{
public:
static A& getInstance();
setup(){...}
private:
A();
A(const A& rhs);
...
};
A& A::getInstance(){
static A a; //静态的a放在函数中
return a;
}
//调用函数:
A::getInstance().setup();
cout
ostream类型
template,模版
类模版
//class template
template<typename T>
class complex{...};
//使用
complex<double> c1(2.5, 1.5);
complex<int> c2(2, 1);函数模版
//function template
//函数功能:比大小
template <class T>
inline const T& min(const T& a, const T& b){
return b < a ? b : a;
}
//编译器会对function template进行引数推导argument deduction(实参推导)
//函数调用
stone r1(2, 3), r2(3, 3), r3;
r3 = min(r1, r2);
namespace
//语法
namespace std
{
...//std是一个标准库
}
//被包装在std这个命名空间命名空间 的打开方式
//1.using directive直接打开
#include <iostream.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cin << ...;
cout << ...;
return 0;
}
//2.using declaration使用声明
#include<iostream.h>
using std::cout;
int main(){
std::cin << ...;
cout << ...;
return 0;
}
//3.不用using
#include <iostream.h>
int main(){
std::cin << ...;
std::cout << ...;
return 0;
}面向对象
Object Oriented Programming, Object Oriented Design -- OOP, OOD
Inheritance,继承
Composition,复合
Delegation,委托
复合Composition,表示has-a
//Adapter -- 适配器
template <class T, class Sequence = deque<T> >
class queue {
...
protected:
Sequence c; //底层容器,类似于 deque<T> c;
public:
//以下完全利用deque c的操作函数完成,queue借用了deque类中的功能
bool empty() const {
return c.empty();
}
size_type size() const {
return c.size();
}
reference front() {
return c.front();
}
reference back() {
return c.back();
}
//deque是两端可进出,queue是先进先出(末端进前端出)
void push(const value_type& x) {
c.push_back(x);
}
void pop() {
c.pop_front();//用deque中前端出的功能用作queue的调出功能
}
};Composition关系下的构造和析构
Container object 包含于 Component part
构造由内而外:Container的构造函数首先调用Component的default构造函数,然后才执行自己
Container::Container(...): Component() { ... };析构函数由外而内:Container的析构函数首先执行自己,然后才调用Component的析构函数
Container::~Container(...){ ... ~Component() };Delegation(委托) -- Composition by reference
reference counting引用计数 -- 共享相同的内容
// file String.hpp
class StringRep;
class String {
public:
String();
String(const char* s);
String(const String& s);
String &operator=(const String& s);
~String();
...
private:
StringPep* rep; //pimpl -- Pointer toimplementation
}
//n个字符串可以共享同一份
//👆Handle 👇Body -- plmpl
// file String.cpp
#include "String.hpp"
namespace{
class StringRep {
friend class String;
StringRep(const char* s);
~StringRep();
int count;
char* rep;
};
}
String::String(){ ... }
...Pimpl(Pointer to implementation) 是一种减少代码依赖和编译时间的C++编程技巧,其基本思想是将一个外部可见类(visible class)的实现细节(一般是所有私有的非虚成员)放在一个单独的实现类(implementation class)中,而在可见类中通过一个私有指针来间接访问该实现类。 --知乎,C++编程技巧: Pimpl
Inheritance(继承),表示is-a
构造由内而外(先父后子),析构由外而内(先子后父)
base class的dtor必须是virtual,否则会出现undefined behavior
inheritance with virtual function
函数继承 -- 继承权
成员函数 1.非虚函数;2.虚函数(希望子类重新定义override且有默认定义);3.纯虚函数(希望子类一定要重新定义,你对它没有默认定义)
class Shape{
public:
virtual void draw() const = 0;//pure virtual
virtual void error(const std::string& msg);//impure virtual
int objectID() const;//non-virtual
...
};
class Rectangle: public Shape{...};
class Ellipse: public Shape{...};...
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//Base类
class CDocument{
public:
void OnFileOpen(){
//这是个算法,每个cout输出代表一个实际动作
cout << "dialog..." << endl;
cout << "check file status..." << endl;
cout << "open file..." << endl;
Serialze();//加载
cout << "close file..." << endl;
cout << "update all views..." << endl;
}
virtual void Serialize() { };
};//Derive类
class CMyDoc : public CDocument{
public:
virtual void Serialize(){
//只有应用程序本身才知道如何读取自己的文件
cout << "CMyDoc::Serialize()" << endl;
}
};int main(){
CMyDoc myDoc;
myDoc.OnFileOpen();//通过子类对象调用父类函数
}Inheritance + Composition

Delegation + Inheritance --三大关系中功能最强大的一种组合
观察者Observer
class Observer{
public:
virtual void update(Subject* sub, int value) = 0;
}//一个subject有很多observer
class Subject{
int m_value;
vector<Observer*> m_views;//使用容器放指针指向observer
public:
//将数据放入
void attach(Observer* obs){
m_views.push_back(obs);
}
void sct_val(int value){
m_value = value;
notify();
}
//遍历通知
void notify(){
for(int i = 0; i < m_views.size(); ++i)
m_view[i] -> update(this, m_value);//更新数据
}
}; 组合模式Composite
组合模式Composite
//Base类
class Component{
int value;
public:
Component(int val){
value = val;
}
virtual void add(Component*){ }
};
class Composite: public Component{
vector<Component*> c;
public:
Composite(int val):Component(val){ }
//参数 是 指向父类的指针
void add(Component* elem){
c.push_back(elem);
}
...
};
//代表flie的class,基本的
class Primitive: public Component{
public:
Primitive(int val):Component(val){}
}; Prototype原型模式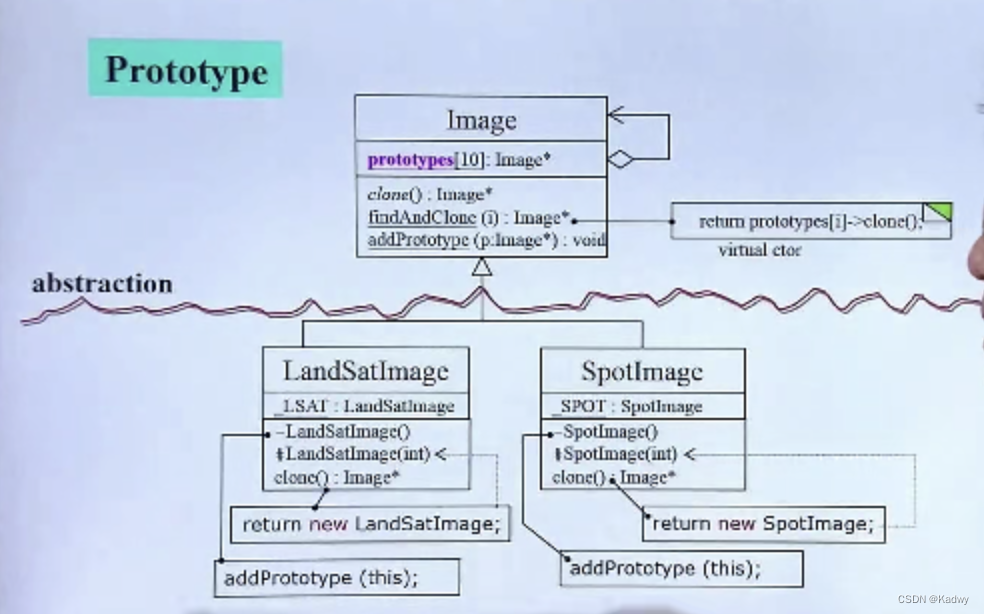
加下划线 代表是 一个静态对象;
“-”(负) 代表 私有的private
“#” 代表 protected
源代码:
//Base类
#include <iostream.h>
enum imageType{
LAST,SPOT
};
class Image{
public:
virtual void draw() = 0;
static Image *findAndClone(imageType);
protected:
virtual imageType returnType() = 0;
virtual Image *clone() = 0;
static void addPrototype(Image *image){
_prototype[_nextSlot++] = image;
}
private:
static Image *_prototype[10];
static int _nextSlot;
};
//给类内的静态变量/函数去定义
Image *Image::_prototypes[];
int Image::_nextSlot;
//Client calls this public static member function when it needs instance of an Image subclass
Image *Image::findAndClone(imageType type){
for(int i = 0; i < _nextSlot; i++)
if(_prototype[i]->returnType() == type)
return _prototypes[i]->clone();
}//Derive类--LSAT
class LandSatImage:public Image{
public:
imageType returnType(){
return LSAT;
}
void draw(){
cout << "LandSatImage" << _id << endl;
}
//When clone() is called, call the one-argument ctor with a dummy arg
Image *clone(){
return new LandSatImage(1); //new一个自己
}
protected:
//This is only called from clone()
LandSatImage(int dummy){
_id = _count++;
}
private:
//Mechanism for initializing an Image subclass - this cause the default ctor to be called, which registers the subclass's prototype
static LandSatImage _landSatImage;
//this is only called when the private static data member is inited
LandSatImage(){
addPrototype(this);
}
//Nominal "state"per instance mechanisim
int _id;
static int _count;
};
//Register the subclass's prototype
LandSatImage LandSatImage::_LandSatImage;
//Initialize the "state" per instance mechanism
int LandSatImage::_count = 1;























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








